COGNITIVE LIMITATIONS
&
RISK MANAGEMENT


Laurens Doedes Breuning ten Cate
NNBS x SNS
14.06.16
X
Cees Koomen - Supervisor
Joop Rabou - SNS Internship Supervisor
Herman van der Meulen - Panelist
Pim van Berkel - Panelist
Introductions
Amsterdam x Utrecht
Background x MP
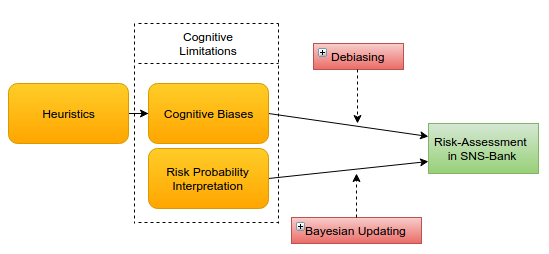
Biases - Kahneman & Tversky (1973)
Probabilities - Anderson (2013)
Impact - Yudkowsky (2008)
Example 1
The mean IQ of the population of eighth graders in a city is known to be 100. You have a selected a random sample of 50 children for a study of educational achievements. The first child tested has an IQ of 150.
What do you expect the mean IQ to be for the whole sample?
Tom is of high intelligence, although lacking in true creativity. He has a need for order and clarity, and for neat and tidy systems in which every detail finds its appropriate place. He seems to feel little sympathy for other people and does not enjoy interacting with others. Self-centred, he nonetheless has a deep moral sense.
Example 2
Which is more probable?
A. Tom is an engineer
B. Tom is an engineer and is an avid player of video games
Research Questions
“How can a retail bank reduce the impact of humans inherent cognitive limitations in risk
assessment & decision-making?”
1. Can the results from my thesis be extrapolated to SNS-bank?
2. How can Debiasing be effectively implemented in SNS-bank
3. How can Bayesian Updating be effectively implemented in SNS-bank
4. Are the solutions recommendable and how can they effectively be implemented?
Methodology
Interviews - 3 ORM, 1 MV & 1 RC
- Link with Desk Research
Desk Research - Solution design
- Top-down vs Bottom-up
Surveys - Training & Control
- Pre & Post
- Survey noise
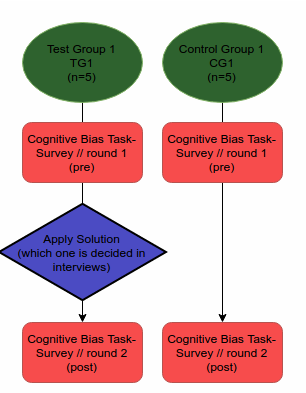
Surveys
- Statistics
- Sample size limitations
- Validity
Solution design
- Top-down as optimal
- IARPA SIRIUS project inspired
- Single training intervention
Debiasing - Morewedge et al. (2015)
SIRIUS project - IARPA (2016)
Sample & Skill
- Bias training group 12% up
- Probability training group 16% up
- Training had 'confidence effect'
- 44y old, 78.9% Male
- Bias group (n=19) // Probility group (n=13)
- Validity of sample

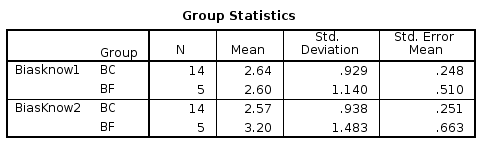
Cognitive Bias Results
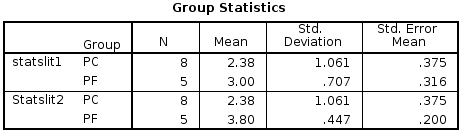
1. H0: The performance of risk managers in avoiding cognitive biases has not improved by at least 10% compared to the control group after application of the proposed solution.
1. Extrapolation (MP vs SNS): 61.74% vs 62.6%
2. Training (Pre vs Post): 62.6% vs 19.8% (Δ=42.8%)
3. Control (Pre vs Post): 62.6% vs 57.3% (Δ=5.3% 'noise')
Total: 42.8% - 5.3% = 37.5% performance increase
p>0.05
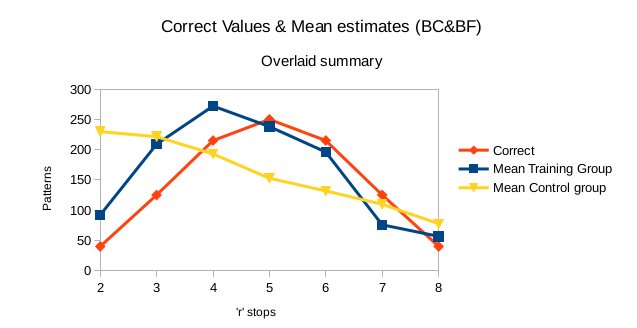

Bayesian Updating results
2. H0: The performance of risk managers in avoiding issues with probability interpretation has not improved by at least 10% compared to the control group after application of the proposed solution.
1. Extrapolation (MP vs SNS): 71% vs 82%
2. Training (Pre vs Post): 82% vs 46.67 (Δ=35.3%)
3. Control (Pre vs Post): 82% vs 87.5% (Δ=+5.5% 'noise')
Total: 35.3% + 5.5% = 40.8% performance increase
p>0.05

Predictors & Correlations - 1
- Prediction value check to find validity thru Multi-var linear regression
Independents: Pre-survey variables & 'group variable'
Dependent: Recoded Post-survey variables into 1 performance variable
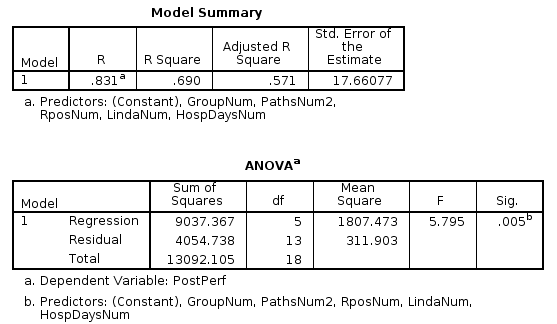
Model
p<0.05
R = 0.831
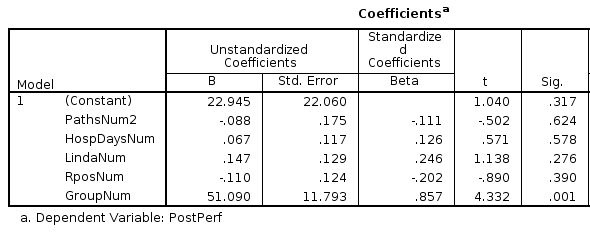
GroupNum
R = 0.857
p<0.05

Predictors & Correlations - 2
- Prediction value check to find validity thru Multi-var linear regression
Independents: Pre-survey variables & 'group variable'
Dependent: Recoded Post-survey variables into 1 performance variable
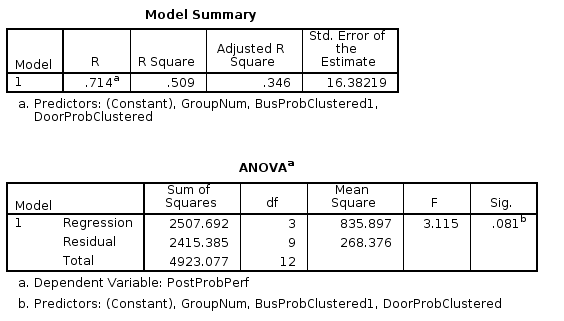
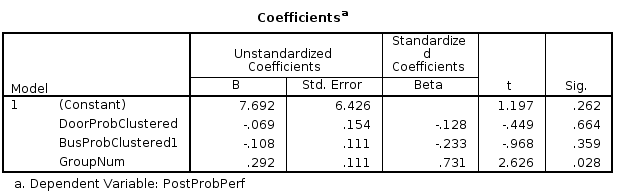
Model
p<0.10
R = 0.714
GroupNum
R = 0.731
p<0.05
Conclusion
- Performance gains not significant (barely)
- Predictor value very significant
- Morewedge et al. implies generalizability & Reverse extrapolation from industry wide sample strengthens this
Debiasing - Morewedge et al. (2015)
MP sample - Doedes Breuning ten Cate (2016)
Recommendations
1. IARPA
2. Debiasing training
3. Bayesian Updating training
4. Bayesian Updating in Modelling
IARPA x Debiasing

- Scalability & long-term peer-reviewed effects
- Classification issues
- Leveraging SNS
Debiasing - Morewedge et al. (2015)
IARPA - IARPA (2016)
Leidos/522prod/Cretecinc - IARPA (2016)
Bayesian Updating
- Top-down application
- 'Training saturation'
- Scalability
- Bias performance as predictor (low cost)
Predictor - Doedes Breuning ten Cate (2016)
Bayes in Modelling
Stress Testing
- Regulatory push
- Decreased reliance on historical data
- Profiling with probability based prediction models
- Markov Chain Monte-Carlo Simulations
- Underlying NFR models
- Faster updating due to passivity
Default Risk predictions
Bayesian Belief Networks
Stress Tests - Federal Reserve (2016)
Current Developments
- Training two full departments (Compliance & CMO)
{- Training Board of Directors}
- IARPA licensing deal (100 - 200)
- Exploring modelling solutions



Stakeholders

Acknowledgements
Nyenrode
Cees Koomen
SNS
Joop Rabou
ORM team
Externals
Danny van der
Ploeg
Questions?
References
Doedes Breuning ten Cate, L. (2016). “ How limitations of our cognitive abilities influence
risk assessments .”
Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA). (2016). About IARPA. Retrieved
May 4, 2016, from https://www.iarpa.gov/index.php/about-iarpa
Jensen, J. (2016). Stress Testing with the Help of Bayes’ Theorem - Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta. Retrieved May 10, 2016, from https://www.frbatlanta.org/cenfis/publications/notesfromthevault/1602
Leidos Inc. (2016). About Leidos. Retrieved May 21, 2016, from
https://www.leidos.com/about
Morewedge, C. K., Yoon, H., Scopelliti, I., Symborski, C. W., Korris, J. H., & Kassam, K. S.
(2015). Debiasing Decisions: Improved Decision Making With a Single Training
Intervention. Policy Insights from the Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 2(1), 129–140.
http://doi.org/10.1177/2372732215600886
Tversky, A., & Kahneman, D. (1973). Judgement under uncertainty: heuristics and biases.
http://doi.org/10.1126/science.185.4157.1124
Yudkowsky, E. (2008). Cognitive Biases Potentially Affecting Judgment of Global Risk. Retrieved October 22, 2015, from https://intelligence.org/files/CognitiveBiases.pdf