Rolf Bolte / Laurens ten Cate / Max Misovic Maarten-Lucas van der Meeren / Olivia Oscar
Case Analysis:
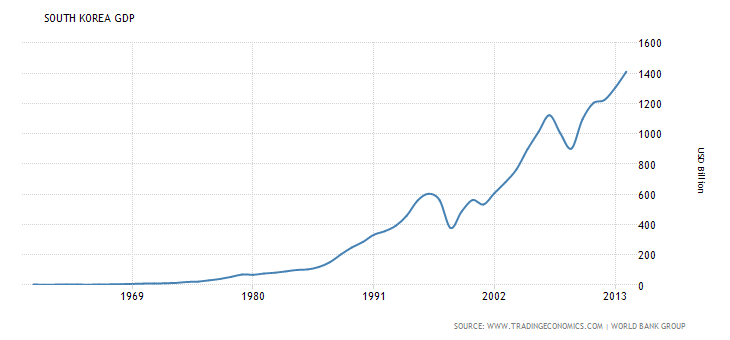
South Korea Currency Crisis
Introduction
Main Drivers
- Inflation
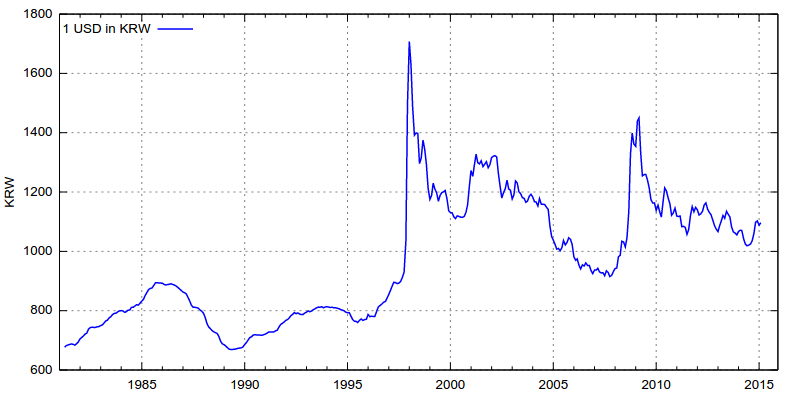
- Won Appreciation
- Relaxations of Capital controls
- Bad investments
IMF Rescue Package
16/Jan/1998
S&P credit rating
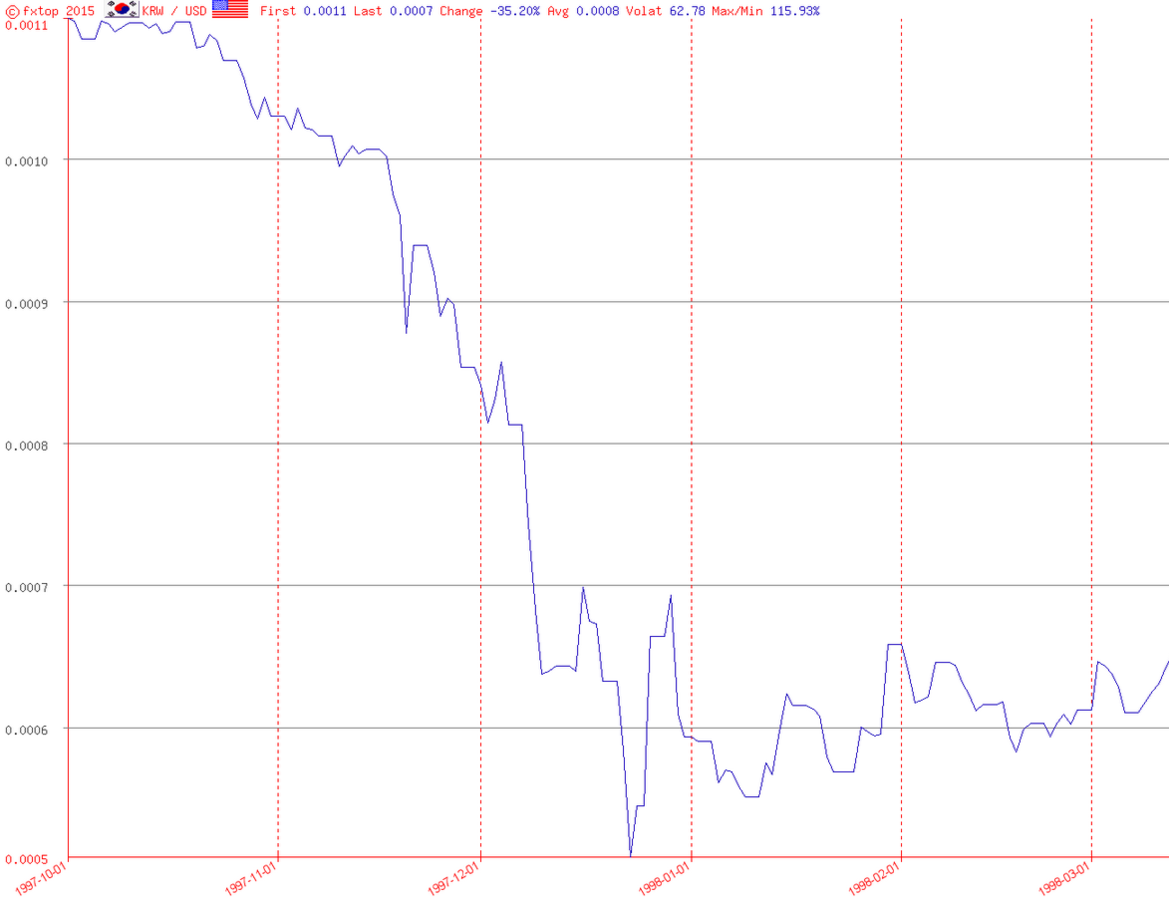
7/Nov/1997
Kospi Plunge
3/Dec/1997
IMF Bailout
24/Dec/1997
Quicker Funds
4/Jan/1998
1 month rollover
Conditions IMF bailout
- Restructuring of financial sector
- Liberalization of International trade
- Raise interest rate
- Reduce government deficit
Effect of conditions
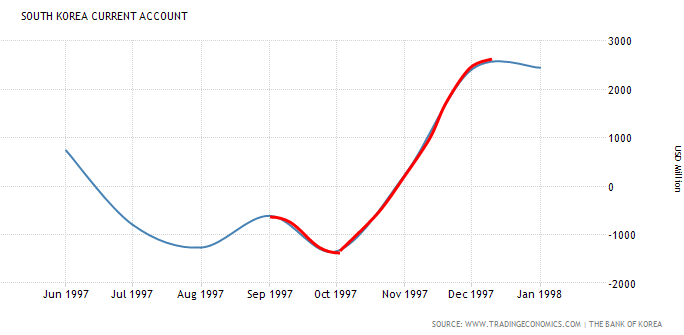
J-Curve effect
"To reverse this process, countries have to make it more attractive to hold domestic currency, and that means temporarily raising interest rates, even if this complicates the situation of weak banks and corporations."-Stanley Fischer
Effect of Capital flight & SK
- Capital inflow & investor confidence
- Currency drop & Capital flight spiral
- SK currency drop 2nd effect