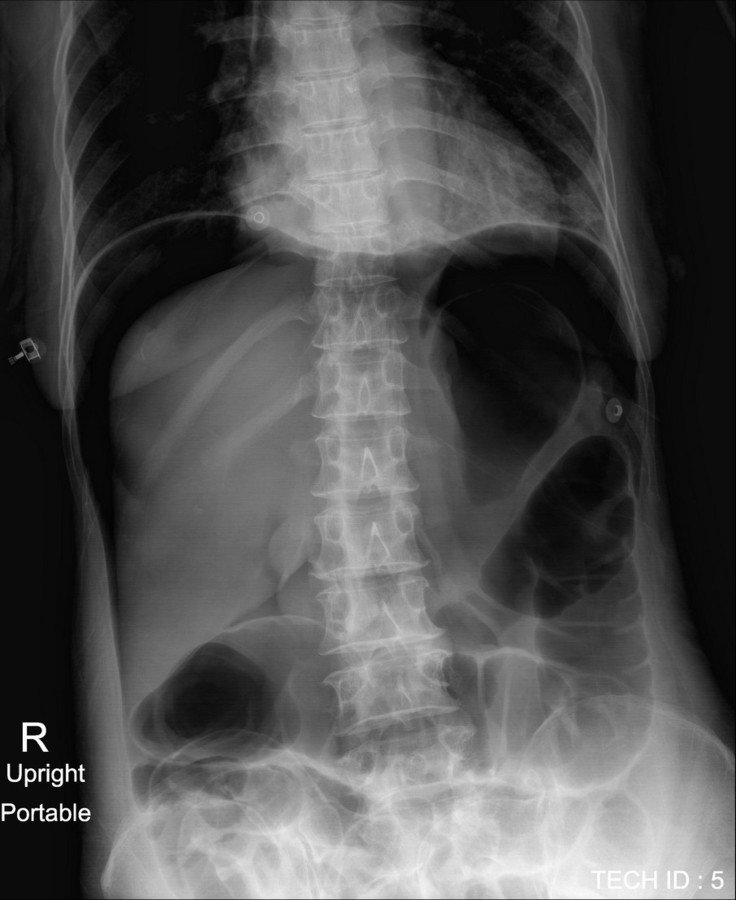
Abdomen : Case 7
History : A 60-year-old man. The patient had colonography and polypectomy with abdominal pain
The salient abnormality in this film?
A. Large bowel dilatation
B. Small bowel dilatation
C. Free air
D. All are correct
D. All answers correct:
- Large and small bowel dilatation due to post colonography
- Free air due to rupture of the colon
Additional abdominal radiograph : upright view
- Crescentic free air under both dome of the diaphragm, representing subdiaphragmatic free gas
Pneumoperitoneum :
* Gas within the peritoneal cavity
* Most common cause of a pneumoperitoneum is from the disruption of the wall of a hollow viscus
* Cause :
-
Perforated hollow viscus
- Postoperative free intraperitoneal gas
- Peritoneal dialysis
- Vaginal "aspiration"
- Mechanical ventilation
- Pneumomediastinum
- Pneumothorax
Abdominal Radiograph :
* Free air can be detected on an abdominal radiograph
* Important signs on supine film include:
-
Bowel related signs
- Double wall sign (Rigler's sign or bas-relief sign)
- Telltale triangle sign (Triangle sign)
-
Peritoneal ligament related signs
- Football sign
- Falciform ligament sign
- Lateral umbilical ligament sign (inverted "V" sign)
- Urachus sign
- Right upper quadrant signs
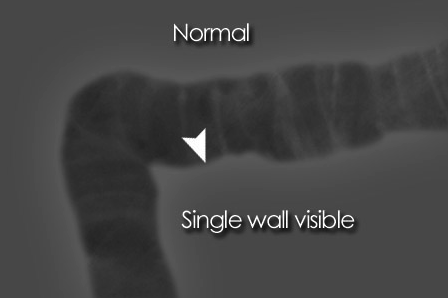
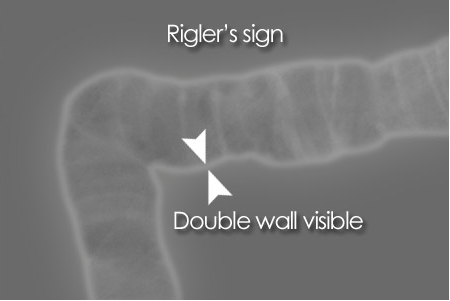
Rigler's/double wall sign :
- Normally only the inner wall of the bowel is visible
- If there is pneumoperitoneum both sides of the bowel wall may be visible
Rigler's/double wall sign :
Football sign :
- A large volume of free gas has risen to the front of the peritoneal cavity resulting in a large round black area - 'football sign'
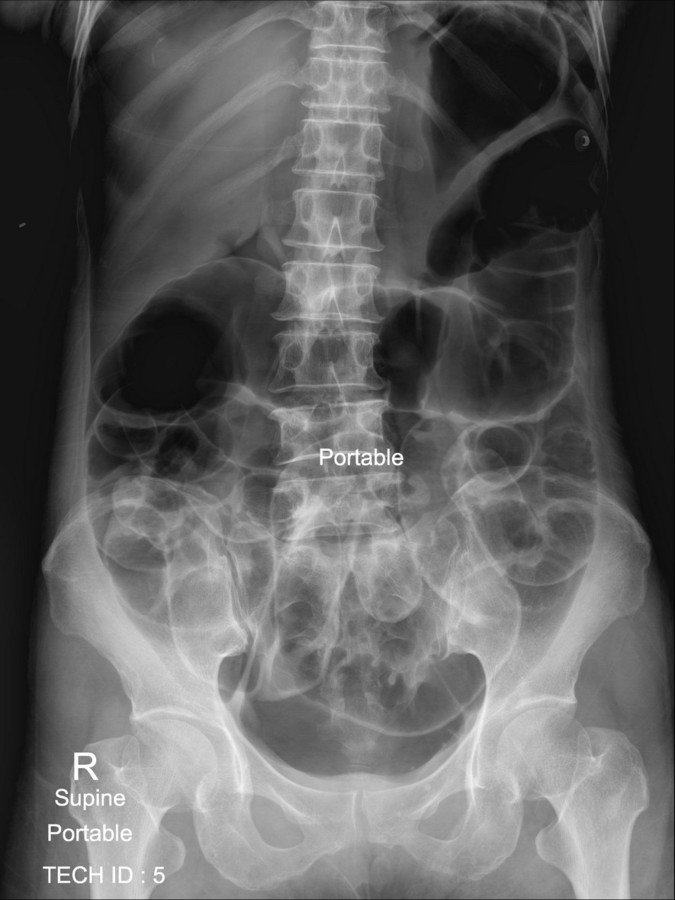
Lucent liver sign :
- Represented by a reduction of hepatic radiodensity on supine radiograph when there is a collection of free intraperitoneal air located anterior to the liver
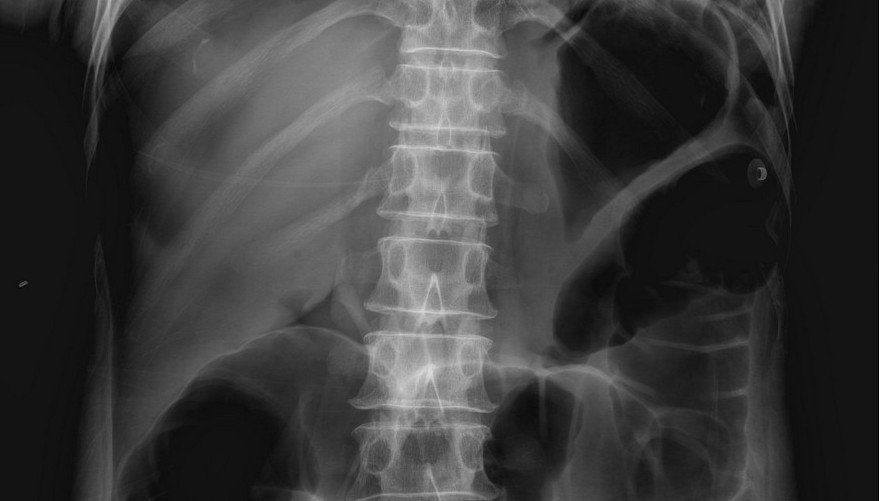
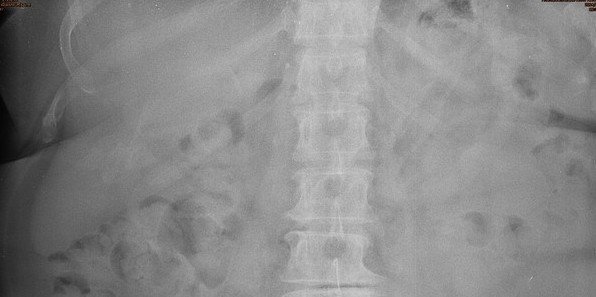
Normal liver shadow
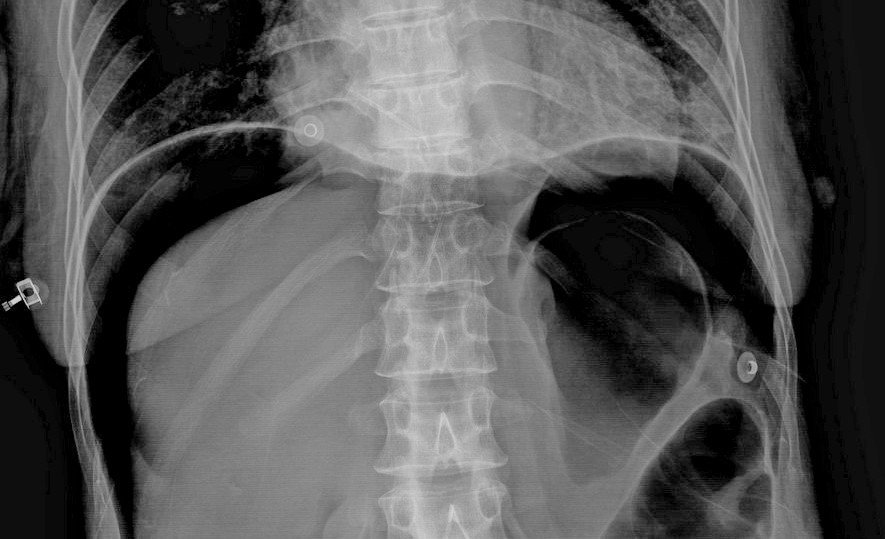
Plain abdominal radiograph :
Double wall sign
Lucent liver sign
Lateral umbilical ligament sign (inverted "V" sign)