Networks
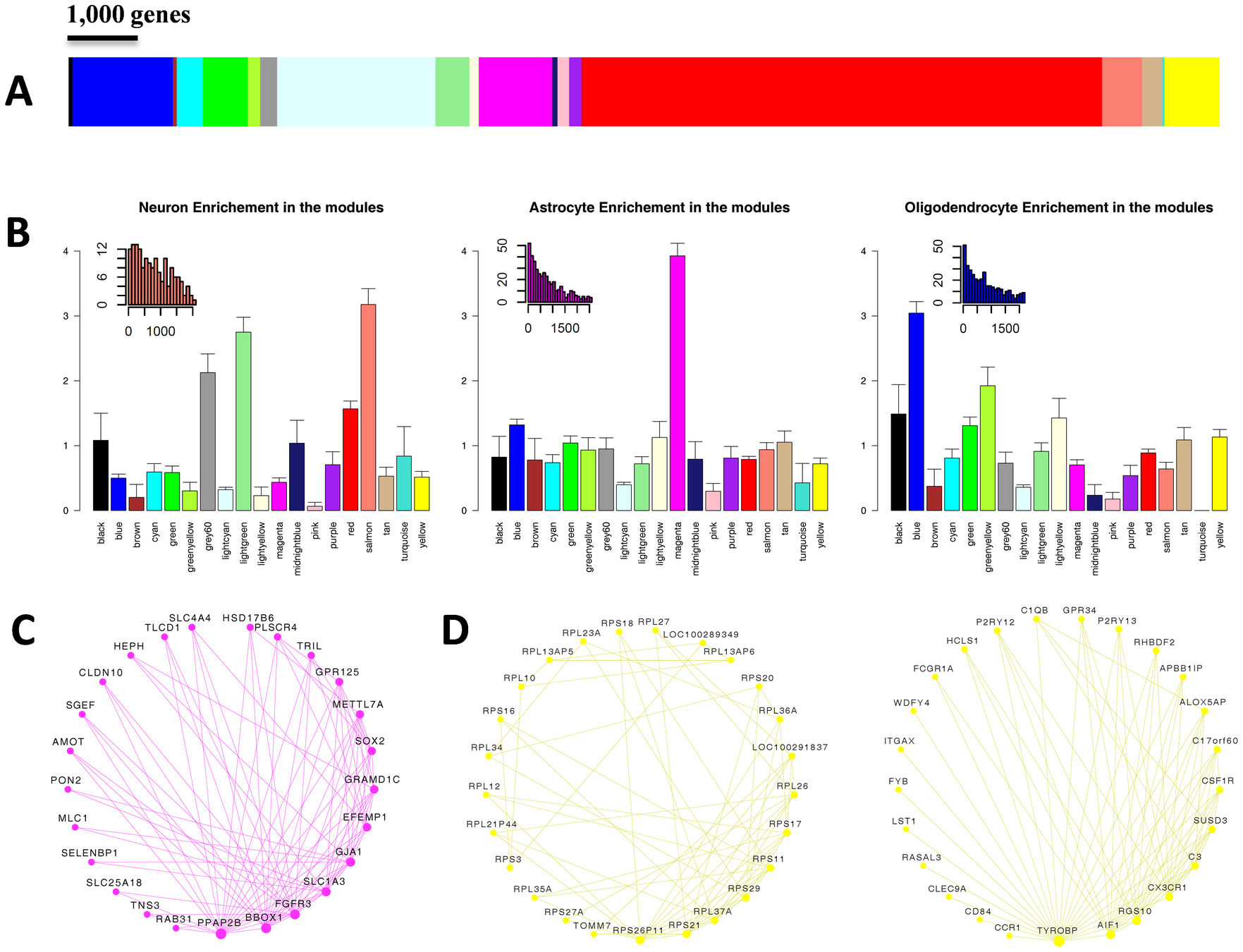
Coexpression network analysis of neural tissue reveals perturbations in developmental processes in schizophrenia (2012 Genome Res)
We performed integrated gene coexpression network analysis on two large microarray-based brain gene expression data sets generated from the prefrontal cortex
Twenty-eight modules of coexpressed genes with functional interpretations were detected in both normal subjects and those with schizophrenia. Significant overlap of “case” and “control” module composition was observed, indicating that extensive differences in underlying molecular connectivity are not likely driving pathology in schizophrenia
Modules of coexpressed genes were characterized according to disease association, cell type specificity, and the effects of aging
... altered expression in schizophrenia clustered into distinct coexpression networks and that these were associated primarily with neurons. We further identified a robust effect of age (included it in LM) on gene expression modules that differentiates normal subjects from those with schizophrenia. In particular, we report that normal age-related decreases in genes related to central nervous system developmental processes, including neurite outgrowth, neuronal differentiation, and dopamine-related cellular signaling, do not occur in subjects with schizophrenia during the aging process
Networks of Neuronal Genes Affected by Common and Rare Variants in Autism Spectrum Disorders
Eyal Ben-David, Sagiv Shifman (2012 plos genetics)
co-expression network based on a widespread survey of gene expression in the human brain
By integrating known rare mutations and the results of an ASD genome-wide association study (GWAS), we identified two neuronal modules... involved in synaptic and neuronal plasticity and that are expressed in areas associated with learning and memory and sensory perception
analysis of the combined contribution of common variants in the neuronal modules revealed a polygenic component to the risk of ASD
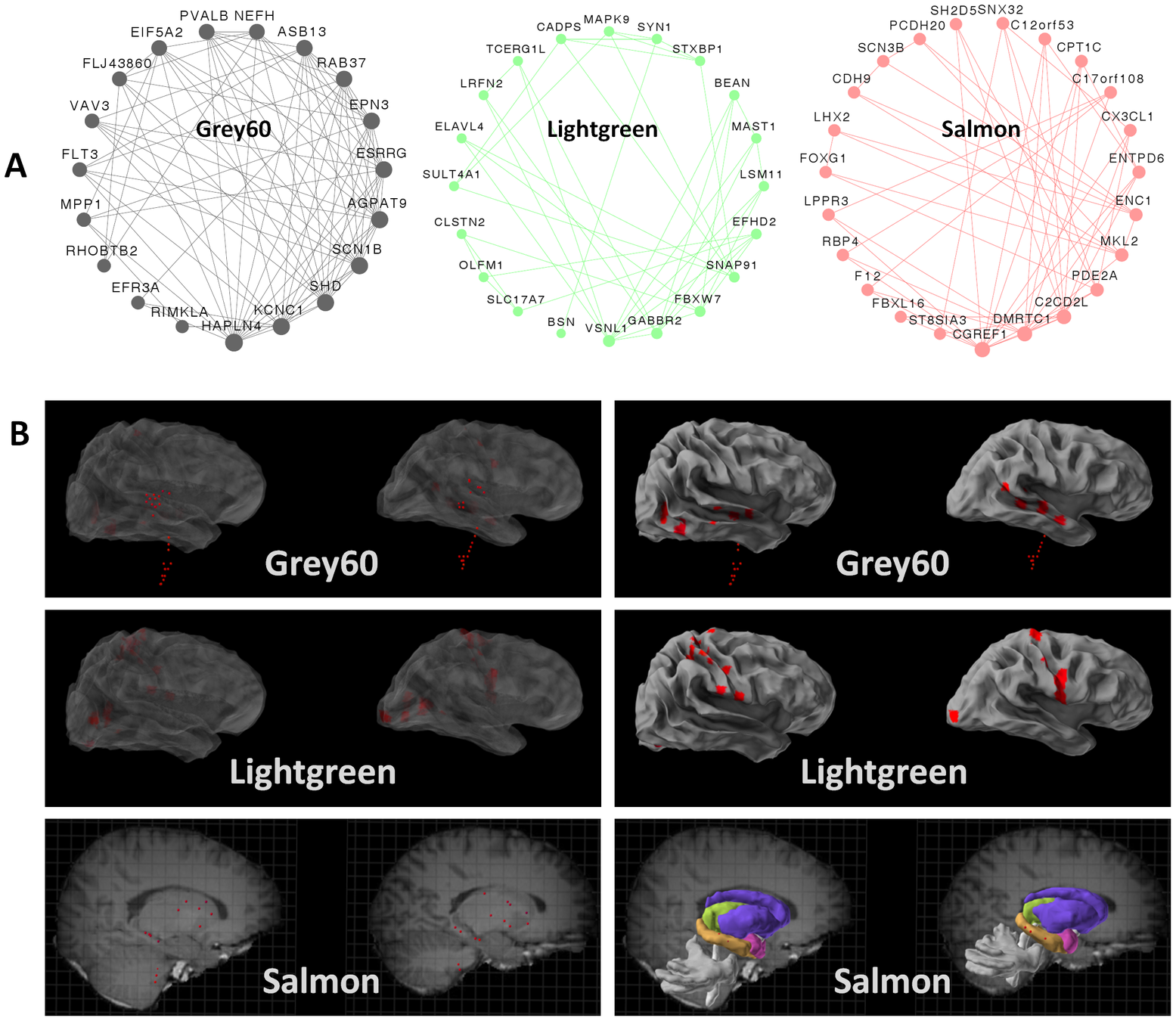
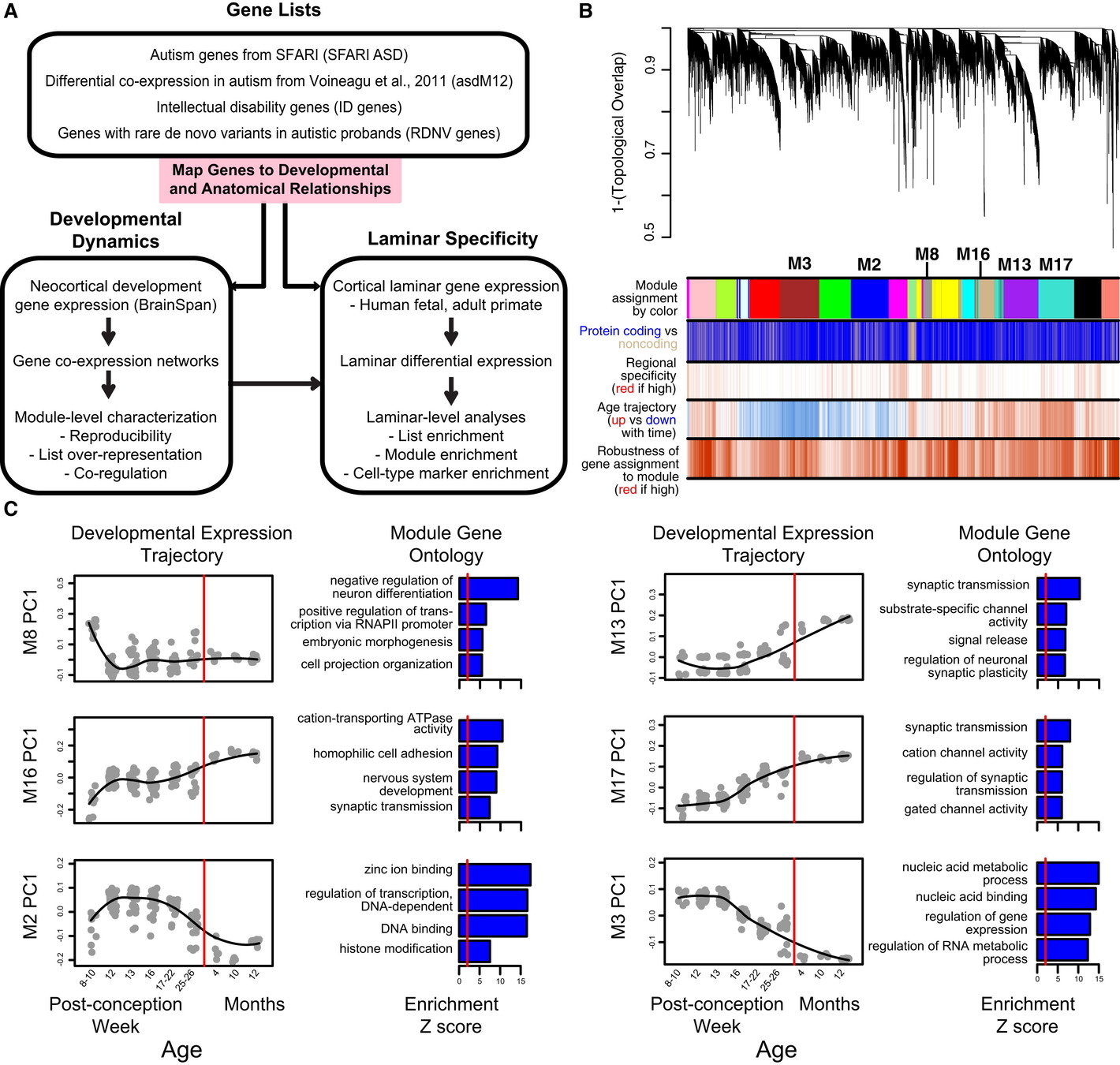
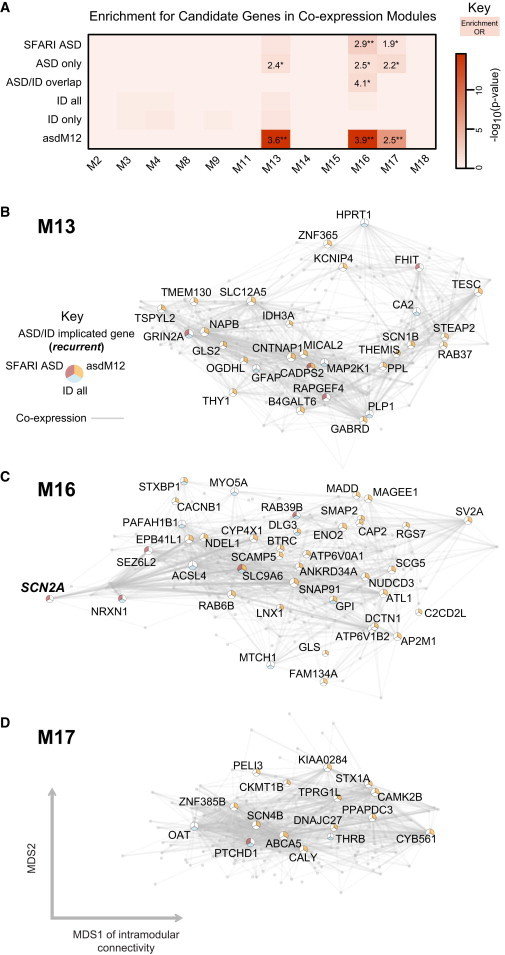
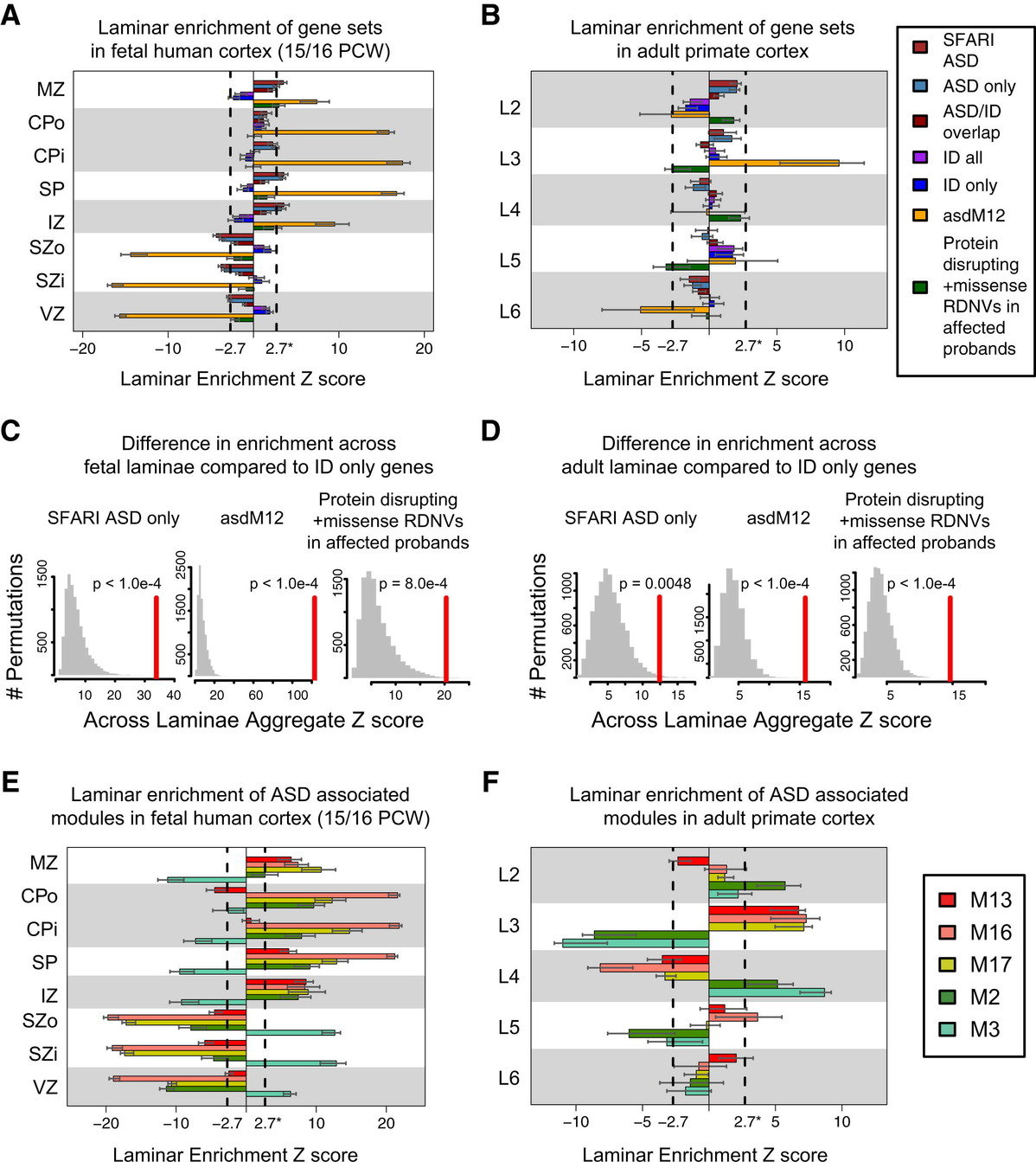
Integrative Functional Genomic Analyses Implicate Specific Molecular Pathways and Circuits in Autism
Geschwind group 2013
mapped ASD and ID risk genes onto coexpression networks representing developmental trajectories and transcriptional profiles representing fetal and adult cortical laminae. ASD genes tightly coalesce in modules that implicate distinct biological functions during human cortical development, including early transcriptional regulation and synaptic development
ASD genes are enriched in superficial cortical layers and glutamatergic projection neurons