PV226 ML: Clustering
Content of this session
Introduction to clustering
K-moods
Clustering algorithms
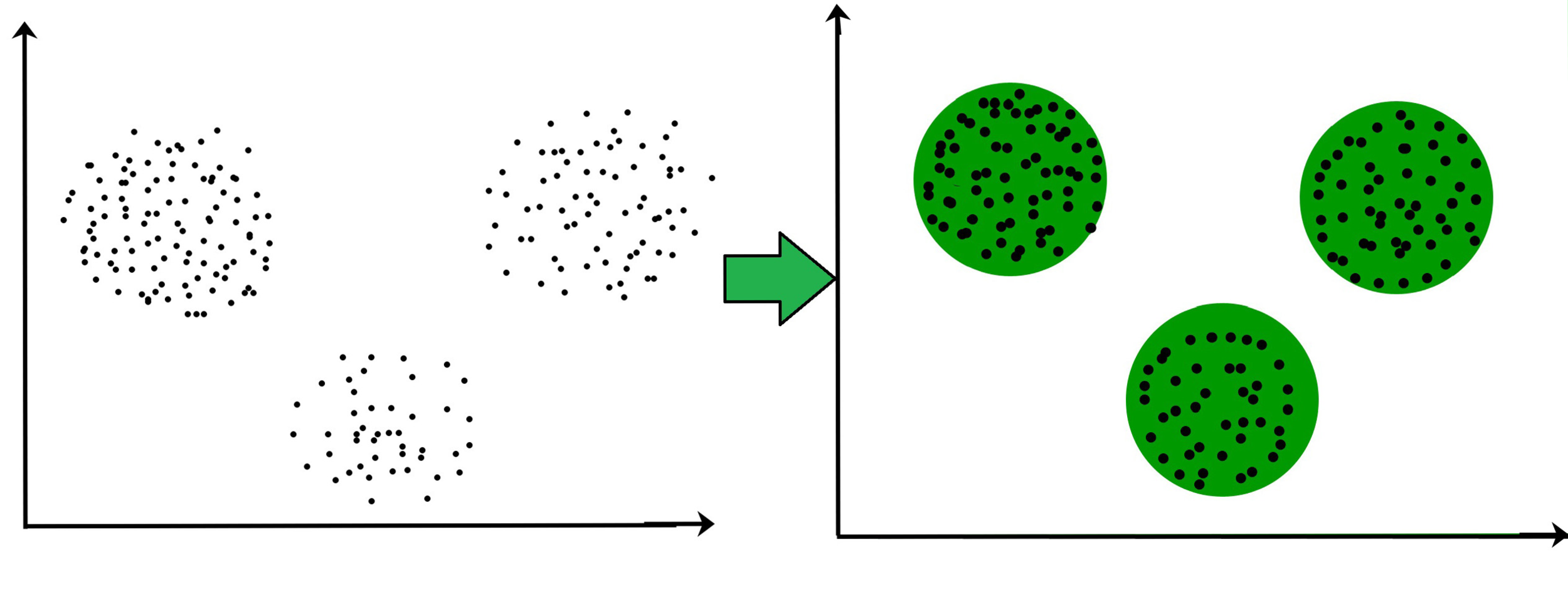
So what is clustering?
- Unsupervised learning
- Dividing data points into a number of clusters based on similarity
- Many tasks require additional analysis
- Results very much depend on the approach
Tasks
- Can be used to supply missing data
- Can find outliers
- Can be used for segmentation
- Can be used to create recommendations
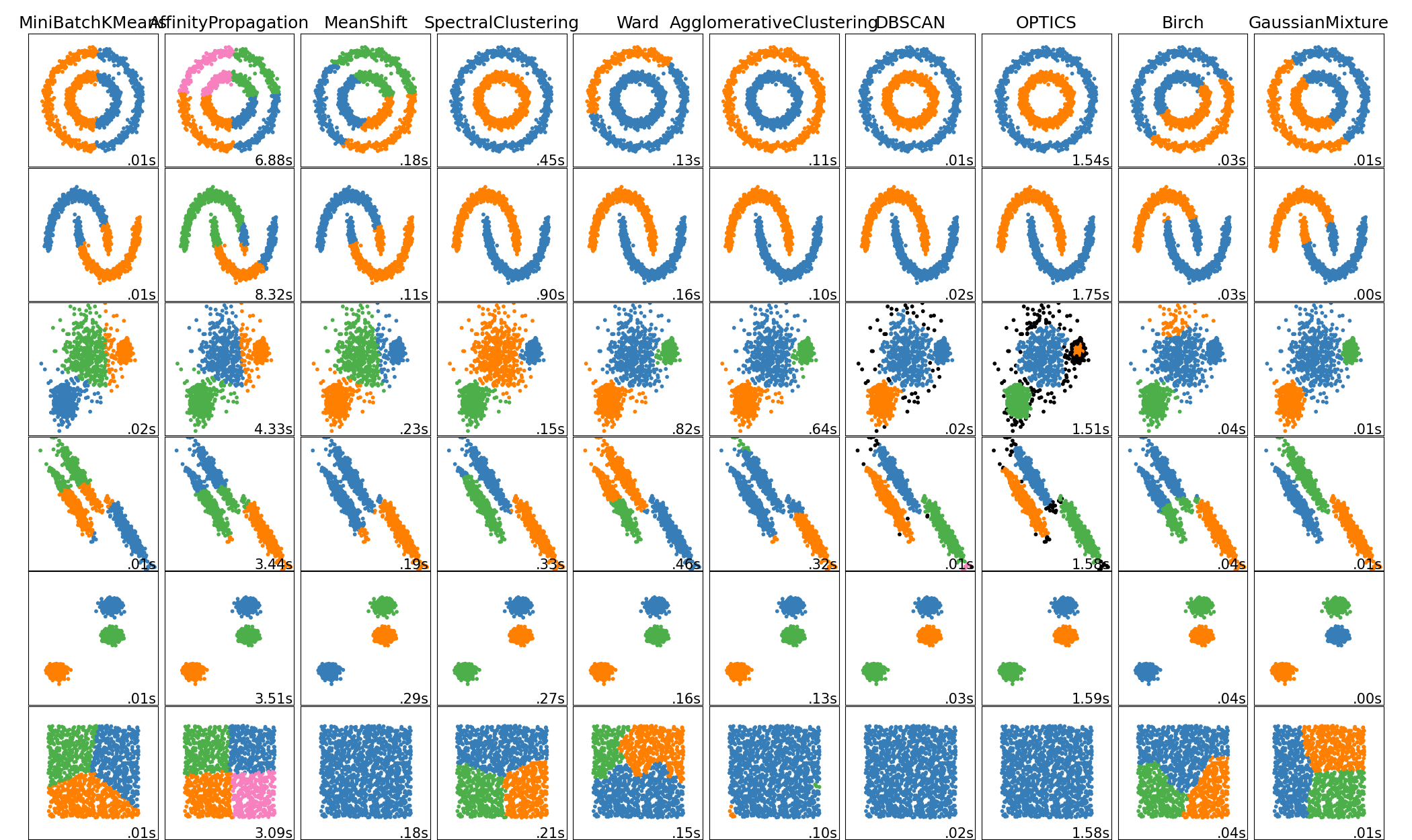
Different Algorithms from Scikit
Issues with categorical data
- K-modes
- Create a function to specify distances
- Alternative approches: SOM
After clustering:
- understanding clusters
- using clusters as training labels
Don't be afraid to experiment
K-modes
Installation
pip install kmodesUsage
import numpy as np
from kmodes.kmodes import KModes
# random categorical data
data = np.random.choice(20, (100, 10))
km = KModes(n_clusters=4, init='Huang', n_init=5, verbose=1)
clusters = km.fit_predict(data)
# Print the cluster centroids
print(km.cluster_centroids_)K-means
Installation
pip install scikitUsage
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
km = KMeans(
n_clusters=3, init='random',
n_init=10, max_iter=300,
tol=1e-04, random_state=0
)
y_km = km.fit_predict(X)