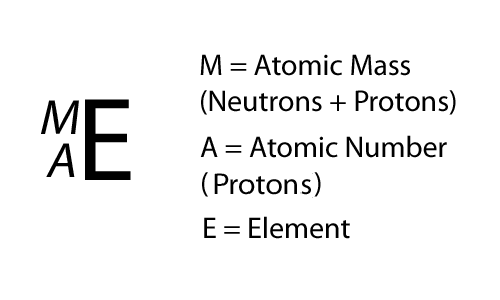
Nuclear
Unit 2
Isotopes

Neutrons
Each atom's nucleus is made of protons and neutrons stuck together.
Isotope
Isotopes are elements that have different numbers of neutrons.
For example, lithium normally has 3 protons and 3 neutrons. There is a kind of lithium though, that has 4 neutrons; one extra neutron!
Isotopes



Get this!
Neutrons are like the atom's glue
Stable
When the number of protons and neutrons is equal, there is enough glue (neutrons) to hold everything together, and nothing breaks down.
unstable/radioactive
When atoms get really large (like Uranium), they need more glue to hold them together. If they are big enough, they can't hold on to everything and pieces fly off. They're unstable
Isotopes
In other words, you need enough glue (neutrons) to hold it all together!
Magnets
What happens when you put the (+) sides of two magnets together?
unstable/radioactive
All of the protons really want to get away from each other! If there is enough of them working together, they can overcome the neutron glue and the nucleus will decay (break down) to become stable
But...WHy?

Writing it out
= 6
6
SYmbolic notation


Which isotope is radioactive?
6-protons
6-neutrons
12 -
= 8
6
14 -
6-protons
8-neutrons
Remember, unstable isotopes have different amounts of protons and neutrons
you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Types
of
Radiation
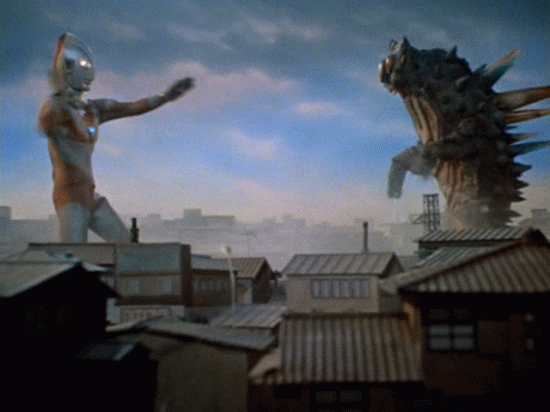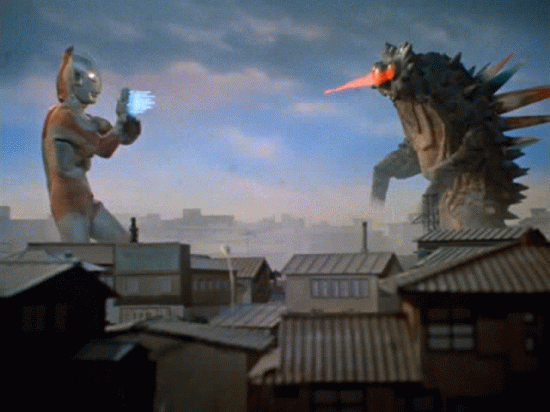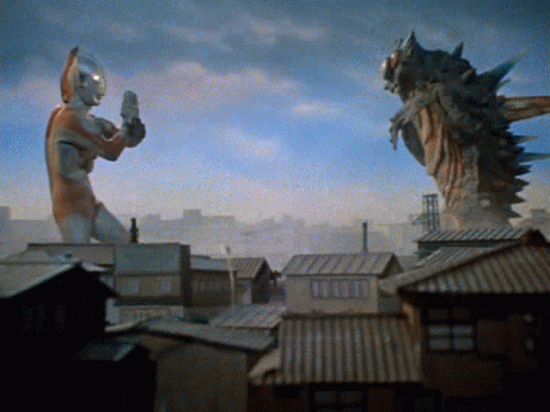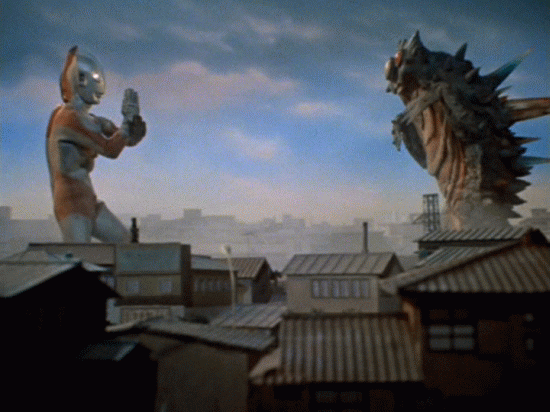
Nuclear Radiation
Comes in 3 flavors.
Nuclear decay

We can't detect alpha, beta, or gamma radiation with any of our senses. We need tools to detect them
Alpha Decay
A nucleus gives off two protons and two neutrons
Nuclear Radiation
As a result, the original atom hops down the periodic table by 2 (because it has lost two of its protons) and is now more stable

example...
An atom of Uranium goes through alpha decay, and we are left with Thorium

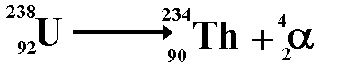
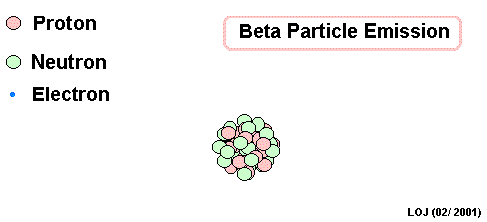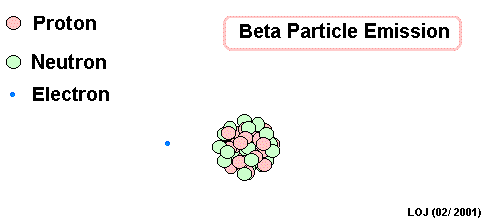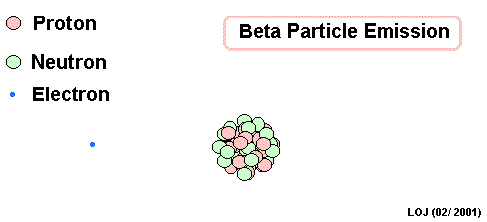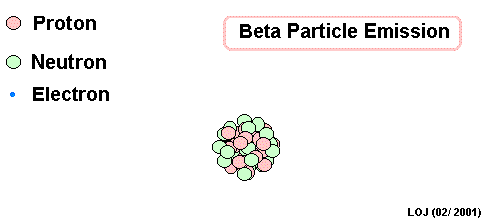
beta Decay
A neutron decays into a proton and an electron
Nuclear Radiation
As a result, the original atom hops up the periodic table by one (it has one more proton) and is now more stable.
example...
An atom of carbon goes through beta decay so that one of its neutrons turns into a proton and electron. The mass stays the same, but it now has an atomic number of 7, making it nitrogen!


The electron flies off to live its own life...We call it a beta particle
Gamma Decay
A nucleus emits pure energy.
This energy comes in the form of a high frequency photon (particle of light)
Nuclear Radiation
Nuclei can be too energetic as a result of other interactions... and it just needs let the energy out.
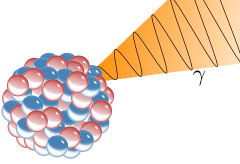
The nucleus does not change mass or charge; just emits pure energy.
Alpha decay
Symbolic notation can help us keep track of what happens to the atomic number, and mass of an atom after decay.
Symbolic Notation
beta decay
gamma decay
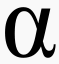



you've reached the bottom
head back to the top
Practice
makes
perfect

polonium alpha decay
What goes in the blank?
Alpha Decay

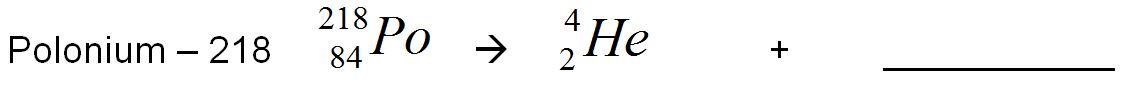
Polonium loses 2 protons and 2 neutrons (the alpha particle). Its atomic number goes down by two, and its has lost a total of 4 amu
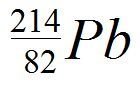
Our nucleus is now lead-214
Strontium beta decay
What goes in the blank?
beta Decay


Strontium has one of its neutrons turn into both a proton and an electron. The proton stays put and increases the atomic number by one. The mass does not change.
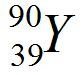
Our nucleus is now yttrium-90
Lead Gamma decay
What goes in the blank?
Gamma
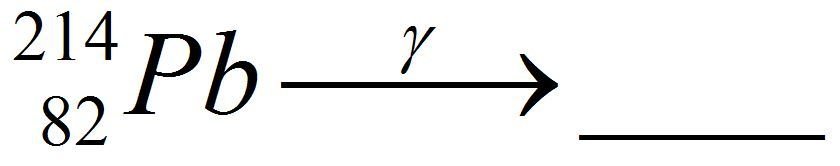
Lead-214 releases some pure energy (as a photon). It does not change mass nor does it change charge.
Our nucleus is still lead-214

