koa 的 source code 微介紹
Node.js 的原生 http library
const http = require('http');
http
.createServer((req, res) => {
res.write('hello world');
res.end();
})
.listen(3000);
hello world
我們把 (req, res) => { ... } 叫做
http library 的 "handleRequest"
如果 server 要處理很多狀況
import http from 'http';
http
.createServer((req, res) => {
if (req.method === 'GET' && req.url === '/') {
res.write('hello world');
res.end();
}
if (req.method === 'GET' && req.url === '/users') {
res.write('no users');
res.end();
}
...
})
.listen(3000);
這個 handleRequest 就會變得很長
Koa
是一個基於 Node.js 的 http library 的框架
他的核心運作方式
就是
middleware
middleware1
middleware2
middleware3
...
大的 function
compose
http 的
handleRequest
包裝一下
middleware
例如
logger
auth-checker
body-parser
...
(req, res)
response
middleware
middleware
middleware
middleware
middleware
routing
/
/home
/explore
...
(req, res)
middleware
middleware
middleware
middleware
response
koa vs express
Philosophically, Koa aims to "fix and replace node", whereas Express "augments node".
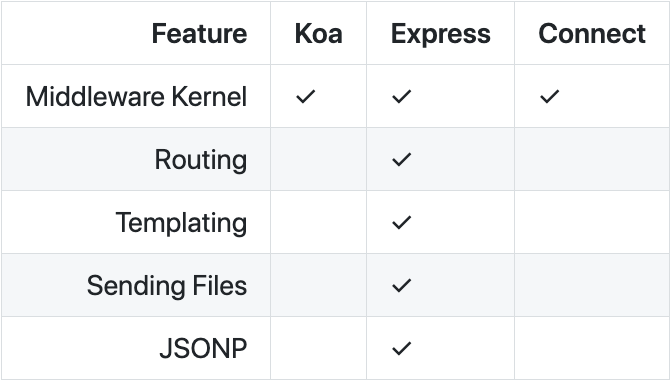
koa 的特點
1. 單純基於 middleware
2. 自己有另一套 api (ctx)
koa 有自己的 ctx API


hello world
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => {
res.send('Hello World!');
});
app.listen(3000);
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(ctx => {
ctx.response.body = 'Hello World!';
});
app.listen(3000);
express
koa
middleware stack
import Koa from 'koa';
const app = new Koa();
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body = 17;
return next();
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body += 2;
return next();
});
app.use((ctx) => {
ctx.response.body *= 5;
});
app.listen(3000);
middlewareA
middlewareB
middlewareC
koa 的設計
middlewareA
(req, res)
middlewareB
middlewareC
createContext
ctx
ctx
pass ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
respond (操作 res)
http 的 handleRequest
fnMiddleware
response
pass ctx
pass ctx
pass ctx
koa 的設計
1. 事先把 middleware 組成一個 fnMiddleware
2. 當 request 來的時候
(1) 產生 ctx
(2) 把 ctx 丟到 fnMiddleware
(3) 以 ctx 的結果去操作 res,產生 response
compose
createContext
respond
產生 http 的 handleRequest
callback() {
const fnMiddleware = compose(this.middleware);
...
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware);
};
return handleRequest;
}
(array)
koa 的 source code
import Koa from 'koa';
const app = new Koa();
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body = 17;
return next();
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body += 2;
return next();
});
app.use((ctx) => {
ctx.response.body *= 5;
});
app.listen(3000);
回頭看一下
Application 的 use 方法
class Application extends Emitter {
...
constructor(options) {
...
this.middleware = [];
...
}
...
use(fn) {
...
this.middleware.push(fn);
...
}
...
}
Application 的 listen 方法
class Application extends Emitter {
...
listen(...args) {
...
const server = http.createServer(this.callback());
return server.listen(...args);
}
...
callback() {
const fnMiddleware = compose(this.middleware);
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware);
};
return handleRequest;
}
...
}
產生 http 的 handleRequest
Application 的 handleRequest 方法
class Application extends Emitter {
...
callback() {
const fnMiddleware = compose(this.middleware);
const handleRequest = (req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
return this.handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware);
};
return handleRequest;
}
...
handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware) {
...
return fnMiddleware(ctx).then(() => respond(ctx)).catch(onerror);
}
...
}
基本上就是把 ctx 丟給 fnMiddleware,
fnMiddleware 層做完以後它再接手 respond
小總結
use 把我們寫的 function 加到 middleware
class Application extends Emitter {
...
use(fn) {
...
this.middleware.push(fn);
...
}
...
}
小總結
然後 listen 的時候幫我們把 middleware 組起來
再包成 http 的 handleRequest 丟給 http.createServer
class Application extends Emitter {
...
listen(...args) {
...
const fnMiddleware = compose(this.middleware);
const server = http.createServer((req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
return fnMiddleware(ctx).then(() => respond(ctx)).catch(onerror);
});
return server.listen(...args);
}
...
}
createContext
class Application extends Emitter {
...
createContext(req, res) {
const context = Object.create(this.context);
const request = context.request = Object.create(this.request);
const response = context.response = Object.create(this.response);
context.app = request.app = response.app = this;
context.req = request.req = response.req = req;
context.res = request.res = response.res = res;
request.ctx = response.ctx = context;
request.response = response;
response.request = request;
context.originalUrl = request.originalUrl = req.url;
context.state = {};
return context;
}
...
}
respond
function respond(ctx) {
...
// responses
if (Buffer.isBuffer(body)) return res.end(body);
if ('string' === typeof body) return res.end(body);
if (body instanceof Stream) return body.pipe(res);
body = JSON.stringify(body);
if (!res.headersSent) {
ctx.length = Buffer.byteLength(body);
}
res.end(body);
}
koa-compose
function compose (middleware) {
...
return function (context, next) {
// last called middleware #
let index = -1
return dispatch(0)
function dispatch (i) {
if (i <= index) return Promise.reject(new Error('next() called multiple times'))
index = i
let fn = middleware[i]
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve()
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1)));
} catch (err) {
return Promise.reject(err)
}
}
}
}
把 middleware (array of functions) 組成 fnMiddleware (function)
koa-compose
function compose (middleware) {
...
return function (context) {
function dispatch (i) {
const fn = middleware[i];
if (!fn) return;
return fn(context, dispatch(i + 1));
}
return dispatch(0);
}
}
不檢查錯誤 + 不考慮非同步 + 不 call next + 不管 this 的版本
koa-compose
function compose (middleware) {
...
return function (context, next) {
function dispatch (i) {
let fn = middleware[i];
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next;
if (!fn) return;
return fn(context, dispatch(i + 1));
}
return dispatch(0);
}
}
把 next 加回來的版本
koa-compose
function compose (middleware) {
...
return function (context, next) {
function dispatch (i) {
const fn = middleware[i];
if (i === middleware.length) fn = next;
if (!fn) return Promise.resolve();
try {
return Promise.resolve(fn(context, dispatch(i + 1)));
} catch (error) {
return Promise.reject(error);
}
}
return dispatch(0);
}
}
把 middleware (array) 組成 fnMiddleware
把 next 加回來 + async function 的版本
koa-compose
可以把幾個 middleware 組成一個更大的 middleware
compose 出來的 function 一樣是以 (ctx, next) 為參數的 function
koa-compose
其實 compose 出來的 fnMiddleware 沒有用到 next
class Application extends Emitter {
...
handleRequest(ctx, fnMiddleware) {
...
return fnMiddleware(ctx).then(() => respond(ctx)).catch(onerror);
}
...
}
但是 koa-compose 是一個獨立的套件
給別人用很方便
koa-router
是另外一個 koa 生態系的 library
他 library 裡面也是用 koa-compose 來組出一個大 middleware
var Koa = require('koa');
var Router = require('koa-router');
var app = new Koa();
var router = new Router();
router
.get('/', (ctx, next) => {
ctx.body = 'Hello World!';
})
.post('/users', (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
.put('/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
.del('/users/:id', (ctx, next) => {
// ...
})
app.use(router.routes());
app.listen(3000);
middleware 也可以這樣寫
import Koa from 'koa';
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body = 17;
await next();
ctx.response.body *= 5;
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body += 2;
return next();
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
return next();
});
app.listen(3000);
所以 koa 的 middleware 層更像是這樣
middelware
middelware
middelware
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
import Koa from 'koa';
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body = 17;
await next();
ctx.response.body *= 5;
});
app.use((ctx) => {
ctx.response.body += 2;
return;
});
app.use((ctx, next) => {
ctx.response.body = 999;
return next();
});
app.listen(3000);
或是像這樣
middelware
middelware
middelware
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx
ctx