Getting Started With React

Swarup Karavadi
@swazza85
About Me
- Full Stack javascript developer
- React Aficionado
- Wannabe polyglot
Today's Talk
- What is React?
- Why React?
- React Philosophy
- Virtual DOM
- Unidirectional Data Flow
- JSX
- React Ecosystem
- Code Time!!!
- ES6+ Features
- Challenges
- Q & A
What is React?
- View rendering framework
- Created by Facebook
- Facebook calls it a "javascript library for building user interfaces"
- I call it a framework - paradigm shift in thinking about building UIs
Why React?
Declarative Code
Tell javascript 'what' to render, don't worry about the 'how'.
<AppContainer>
<AppLayout>
<Navbar />
<Sidebar />
<AppContent />
</AppLayout>
</AppContainer>=>

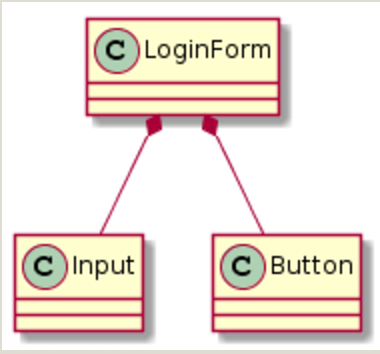
Composability
- All components are composable by default
- Reusability via compasability
const Button = (text, onClick) => (
<button type={type} onClick={onClick}>
{text}
</button>
)
const Input = (type, placeholder) => (
<input type={type} placeholder={placeholder} />
)
const LoginForm = () => (
<form>
<Input type="email"
placeholder="Enter your email" />
<Input type="password"
placeholder="Enter your password" />
<Button type="submit" text="Submit" />
</form>
)
<=>
Think in terms of "State"
- Model your app around 'state' instead of DOM
- No more DOM manipulations in your app code - only state updates!
Learn once - render anywhere
- Browser DOM
- Server
- Web Worker
- Mobile - iOS & Android
- Even to webgl and web-vr!
React Philosophy
The Notion of State
state: "the particular condition that someone or something is in at a specific time"
in react: "the particular condition that the UI is in at a specific time"
component state: "the particular condition that a component is in at a specific time"
V = f(S)
View is a function of state
UI State changes with time -
- DOM Events
- AJAX Callbacks
- Timer events
- Route Changes, etc
setState
React's setState method allows you to set the state of your UI
A React component subscribes to events that require state mutations
It uses setState to request React to update the view based on the latest state
setState - example
class Counter extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = { count: 0 }
}
updateCount(delta) {
let { count } = this.state;
this.setState({count: count + delta});
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<button
onClick={() => this.updateCount(-1)}>
-
</button>
{count}
<button
onClick={() => this.updateCount(+1)}>
+
</button>
</div>
)
}
}State @ T0
DOM Subscriptions
State Mutations @ T1, T2, T3, ... , Tn
Virtual DOM
Implementation Detail
An in-memory tree data structure that represents a view at any given point of time
Virtual DOM allows React to be independent of DOM
This implies React can render to DOM or iOS or Android or other targets
diff => patch => apply
VDOM@T0
VDOM@T1
View@T0
State@T0
External Stimuli
State@T1
Diff@T0
Patch@T0
View@T1
Initial State
Create VDOM
Render to View
uses setState to mutate state
New state is calculated
Create VDOM
VDOMs at T0 & T1 are diffed
A DOM Patch is created
Patch applied to render View
Unidirectional Data Flow
No Two-Way Binding
state is the only source of truth for a view
state can only be explictly mutated via setState
DOMEvents, AJAX Callbacks, etc cannot mutate state directly (unlike ngModel from ng 1.x)
Enabler for Flux Architecture
https://facebook.github.io/flux/
JSX
Templating language for creating react views
Typical React Components are created using React.createElement method
Readability nightmare when creating highly composable UIs
JSX is JS!
React: No JSX
export const FormWithoutJsx = () => {
return React.createElement(
'form',
{ onSubmit: (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
console.log('Form Submitted!')
}
},
React.createElement(
'input',
{ type:"text", placeholder:"username" },
null
),
React.createElement(
'input',
{ type: "password", placeholder: "password" },
null
),
React.createElement(
'button',
{ type: "submit" },
"Submit"
)
)
}React: JSX
export const FormWithJsx = () => {
return (
<form onSubmit={(e) => {
e.preventDefault()
console.log('Form Submitted')
}}>
<input type="text" placeholder="username" />
<input type="password" placeholder="password" />
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
</form>
)
}Transpiling JSX to JS
Use "React JSX transform" - a babel plugin
Multiple ways to use babel. Most popular being with webpack.
React Ecosystem











Create React App
npm install -g create-react-app
create-react-app my-app
cd my-app/
npm startAnd you are all set!
Demo Time!!
Frequently used ES6+ Features
- Object Destructuring
- Arrow Methods
- Static fields
- Classes
- Imports
- String Literals
import React, { Component, PropTypes } from 'react';
export class Input extends Component {
static propTypes = {
value: PropTypes.string,
hasError: PropTypes.bool,
onInputChange: PropTypes.func
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
}
render() {
let { value, hasError, onInputChange } = this.props;
return (
<input type="text"
value={value}
className={`input ${hasError ? 'error' : ''}`}
onChange={(e) => onInputChange(e.target.value)} />
)
}
}Imports
Exports & Class
String Literals
Arrow Methods
Static Fields
React Challenges
Very easy to write non-view related logic in React Components
As your app grows, state management becomes a non-trivial task
React ecosystem CAN be a put-off to new comers
Gives you great power - and with it comes great responsibility
ONLY a view rendering framework - you need to figure out the rest of your UI stack (like router, data fetching, state management, etc)
Encourages functional programming. Involves a relatively steep learning curve to make the most out of React.