Javascript Introduction
Lasted updated: 06/03/2024
part 1
History
As is well known at this point, I created JavaScript in ten days in May 1995, under duress and conflicting management imperatives—“make it look like Java,” “make it easy for beginners,” “make it control almost everything in the Netscape browser.”
Version
ECMAScript 5 .1
all modern browsers fully support
December 2009
ECMAScript 2015
Class、Arrow Function、Default parameters...
June 2015
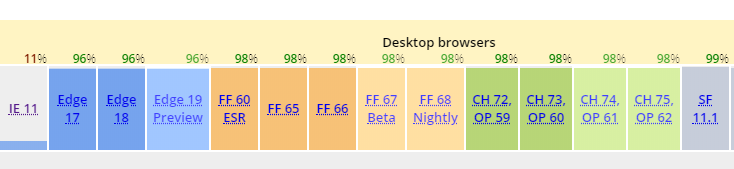

11%
ES6
> 96%
caniuse.com
| Edition | Name | Date | Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | ES2015 | June 2015 | Class, Module, Arrow Function, Default parameters, Promise ... |
| 7 | ES2016 | June 2016 | Array.prototype.includes, Exponentiation Operator |
| 8 | ES2017 | June 2017 | async/await, Object.values(), Object.entries(), String padding |
| 9 | ES2018 | June 2018 | ... |
Version History
10.15.3 LTS

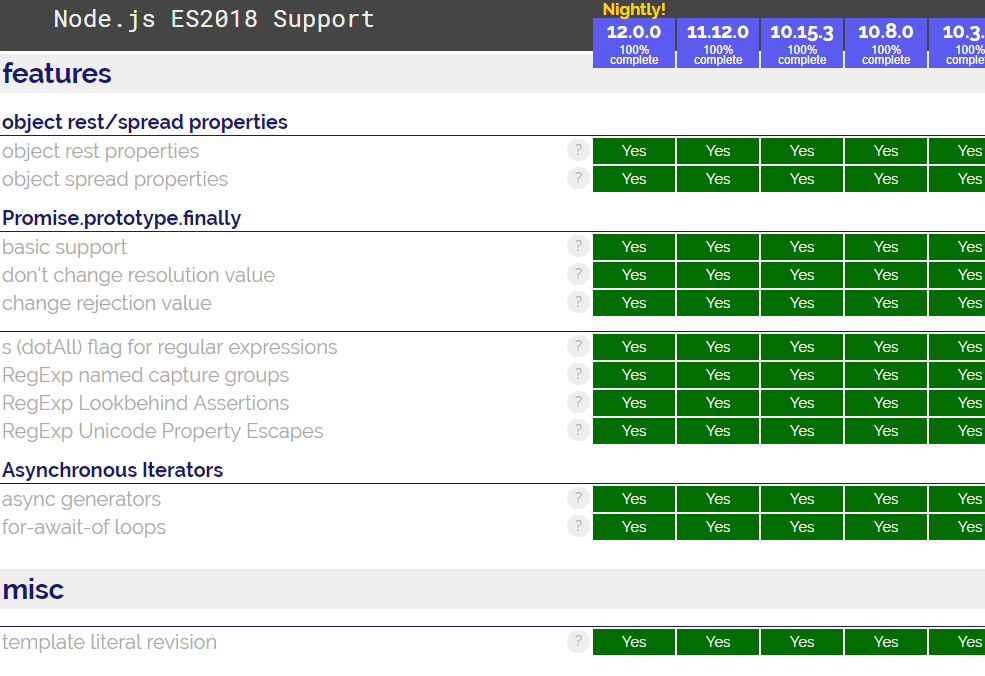
Polyfill
// ES6 Number.parseInt()
Number.paseInt("123"); // 123
// es5
parseInt("123"); // 123
//polyfill
if(Number.parseInt === undefined) Number.parseInt = window.parseInt;Babel
Babel
var four = 2 ** 3; // 8var four = Math.power(2, 3);Put in next-gen JavaScript
Get browser-compatible JavaScript out
Overview
Variables
Loosely-typed Variables
// overriding
var num = 1;
num = "my string";
num = [];
// or re "var"
var num = false;
你可以用
typeof num; // "number"來判斷類型
Identifiers are used to name variables, the first character must be a letter, an underscore (_), or a dollar sign ($).
var $foo = "blablabla";
// 合法的開頭Unicode字元
var 變數 = "var";
// unicode character
var \u0069 = "i";
var a, b, c; // all undefinedDeclare a Variable without var Keyword
foo = 1;
num = 123;
// in browser
window.foo; // 123
當你漏掉 var 時,程式還是會正常運作,但是會導致在全域變數 (global) 中暴露這個變數,後面會介紹嚴格模式 "use strict" 來避免這個問題
Keywords
/* Reserved keywords as of ECMAScript 2015 */
`break case catch class const continue
debugger default delete do else export
extends finally for function if import
in instanceof new return super switch
this throw try typeof var void
while with yield`
/* Future reserved keywords */
// These are always reserved:
`enum`
// only reserved when they are found in "strict mode" code:
`implements interface let package private
protected public static`
// and more ...see more at MDN
Object types
Primitive types
Type
There are 5 primitive types
Number、String、Boolean、Undefined、Null
Primitive types

ES6 新增了 Symbol ,這裡還不會提到
Number
Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
undefined
true
false
null
'single quotes'
" "
"\n"
"\u003e"
' "hello" '
" \"world\" "
Unicode character
NaN
.14
3.14
2e+4
-Infinity
-0
0x11
IEEE 754 64-bit doubles
Primitive Type & their primitive value
UTF-16
Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
NaN
.14
3.14
2e+4
-Infinity
-0
0x11
var num = 100;
var num2 = Number('100'); // 100
1 / 0; // Infinity
-1 / 0; // - Infinity
-0 / 1; // -0
0x11; // 17Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
NaN
.14
3.14
2e+4
-Infinity
-0
0x11
// Math 物件
Math.abs(-1); // 1
// global function
parseInt("123", 10); // 123
parseInt("010", 2); // 2 (radixes is 2)

ES6 新增了 Number.parseInt() 兩者是一樣的
Number.parseInt === parseInt; // trueUndefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
NaN
.14
3.14
2e+4
-Infinity
-0
0x11
// NaN
parseInt("abc", 10); // NaN, means Not a number
isNaN(NaN); // true
NaN === NaN; // false
NaN > NaN; // false
NaN < NaN; // false
// double-precision 64-bit format IEEE 754 values
0.1 + 0.2; // 0.30000000000000004Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
var str = 'hello';
var omega = '\u2126'; // "Ω"
// String.prototype.length
'hello'.length; // 5
'hello'.charAt(0); // "h"
'hello'.toUpperCase(); // "HELLO"
'hello'[1]; // "e"'single quotes'
" "
"\n"
"\u003e"
' "hello" '
" \"world\" "
Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
//Truthy
Boolean(true);
Boolean(123);
Boolean("A");
Boolean(-Infinity);
Boolean("0");
Boolean([]);
Boolean({});true
false
Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
var bool = false;
//Falsy
Boolean(bool); // false
Boolean(null); // false
Boolean(undefined); // false
Boolean(0); //false
Boolean(""); //falsetrue
false
function point(x, y) {
if (!x) {
x = 320;
if(!y) {
y = 240;
}
return {x: x, y: y}
}
point(0,0); //{x:320, y:240}Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
typeof notExist; // "undefined"
var foo; // undefined
function nothing() {}
nothing(); // undefinedtrue
false
Undefined
Boolean
String
Null
Number
Primitive Type
var foo = null;
foo; //null
// null 通常用來表示物件或是節點為空null
Object types
Primitive types
Type
Object types
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var obj = {}create an empty objec
Object
Function
Array
objects can be thought of as simple collections of key-value pairs
Object types
var obj = {userName: 'petter'}key
Value
Other programming languages have similar concepts, e.g., Map, Dictionary, Hash Table
Object
Function
Array
Object types
Initialize an object
var book = {
name: 'Harry Potter',
ISBN: 9780545010221,
details:{
coverColor: 'orange',
size: 'A4',
},
};var book = {};
book.name = 'Harry Potter';
book.ISBN = 9780545010221;
book.details = {
coverColor: 'orange',
size: 'A4'
};=
Object
Function
Array
Object types
Attribute access can be chained together:
book.details.size; // 'A4';
book['details']['coverColor']; // 'orange'Object
Function
Array
Object types
Set、Remove Property
var obj = {
1 : "a number",
"3": "string",
foo: 101,
bar: true,
"" : null
};
obj.foo = 123;
delete obj.bar;
obj['3'] = 'four'Object
Function
Array
Object types
var obj = {
name: 'Jeff',
};
var obj2 = obj;
obj2.name = 'Harry';
obj.name; // "Harry"Any value of object is actually a reference
Object
Function
Array
Object types
// parse
var myJson =
'{"userId": 1, "detail": { "name": "Jeff", "age": 13}';
var obj = JSON.parse(myJson);
obj.detail.name; // "Jeff"
// stringify
var obj = {foo: 1, bar:2};
JSON.stringify(obj); // '{"foo":1,"bar":2}'JSON.parse()、JSON.stringify();
Object
Function
Array
Object types
function add(x, y){
return x + y;
}
add(2, 3); // 5Function Declaration
Object
Function
Array
Object types
function foo(x) {
}
foo(); // undefined;Object
Function
Array
Default return value is undefined
Object types
function add(x, y = 2){
return x + y;
}
add(3); // 5Default parameters
Only available in ES6
function add(x, y){
if(y === undefined) y = 2;
return x + y;
}
add(3); // 5ES5
Object
Function
Array
Object types
function add(x, y) {
var total = x + y;
return total;
}
add(); // NaN
add(2, 3, 4); // 5
// 4 was ignoredObject
Function
Array
Ignore Extra parameters
Object types
function add() {
var sum = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
sum += arguments[i];
}
return sum;
}
add(1, 2, 3, 4); // 10arguments
Object
Function
Array
Object types
// anonymous
var myFunc = function(x, y){
return x + y;
};
// or naming function
var myFunc = function add(x, y){
return x + y;
};
myFunc(1, 2); // 3Function as a variable's value
function Identifieropt ( FormalParameterListopt ) { FunctionBody }
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var foo = function fib(n) {
if (n === 0) return 0;
if (n === 1) return 1;
if (n > 1) return fib(n - 1) + fib(n - 2);
};
foo(10); //55
fib(10); // ReferenceError: fib is not defined
Recursive
The name “fib” is accessible
only inside the function itself
Object
Function
Array
Object types
(function(){
if(window.env === "IOS")
// ...
})();
// or
(function(){
}());
IIFE (immediately-invoked function expression)
!function(){ /* ... */}();
+function(){/* ... */ }();
// or in ES6
void function(){
// ...
}();
IIFE 通常會用在建立 private、初值設定或是建立 module、閉包 (closure)
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var cat = {
name: 'Kitty',
bark: function(){
return 'meow~';
}
};
cat.bark(); // "meow~"Function as Object's method
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var Cat = function(name){
this.name = name;
}
cat.prototype.bark = function(){
return 'meow~';
};
var cat = new Cat('Kitty');
cat.name; // "Kitty"
cat.bark(); // "meow~"Function as Constructor
Object
Function
Array
Object types
window.x = 10;
function getX(){ return this.x}
var obj = {
x: 20,
getX: function(){
return this.x;
}
};
getX(); // 10
obj.getX(); // 20
"this" in Object
Object
Function
Array

this 指向調用該函釋之物件,沒有的話指向 Global (嚴格模式例外)
Object types
var ary = [];
ary.push(1); // [1]
ary.unshift(2); // [2, 1]
// change array.length
var ary = []; // []
ary.length = 5; [undefined, ... x5]Create/initialize an Array
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var ary = [];
ary[0] = 1;
ary[1] = 'A';
ary[2] = {foo:3};
ary; // [1, 'A', {foo: 3}]Create/initialize an Array
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3, 4];
for (var i = 0; i < ary.length; i++){
console.log(i);
}
// 1, 2, 3, 4Enumerate (1/2)
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3, 4];
ary.forEach(function(element, index, ary)()=>{
console.log(element, index, ary);
});
// 1, 0, [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 2, 1, [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 3, 2, [1, 2, 3, 4]
// 4, 3, [1, 2, 3, 4]Enumerate (2/2)
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3];
var result = ary.map(function(currentValue, index, array){
return currentValue * 2
});
// [2, 4, 6]map、filter、reduce
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3];
var result = ary.filter(function(currentValue, idx, array){
return currentValue > 1;
});
// [2, 3]map、filter、reduce
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3];
var result =
ary.reduce(function(accumulator, val, idx, array){
return accumulator + currentValue;
});
// 6;map、filter、reduce
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var ary = [1, 2, 3];
var result =
ary.reduce(function(accumulator, val, idx, array){
return accumulator + currentValue;
}, 1); // <= default value
// 6;map、filter、reduce
Object
Function
Array
Object types
map([🌽, 🐮, 🐔], cook)
=> [🍿, 🍔, 🍳]
filter([🍿, 🍔, 🍳], isVegetarian)
=> [🍿, 🍳]
reduce([🍿, 🍳], eat)
=> 💩map、filter、reduce
Object
Function
Array
Object types
var obj = {a:1, b:2, c:3};
var keys = Object.keys(obj); // ["a", "b", "c"];
keys.forEach(function(key, idx, ary){
console.log(obj[key]);
});
// 1
// 2
// 3
You Can Enumerate An "Object"
Naming Convention
// 變數以駝峰命名
var variableAreCamelCase;
// function 也是
var functionNameAreCamelCase;
// 私有成員加底線
var obj = {
_privateMemberStartWithUnderLine: 100
};
// 建構函式首字大寫
var ConstructorFirstCharacterAsCapital;
// 常數全大寫
var CONST_ALL_CAPITAL;"use strict"
Strict mode
- 透過拋出錯誤的方式消除一些安靜的錯誤(意指不再靜默地忽略某些錯誤)
- 修正會阻礙 JavaScript 引擎進行最佳化的錯誤: 相同的程式碼在嚴格模式有時候能運行得比非嚴格模式來的快
- 禁止使用一些有可能被未來版本 ECMAScript 定義的語法
without "use strict"
function fn() {
foo = 1;
}
fn();
console.log(foo); // 1with "use strict"
"use strict"
function fn() {
foo = 1;
}
fn();ReferenceError: foo is not defined
"use strict" 作用範圍
function() fn(){
"use strict"
foo = 1;
}
bar = 2;ReferenceError
work
嚴格模式的限制
"use strict"
// 未宣告
foo = 1;
// 刪除變數
var foo = 1;
delete foo;
// 刪除函數
function add(){}
delete add;
// 參數同名
function foo(bar, bar){}這些都會拋出錯誤
嚴格模式的限制
"use strict"
// 不允許使用 8 進制
// 8 進制並不是 ES5 的標準規範,但是瀏覽器都有實做
var num = 010;
// this 不再指向 global
window.myGlobal = 'global'
function foo(){
return this.myGlobal;
}這些都會拋出錯誤
see more at MDN strict mode
Hoisting
console.log(a);Uncaught ReferenceError: a is not defined
console.log(a);
var a = 1;What is hoisting
// undefined
console.log(a);
var a = 1;What is hoisting
JavaScript interpreter move all declarations to the top of the current scope.
var a; //undefined
console.log(a);
a = 1;function foo() {
return bar();
function bar() {
return 'hi';
}
}
foo(); //hifunction foo() {
function bar() {
return 'hi';
}
return bar();
}
foo(); //hiWhat is hoisting
This feature also occurs function inside.
for(var i = 0; i < 10; i++){ /* ... */}
console.log(i); // 10What is hoisting
At for-loop structures
function foo(){
function bar() {
return 3;
}
return bar();
function bar() {
return 8;
}
}
foo();function foo(){
function bar() {
return 3;
}
function bar() {
return 8;
}
return bar();
}
foo();What is hoisting
What is Result Each Case ? (1/3)
foo() = ?

8
var str = "hey";
function foo() {
return str;
var str = "hi";
}
foo();var str = "hey";
function foo() {
var str;
return str;
str = "hi";
}
foo();What is hoisting
foo() = ?
undefined

What is Result Each Case ? (2/3)
function foo(){
return bar();
var bar = function(){
return 3;
};
var bar = function(){
return 8;
};
}
foo();function foo(){
var bar;
var bar;
return bar();
bar = function(){
return 3;
};
bar = function(){
return 8;
};
}
foo();What is hoisting
TypeError: bar is not a function

What is Result Each Case ? (3/3)
function hoisting (param) {
arguments, this;
param;
function myFunc() {
console.log('hello');
}
var bar;
}
What is hoisting

Hoisting order
- Native object (this, arguments)
- Function parameters
- Function declaration
- var declaration
Implicit Coercion
隱式轉換
What is Implicit Coercion ?
"1" == 1; // true
0 == []; // true
2 * "2"; // 4
2 + "1"; // "21"在 Javascript 中,有些情況會發生強制轉型(coercion),強制轉型的結果會是基本型別 (primitive)
when Implicit Coercion happen?
- "-"、"*"、"/" operators
- "+" operator
- If ... else、 "&&"、"||"
- "==" Abstract Equality
String to Number
"1" / "2"; // 0.5
"1" * 4; // 4
"10" - "8"; // 2
"4" % "2"; //0- 、 * 、 / 、 % 皆轉成數字後再運算
Boolean to Number
false + 1; // 1
true + 1 // 2與 number 做運算,Booleans 會轉為 number
The Addition operator ( + )
1 + "2"; // "12"
"2" + 1; // "21"The Abstract Equality Comparison ( == )
var a = 23;
var b = "23"
a == b; //trueThe Abstract Equality Comparison ( == )
var a = "1";
var b = true;
a == b; //truesee more at ecma-262/5.1/#sec-11.9.3
Tool Site
End
Quiz
// 下列程式結果為 true
1 + 2 === 3;
// 下列為 false
0.1 + 0.2 === 0.3;
// 你可以解釋原因嗎?Q1:
// 我們知道 parseInt 可以帶入基數
parseInt(10, 2); // 2
parseInt(11, 8); // 9
// 現在有一個 Array
var ary = [3, 4, 5, 6];
// 跟一個 function
var myParseInt = function(n){
return parseInt(n);
};
// 下列的程式結果為 [3, 4, 5, 6];
ary.map(myParseInt);
// 下列的程式結果為 [3, NaN, NaN, NaN]
ary.map(parseInt);
// 請解釋為什麼會有這樣的結果?Q2:
Q3:
var foo = function foo() {
console.log(foo === foo);
};
foo(); // 會印出什麼結果?Q4:
function aaa() {
return
{
test: 1
};
}
console.log(typeof aaa());
// 會印出什麼結果?Q5:
Number("1") - 1 == 0;
// 會印出什麼結果?Q6:
function bar() {
return foo;
foo = 10;
function foo() {}
var foo = '11';
}
console.log(typeof bar());
// 會印出什麼結果?Q7:
var myArr = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'];
myArr.length = 0;
myArr.push('bin');
// 會印出什麼結果?
console.log(myArr);
Q8:
"1" - - "1";
// 會印出什麼結果?
Q9:
var myArr = ['foo', 'bar', 'baz'];
myArr[2]; // 會拿到?
console.log('2' in myArr); // 結果是?