AGILE METHODOLOGIES
project management in software engineering
Marco Alabruzzo,
Front End Developer @ Growth Street
TBBL, 31 March 2016

QUESTIONS
If you ask them during the presentation maybe you anticipate something
If you wait the end you'll probably forget them
Put them on Slack, I'll read and answer at the end of the presentation
SUMMARY
What is the problem?
What options do we have?
Project's complexity
Communication and Requirements definition
Advantages of SCRUM
SCRUM Roles
SCRUM Artifacts
SCRUM Ceremonies
What is the problem? - 1
Software isn't based on physics.
Instead is based on whatever some random bunch of guys thought was a good idea in the early 1980’s
Software engineering isn't reliable
What is the problem? - 2
Software is constantly changing
What is the problem? - 3
Software does not require any raw material
Good or bad?
What options do we have? - 1
Plan more, the waterfall
Analysis
Week 1
Week 2
Week 3
Week 4
Week 5
Week 6
Integration
Design
Code
Test
Deploy
What options do we have? - 2
Why waterfal doesn't work:
Require perfect knowledge of the project from the beginning
Why waterfal doesn't work:
Why waterfal doesn't work:
Evrey mistake is amplified by a cascade effect
Handovers generate a chinese whisper situation
What options do we have? - 3
Incremental development

Analysis
Week 1
Week 2
Week 3
Week 4
Week 5
Week 6
Integration
Design
Code
Test
Deploy
Analysis
Integration
Design
Code
Test
Deploy
Analysis
Integration
Design
Code
Test
Deploy
What options do we have? - 4
Incremental development

Week 1
Week 2
Week 3
Week 4
Week 5
Week 6



Project's complexity

Modified Stacey's matrix
Communication and Requirements definition - 1
Customer often needs to see the wrong product before they can specify what they really need
Michael James, SCRUM trainer
Customers don't know what they actually want
Gregory Carter, Founder and CRO @ Growth Street
Communication - 2
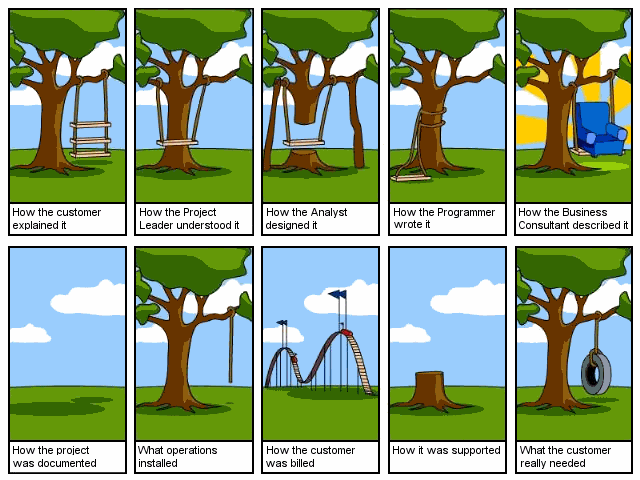
Advantages of SCRUM
Earlier feedback avoid cascade mistake and huge delay
Better definition of requirements faster response to changes
Many small releases
Feedback on product
Software development is seen as a knowledge creation process
Feedback on process
SCRUM Roles - 1
PRODUCT OWNER

SCRUM DEVELOPMENT TEAM


SCRUM MASTER
SCRUM Roles - 2
PRODUCT OWNER
Responsible for Return On Investment (ROI)
Final arbiter of requirements
Decide what add value to the product
Focused on what

SCRUM Roles - 3
SCRUM DEVELOPMENT TEAM
Self-organizing cross functional group
Attempts to build "potentially shippable product" evrey Sprint
Focussed on how and when

SCRUM Roles - 4
SCRUM MASTER
Facilitator
Has no managment authority
Doen't have a project manager role
Resolve impediments and distractions for the development team

SCRUM Artifacts - 1
PRODUCT BACKLOG
User story
task
to do
doing
done
SPRINT BACKLOG
User story
User story
User story
User story
task
task
task
task
task
task
task
task
task
task
task
SCRUM Artifacts - 2
User stories stories represent a distinct business values,
task are simple step in the process of realize user stories
I as lender want to be able to download my monthly statements from the lender's dashboard, so I don't have to depend upon email
Create a monthly statement generation view
Layout monthly statement as pdf
Create a page with the list of available monthly statment
User stories
Tasks
SCRUM Artifacts - 3
PRODUCT BACKLOG
User stories, use case scenarios, what
I – Independent
N – Negotiable
V – Valuable
E – Estimable
S – Small
T – Testable
User story
SCRUM Artifacts - 4
PRODUCT BACKLOG
Independent
Stories are easiest to work with if they are independent, you should be able to schedule and implement them in any order.
Negotiable
It is not an explicit contract for features; rather, details will be co-created by the customer and programmer during development.
A good story captures the essence, not the details.
User story
SCRUM Artifacts - 5
Valuable
A story needs to be valuable to the customer.
Small
A story should be at most a quarter of a sprint, potentially less.
Estimable
A good story can be estimated. We don't need an exact estimate, but just enough to help the customer rank and schedule the story's implementation.
Testable
Ideate a test help indicate that the story is clear, and can be declared as done when the test pass.
User story
SCRUM Artifacts - 6
SPRINT BACKLOG
Task, actual things to do, how
S – Specific
M – Measurable
A – Achievable
R – Relevant
T – Time-boxed
task
SCRUM Ceremonies - 1
Backlog refinement
Sprint planning
Daily SCRUM (stand up)
Sprint review
Sprint retrospective
SCRUM Ceremonies - 2
Backlog refinement
SCRUM team helps the product owner to refine Product backlog.
User stories are refined, the big ones are splitted in more manageable one, criteria of acceptance are negotiated.
SCRUM Ceremonies - 3
SCRUM team write down the task necessary to realise each user story.
The team also commit how much work is going to be realised in the sprint.
Sprint planning
Daily SCRUM (stand up)
Sprint review
Sprint retrospective
SCRUM Ceremonies - 4
What I did yesterday
What I’m going to do today
What is blocking me
Sprint planning
Daily SCRUM (stand up)
Sprint review
Sprint retrospective
SCRUM Ceremonies - 5
Live demonstration of the product
Product owner declare which user stories has been completed
Stakeholder feedback
Sprint planning meeting
Daily SCRUM (stand up)
Sprint review meeting
Sprint retrospective
SCRUM Ceremonies - 6
What went good
What went bad
Action to take in the next sprint
Sprint planning meeting
Daily SCRUM (stand up)
Sprint review meeting
Sprint retrospective