Tundra
By: Maren Wenger, Pierce Hammack, and Ethan Schaefer
Works Cited
Locations
- http://www.marietta.edu/~biol/biomes/tundra.htm
- http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/siberian_tundra.htm
Weather
- http://ths.sps.lane.edu/biomes/tundra4/tundra4c.html
- http://tundrazlove.weebly.com/weather-and-climate.html
- http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/tundra_climate_page.htm
Plants
- http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/caribou_moss.htm
- http://www.blueplanetbiomes.org/arctic_willow.htm
- www.wikipedia.com
Animals
- www.tundraanimals.net
- Wikipedia
- http://wwf.panda.org/about_our_earth/species/profiles/
mammals/arcticwolf/
- https://www.nwf.org/wildlife/wildlife-library/birds/bald-eagle.aspx
- http://www.allaboutbirds.org/guide/tundra_swan/lifehistory
Locations
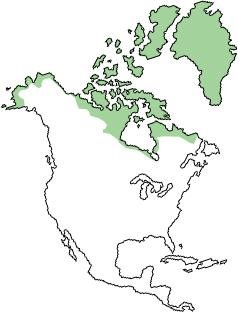
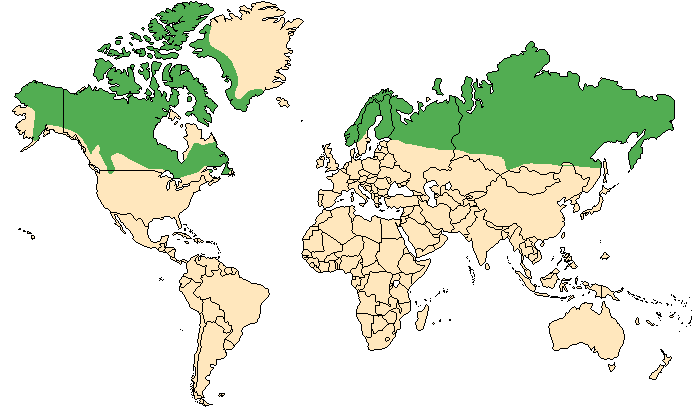
North America
- Southern Greenland
- Northern Alaska
- Canada
Asia
-
Siberia
-
Russia
-
Northern Europe
Weather
Winter
-
Winter storms
-
Average temperature of -30 C
-
Permafrost
-
Nights are longer


Summer
-
3-12 degrees C
- 6-10 inches of rain all year
- 6-10 weeks of summer
- constant wind


Plants
Bearberry
Uses: leaves are picked during the summer and dried for infusions, liquid extracts, medicinal tea bags and tablets; tobacco;
Predators: ptarmigan; arctic hares;
Adaptations: 40,900 seeds per lb of berries;

Caribou Moss
Uses: thickens soups and desserts (powdered); rich in vitamins A & B; boil & eat; tea as medicine for diarrhea
Predators: caribou/ reindeer;
Adaptations: frost has no effect; long periods of time without water (go dormant);


Arctic Willow
Uses: twigs are fuel; medical - toothache, stop bleeding, curing diarrhea and indigestion; poultice on wounds
Predators: musk ox; arctic hares; lemming; caribou; ptarmigan
Adaptations: long lived;shallow root system; fuzzy hairs; natural pesticide


Pasque Flower
Uses: induce abortion & childbirth; sedative; treating coughs;
Adaptations: highly toxic; hairs help protect from cold; blooms in spring


Animals
Polar Bears

Diet: seals; sometimes walruses; occasionally carcasses of whales
Size: largest land mammals on Earth; males can be 700-1400 lbs and 8-10 ft tall; females are slightly smaller- 350-700 lbs
Adaptations: hairs are translucent and clear; skin is black; coat & skin are designed to absorb sunlight and retain heat; short ears
Reproduction: give birth every 2-3 years; mating season in the spring; give birth in winter; litter of 1-2 cubs

Musk Ox
Adaptations: live in herds; outer coat- long, brown hair; inner coat- wool; horns; glands that produce a strong, musky odor
Reproduction: season- late summer to early fall; 1 calf in the spring; males compete for dominance over a harem of females
Predators: wolves and bears


Diet: vegetarian; willow shoots, grasses, shrubs, and lichen
Size: 6-7.5 feet tall; 400-900 lbs; shoulder height of 4-5 feet;
Rock Ptarmigan
Adaptations: change color - brown spots in summer, white in winter; males have red comb over eyes;
Reproduction: females lay between 6-10 eggs; incubation of 3 weeks; male leaves female during incubation; chicks get fledgling in 10-12 days
Predators: hawks, eagles, owls, foxes


Diet: leaves, flowers, berries, buds, twigs; chicks will feed on insects
Size: 12-16 inches
Caribou/ Reindeer
Diet: summer- vegetation (willow leaves); winter - dig through snow to get moss/ lichen
Size: female - 180-200 lbs; males - 400-600 lbs; 35-55 inches at shoulder
Adaptations: wide hooves- help when walking on mud & snow, help caribou swim & dig; migrate; thick fur and skin; shed their antlers; live in herds
Reproduction: mating season (rut) in fall; females give birth in spring; one calf
Predators: golden eagle - preys on calves; grizzly bears; wolves

Snowy Owl
Diet: small rodents (lemmings and voles); rabbits; other birds (ptarmigans); eggs of larger birds
Size: 1.75-2 feet in length; 4.5-5.5 foot wingspan;
Adaptations: can move heads 270 degrees both directions; thick layer of feathers on body and feet; keen eyes; great hearing
Reproduction: mating season - April-June; clutch - 2-14 eggs; 4-5 weeks until they hatch; male & female will tend to the nest before the chicks leave


Arctic Hare
Diet: buds, berries, twigs, mosses, woody plants,
Size: length - 20-26 inches; 8-14 lbs
Adaptations: color change; large hind feet allow them to move quickly through snow; claws help them dig through snow; sometimes forage shelters in snow to protect against bitter cold
Reproduction: mate in early spring; give birth in June-July
Predators: arctic wolves, foxes, and ermines


Arctic Wolf
Diet: musk ox, arctic hares, caribou
Size: 1-1.8 meters long; 45-70 kg
Adaptations: small ears; short snout; white fur; live in packs
Reproduction: typically live in rocky outcrops or caves; 2-3 pups


Bald
Eagle
Diet: tundra swan; fish (salmon); rodents; carcasses
Size: 2.5-3 feet in height; wingspan of 6.5 feet
Adaptations: claws; size; where they build their nests
Reproduction: solitary; mate with same eagle in the spring; lay 2-3 eggs; incubated for 35 days; chicks are brown without white head


Tundra Swan
Diet: aquatic plants, seeds, tubers, grains, some mollusks and arthropods
Size: length~47-58 inches; wingspan~66 in; weight~ 130-370 oz
Adaptations: can sleep on water; travel in flocks; migrate; tip up when eating; leave nest when large predators approach
Reproduction: spread out during breeding season; 3-5 eggs; creamy white;
Predators: nest - foxes, weasels, jaegers (skua or seabird); nest and swan - wolves, bears, people


Ermine
Diet: pikas, voles, rodents; rarely hares; secondary - small birds, fish, shrews
Size: males are 7.5-13 inches in length; females are 6.5- 11 inches; males weigh 258 grams; females weigh 180 grams
Adaptations: dense fur; white fur; coats change color from summer to winter and winter to spring
Reproduction: mate in April-July period; young are born blind, deaf, and toothless;


Pika
Diet: plants and leaves; their own feces
Size: 6-9 inches long; 120-350 grams
Adaptations: burrows; sometimes bring dead birds into their burrows to store for the winter
Reproduction: around 5 young;
Predators: ermine; birds of prey; foxes


Arctic Fox
Diet: small mammals (lemmings; voles), birds and their eggs, carcasses left by other animals (polar bears)
Size: 3-3.5 ft head to tail, 6-9 lbs, femalse are normally smaller than males
Adaptations: fur on paws; thick, dense coat of fur; short ears; small body; large, bushy tail used to curl around it's body
Reproduction: mating season in the spring, build dens, average litter of 6-8 kits

