
Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Problem
- So How does the machine learn and adjust the weights and biases automatically?

Scene 1 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
- So when we have a large cost or error value provided to us by the cost function, we need to adjust our weights and biases accordingly. But how much and should we adjust it up or down?
- This is where gradient descent comes in

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Prediction
- So let's make an assumption about our simple neural network to make it possible to understand gradient descent
- Let's say that our weight is set at a constant 1
- and our bias is 0

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Prediction
- So this means that the input we put in, for example 2m squared, is our prediction of $2M

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
- If we take a step backwards and look at what our cost function actually looks like. So our neural network makes a prediction, that's our general function called f(x), where x is meters squared.
- We subtract that by the actual truth, and in this case it was $2Million
- So what is the best possible prediction we can make?
- You guessed it, at $2million dollars we have 0 cost or error

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
- But what if we predicted wrongly?
- Well if we guessed $1M dollars our cost error would be that much
- If it was a ridiculous $-3M dollars it would be that much, way off
- Similarly if we guessed too much at $6M the error would be there.
- But look at our steep the curve is at the point $6M and -3M.
- It's Very steep!
- We see that in this curve, the steepness is different at each point

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
- That steepness is calculated by the gradient or derivative of the curve
- So if we draw the derivative of the curve it looks like this.
- It's very negative at the point where our prediction is below the target 2M
- It's very flat or low when we are almost reaching our goal.
- It's very high when we are very predicting above the target 2M

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
- So gradient descent uses the steepness of our cost curve to make better predictions each time. And it does this recursively. Meaning it will do it over and over again until it gets it right or in science we say the solution converges

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
So notice that if we predict below our target, we need to make sure our next prediction is higher.
Notice the gradient is negative in this case.
Also notice that if we predict too much, we need to make sure our next prediction is lower. The gradient is postive in this case.
So if we take our prediction and subtract it by our gradient. It will make sure that our next value is closer to the ideal solution

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
Note that if we subtract the gradient by a value that is too high, we will never get a good solution.
In Science, this means it will never converge.
So that's where the learning rate comes in. It's a coefficient that we multiply by our gradient to make sure we converge gradually ensuring our algorithm learns.

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Definition
Now that's gradient descent, but what about our weights and biases?
How does a full architecture neural network learn?
Sign up for more.

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Breakdown
- Show does it do that?
- Let's take a lesson from Feynman and break this complicated architecture down into simple components so that we can understand it.

Scene 3| Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Define Neuron

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised
Our input data does not change, its the truth, we can't change the radius squared in this case. That's our x value.
Our slope which you will see as w, is what our neural network can change in order to make better predictions and learn.
Finally, the b value is our y-intercept which the neural net can change in order to make better initial starting points

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Illustrate equation

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised
So let's say we have a house of 5 Square meters, costing $2M and 9 Square meters costing $2.5M. What if we had 10 Square meters, what's the price? So our neural network will create a general function that will make the optimal predictions for us given input and output data.

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Illustrate equation

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised
So by changing our "w" value, we can see that the slope or the rise over run, changes to make better predictions.
But how good are those predictions? Our cost function will tell us the error of our predictions through the equation.
Prediction - Actual Price.
We then square it in order to make it absolute

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks
Illustrate equation

Scene 2 | Goal Supervised
So let's first manually change the weight in order to make the best outcome. So we
adjust the weights a little, adjust the bias. And, finally, we got the right outcome!
But wait, that was manual. How do you think a machine can do this automatically and learn from its mistakes using deep learning. How does your Tesla car learn, how do you automate reporting, and how do financial predictions actually work. Find out now



Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks

Neuron

Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised
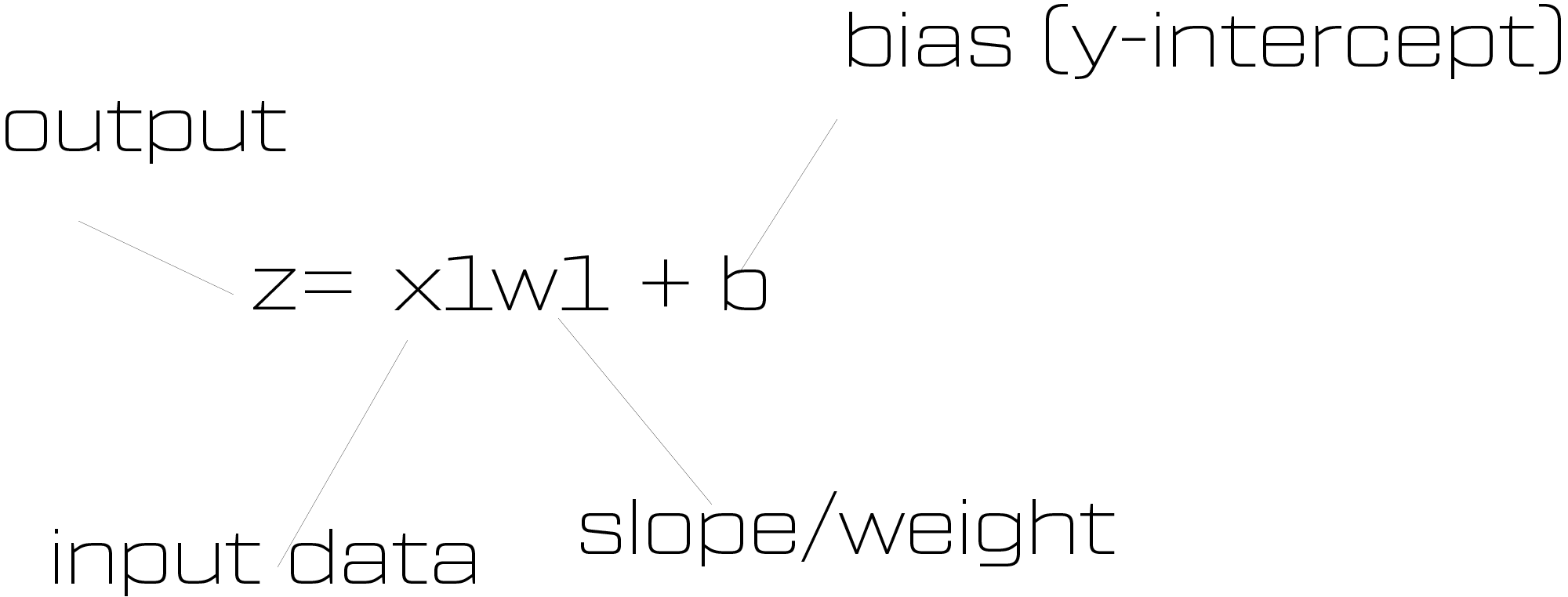

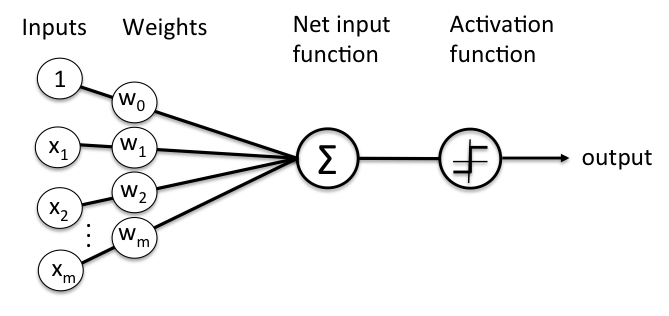
Interactive Intro
Neural Networks

Neuron

Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised

- But what if we had more than one input?
- Surface Area + Location?

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks

Neuron

Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks


Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised
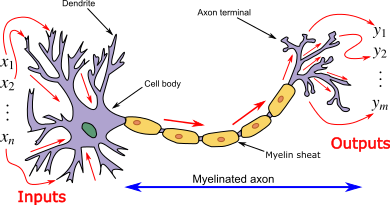

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks

Neuron and synaptic weight

Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised
- synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks


Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks


Chapter 1 | Goal Supervised

Interactive Intro
Neural Networks

Function
-
A function is a block of code which only runs when it is called.
-
You can pass data, known as parameters, into a function.
-
A function can return data as a result.

Chapter 1 | Intro
Create a Function
To create a function, use the keyword def Name():
Example
Create a function named NeuralNet, with a property named and call it

Chapter 1 | Python, class intro


Optimization Parameters
Chapter 5 | Forward propagation Intro
Chapter | Forward propagation Intro

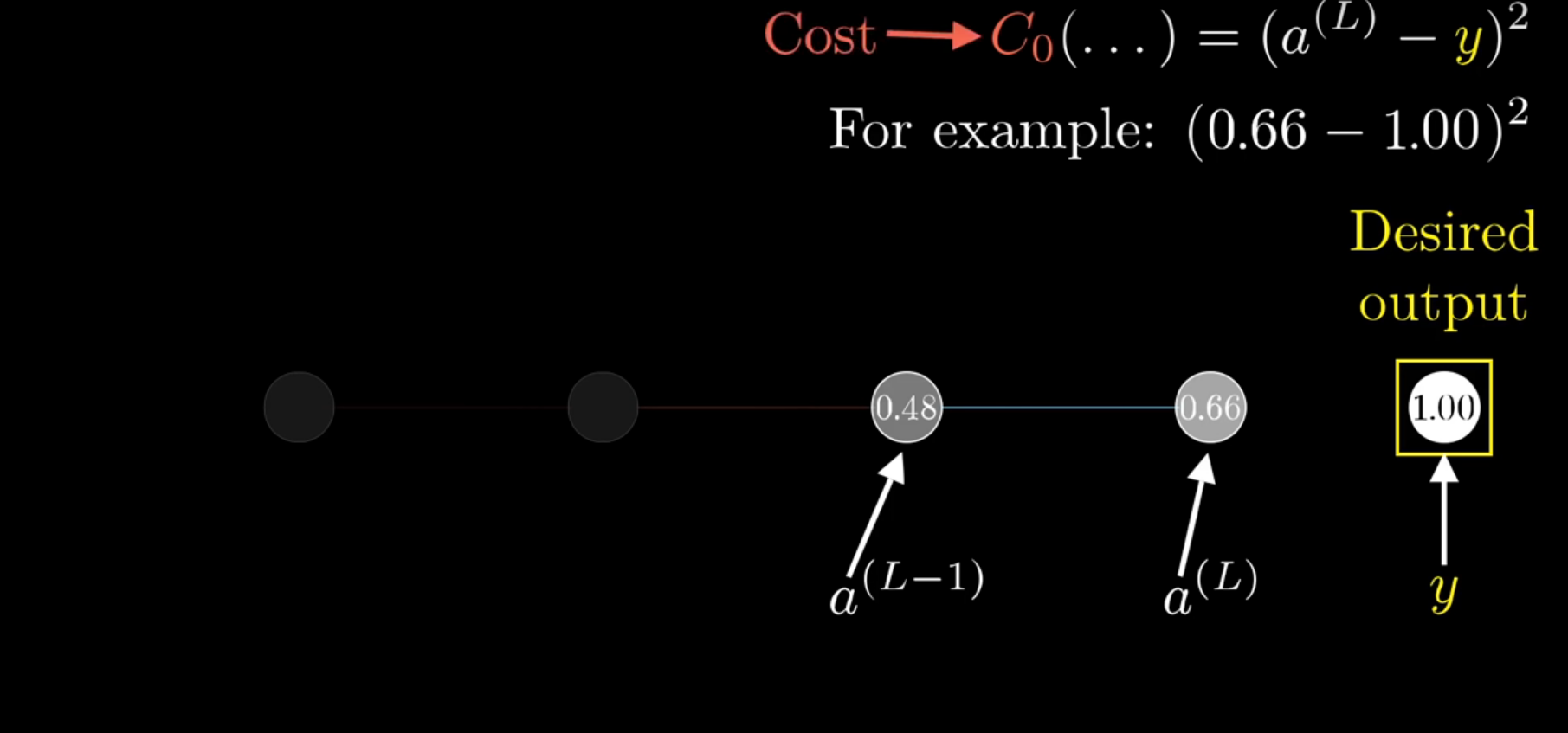
Chapter | Forward propagation Intro

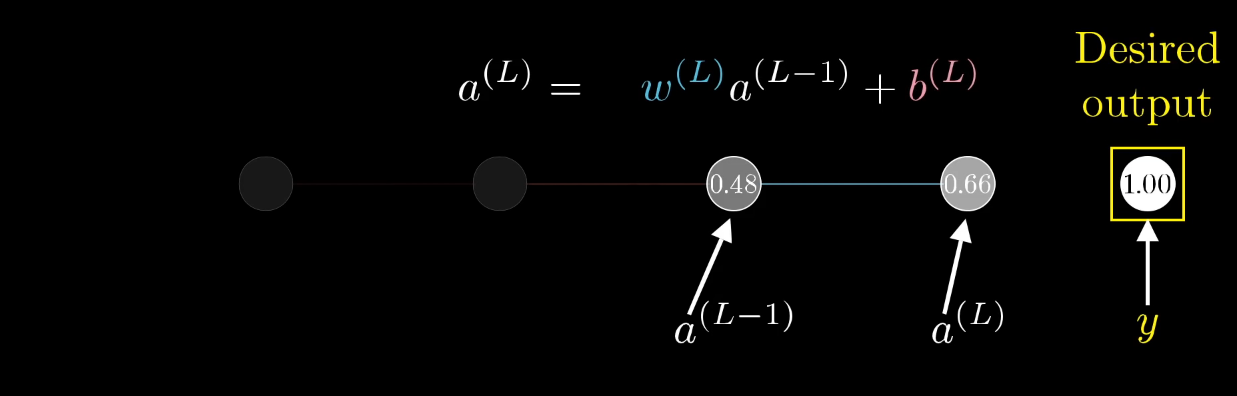

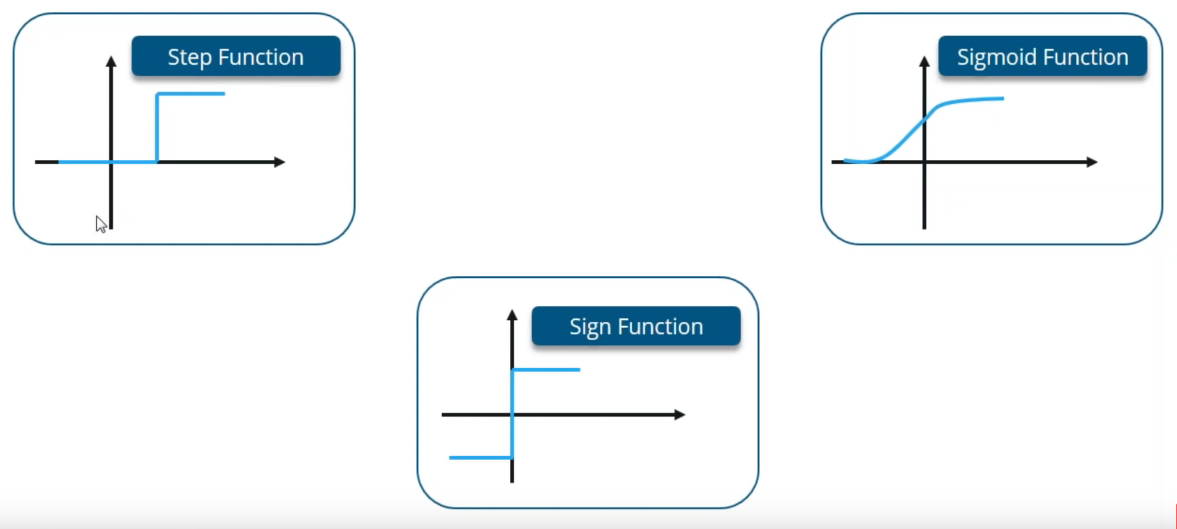
Chapter | Sigmoid Function
OK but what is a cost function?

Chapter | Cost

Chapter | Error Calcuation
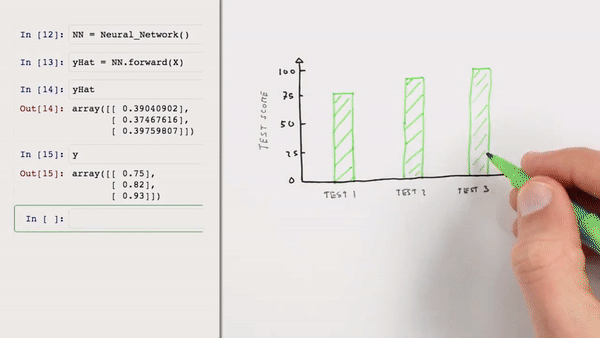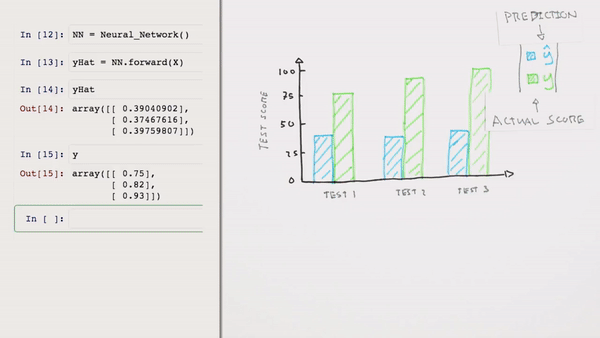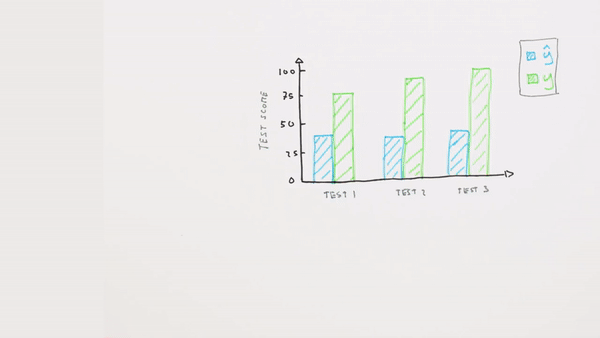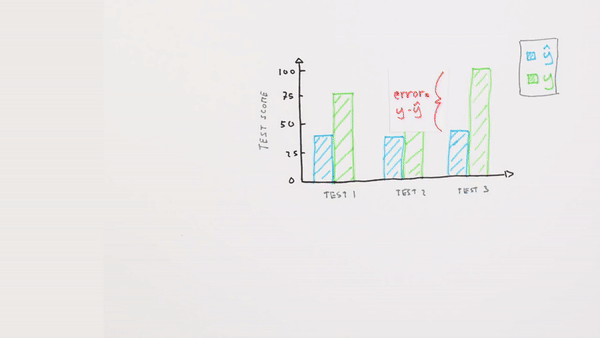


Chapter | Error Calcuation


https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/QY2W2C9
Please give us feedback :)
There are only 5 questions in the Survey