Develop an App with the Odoo Framework
Martin TRIGAUX - Developer

TL;DR
- https://www.odoo.com/documentation/
- Tutorials
- References
You can follow this presentation at
Architecture
- Three-tier client/server/database
- Webclient in Javascript
- Server and backend modules in Python
- MVC framework
- ORM to interact with database
The use case

The Module
- Manage a plant nursery
- list of plants
- manage orders
- keep a customers list
- Learn
- Structure of a module
- Definition of data models
- Definition of views and menus
Structure of a Module
An Odoo module is
- a manifest file
- python code (models, logic)
- data files, XML and CSV (base data, views, menus)
- frontend resources (Javascript, CSS)

Plant Nursery
The manifest file __manifest__.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Part of Odoo. See LICENSE file for full copyright and licensing details.
{
'name': 'Plant Nursery',
'version': '1.0',
'category': 'Tools',
'summary': 'Plants and customers management',
'depends': ['web'],
'data': [
'security/ir.model.access.csv',
'data/data.xml',
'views/views.xml',
],
'demo': [
'data/demo.xml',
],
'css': [],
'installable': True,
'auto_install': False,
'application': True,
}
Describe the models
from odoo import fields, models
class Plants(models.Model):
_name = 'nursery.plant'
name = fields.Char("Plant Name")
price = fields.Float()
class Customer(models.Model):
_name = 'nursery.customer'
name = fields.Char("Customer Name", required=True)
email = fields.Char(help="To receive the newsletter")
plant_nursery/models.py
Watch the result
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<odoo>
<record model="ir.actions.act_window" id="action_nursery_plant">
<field name="name">Plants</field>
<field name="res_model">nursery.plant</field>
<field name="view_mode">tree,form</field>
</record>
<menuitem name="Plant Nursery" id="nursery_root_menu"/>
<menuitem name="Plants" id="nursery_plant_menu"
parent="nursery_root_menu"
action="action_nursery_plant"
sequence="1"/>
</odoo>Watch the result
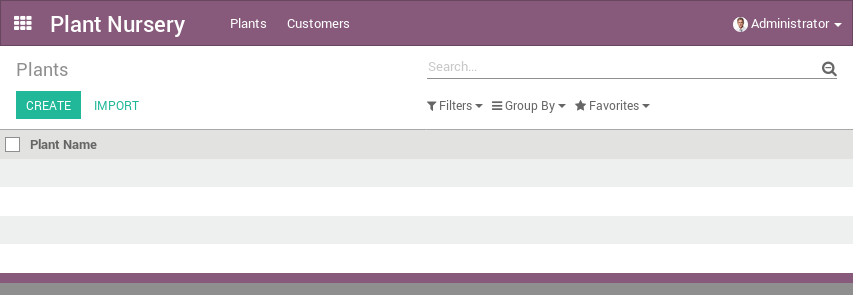
Auto-generated views
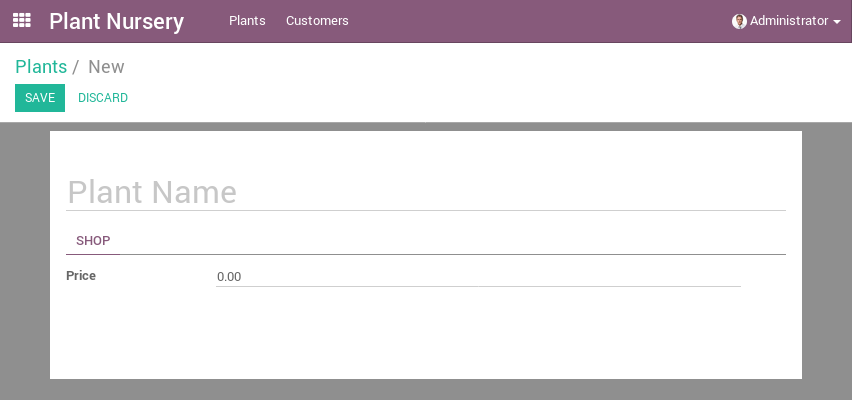
Complex views
<record model="ir.ui.view" id="nursery_plant_form">
<field name="name">Plant Form View</field>
<field name="model">nursery.plant</field>
<field name="arch" type="xml">
<form string="Plant">
<sheet>
<h1>
<field name="name" placeholder="Plant Name"/>
</h1>
<notebook>
<page string="Shop">
<group>
<field name="price"/>
</group>
</page>
</notebook>
</sheet>
</form>
</field>
</record>
Complex views (2)
Relations between models

- Many2one
- One2many
- Many2many
class Orders(models.Model):
_name = 'nursery.order'
plant_id = fields.Many2one("nursery.plant", required=True)
class Plants(models.Model):
_name = 'nursery.plant'
order_ids = fields.One2many("nursery.order", "plant_id", string="Orders")
name = ...Relations (2)
ORM interaction

Basic operations
- read
- write
- create
- unlink
ORM (2)
class Order(model.Models):
_name = 'nursery.order'
def write(self, values):
# helper to "YYYY-MM-DD"
values['last_modification'] = fields.Datetime.now()
return super(Order, self).write(values)
def unlink(self):
# self is a recordset
for order in self:
if order.state == 'confirm':
raise UserError("You can not delete confirmed orders")
return super(Order, self).unlink()
Computed fields

- For complex values
- Trigger for recompute
- Stored or not in database
Computed fields (2)
class Plant(models.Model):
_name = 'nursery.plant'
order_count = fields.Integer(compute='_get_total_sold',
store=True,
string="Total sold")
@api.depends('order_ids')
def _get_total_sold(self):
for plant in self:
plant.order_count = len(plant.order_ids)Model Constraints

- Triggered after every creation or modification
- Instead of overriding create & write
Constraints (2)
@api.constrains('order_count', 'number_in_stock')
def _check_available_in_stock(self):
for plant in self:
if plant.number_in_stock and \
plant.order_count > plant.number_in_stock:
raise UserError("There is only %s %s in stock but %s were sold"
% (plant.number_in_stock, plant.name, plant.order_count))
Thank you !

Credits
Pictures from
https://unsplash.com
- Brooke Cagle
- Annie Spratt
- Fabien Barral
- Mike Enerio
- Thomas Verbruggen
- Eduard Militaru
