This is FFIne
Building Foreign Function Interfaces without shooting yourself in the foot
Marten Wijnja
Infra Team, Channable

Lots of ground to cover for 20mins, here we go!
- We have Haskell and Python codebases
- We have a Hackathon-day every 10 weeks
- This is the story of one such day
Foreign Function Interfaces: Why?
- Do things that are difficult (or impossible) in Python
- Circumvent the Global Interpreter Lock (GIL)
- Do things faster than in Python
- Use a library for which there is no good Python alternative
many of the libraries you commonly use are secretly FFI!
List of Ingredients
- The 'host' language: Python (CPython)
- The 'embedded' language:
Anything that can compile to a dynamic library(`.so` / `.dll`)- C, C++, Rust, Haskell, Go, Fortran, Zig, (Chicken) Scheme, ... etc.
- (Other interpreted languages work too, but require glue code in a compiled lang)
- Python's: 'ctypes' module
Hello FFI world: ctypes in detail
# helloffi.zig -> libhelloffi.so
zig build-lib helloffi.zig -dynamic# helloffi.zig
export fn fancy_add(a: i32, b: i32) i32 {
return a + b;
}# example.py
import ctypes
helloffi = ctypes.CDLL("./libhelloffi.so")
helloffi.fancy_add.argtypes = (ctypes.c_int32, ctypes.c_int32)
helloffi.fancy_add.restype = ctypes.c_int32
def fancy_add(lhs: int, rhs: int): int
"Addition, sneakily using FFI"
return helloffi.fancy_add(lhs, rhs)Hello FFI world: ctypes in detail
>>> example.fancy_add(10, 20)
30
>>> example.fancy_add(10, 1000000000)
1000000010
>>> example.fancy_add(10, 100000000000000000)
1569325066 # Whoops!Foreign Function Interfaces: Why?
- Mapping datatypes between languages is hard
- Manual memory management is hard
- C is difficult to use and rife with undefined behaviour
- etc...
But it's complex, hard and a lot of work...
source: https://gunshowcomic.com/648

What's the alternative?
Separate webservices
Subprocesses
Easy to build, large overhead
full-fledged FFI
Hard to build, low overhead
What's the alternative?
Separate webservices
Subprocesses
Easy to build, large overhead
full-fledged FFI
Hard to build, low overhead
???
What's the alternative?
A simpler FFI!
What's the alternative?
A simpler FFI!

What's the alternative?
A simpler FFI!
- no C required
- higher-level communication between languages
- Support for exceptions
- Support for callbacks
- Only some footguns, which we'll dodge
- We'll build it up in layers
aside: If you want to use Rust, look into PyO3!
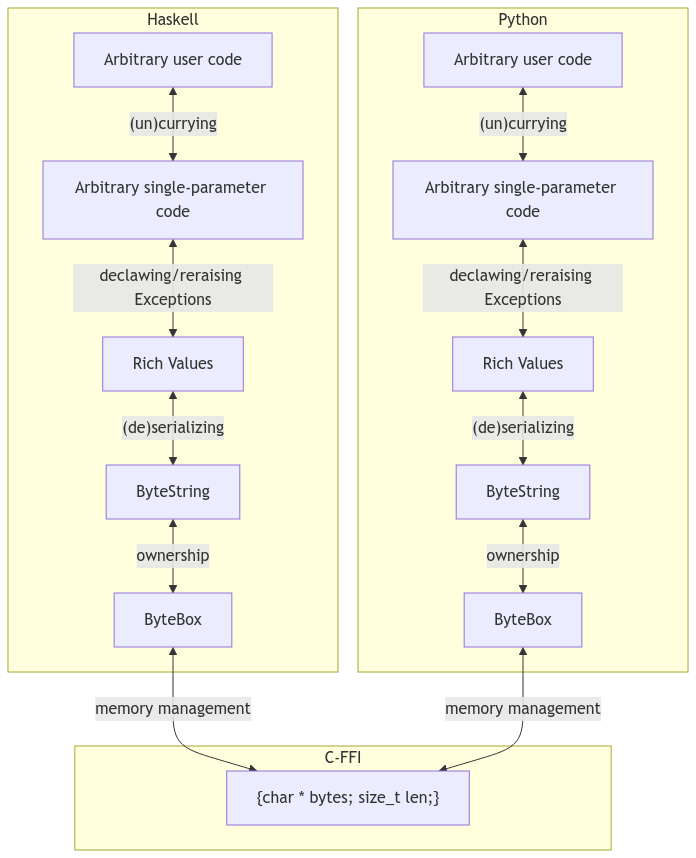
1
2
3
4
Layer 1: ByteStrings & Ownership
C does not support bytestrings!
=> convention:
elems: *byte
size: usize
actual bytestring content here... can contain \0 bytes
}
ByteBox {
Layer 1: ByteStrings & Ownership
class ByteBox(ctypes.Structure):
_fields_ = [
('elems', ctypes.POINTER(ctypes.c_char)),
("size", ctypes.c_size_t)
]
def __init__(self, bytestring):
self.elems = ctypes.create_string_buffer(bytes(bytestring), len(bytestring))
self.size = len(bytestring)
def __bytes__
return self.elems[0:self.size]Layer 1: ByteStrings & Ownership
# What we want
def myfun(input: ByteBox) -> ByteBox:
...
# What we do (better support):
def myfun(input: const ByteBox *, output: mutable ByteBox *) -> None:
...Layer 1: ByteStrings & Ownership
def wrap_external_fun(cdll, fun_name):
fun = getattr(cdll, fun_name)
fun.argtypes = [ctypes.POINTER(ByteBox), ctypes.POINTER(ByteBox)]
fun.restype = None
return fundef lift0to1(self, lower_fun):
def fun(in_bytes: bytes) -> bytes:
in_box = self.ByteBox(in_bytes)
out_box = self.ByteBox()
lower_fun(in_box, out_box)
out_bytes = bytes(out_box)
return out_bytes
return funLayer 1: ByteStrings & Ownership
def lower1to0(self, higher_fun):
def fun(in_box_ptr, out_box_ptr):
in_bytes = bytes(in_box_ptr.contents)
out_bytes = higher_fun(in_bytes)
out_box_ptr.contents.fill_with(out_bytes)
return fundef lift0to1(self, lower_fun):
def fun(in_bytes: bytes) -> bytes:
in_box = self.ByteBox(in_bytes)
out_box = self.ByteBox()
lower_fun(in_box, out_box)
out_bytes = bytes(out_box)
return out_bytes
return funActually, let's go both ways:
- So we can keep talking 100% Python
-
Testability: `myfun(x) == lift(lower(myfun))(x)`
-
Hypothesis: property-based testing
-
- Used for callbacks later
Footgun: Memory allocators

- Different languages allocate differently
- Solution: expose realloc(target_ptr, size)
import ctypes
class AllocHelper():
def __init__(self, dynamic_library):
self.dynamic_library = dynamic_library
# Will break at load-time if no function called `realloc` was exported
self.dynamic_library.realloc.argtypes = [ctypes.c_void_p, ctypes.c_size_t]
self.dynamic_library.realloc.restype = ctypes.c_void_p
def malloc(self, size):
return self.dynamic_library.realloc(None, size)
def free(self, ptr):
self.dynamic_library.realloc(ptr, 0)
return NoneLayer 1: ByteString support
def BYTE_BOX(dynamic_library):
allocator = AllocHelper(dynamic_library)
class ByteBox(ctypes.Structure):
_fields_ = [
('elems', ctypes.POINTER(ctypes.c_char)),
("size", ctypes.c_size_t)
]
def __init__(self, bytestring):
ptr = allocator.alloc(len(bytestring))
ctypes.memmove(ptr, bytestring, len(bytestring))
self.elems = ptr
self.size = len(bytestring)
def __del__(self):
allocator.free(self.elems)
... # Rest is unchangedByteBox, properly:
Layer 2: (de)serialization
def lift1to2(self, lower_fun):
def fun(param):
in_bytes = json.dumps(param)
out_bytes = lower_fun(in_bytes)
try:
out_obj = json.loads(out_bytes)
return {'Ok': out_obj}
except json.JsonDecodeError as ex:
return {'Error': ex}
return fun
def lower2to1(self, higher_fun):
def fun(in_bytes):
try:
in_obj = json.loads(in_bytes)
in_obj = {'Ok': in_obj}
except json.JSONDecodeError as ex:
in_obj = {'Error': sys.exc_info()}
out_obj = higher_fun(in_obj)
out_bytes = json.dumps(out_obj)
return out_bytes
return funlayer 1: bytes -> bytes
layer 2: Any -> Ok(Any) | Error(Any)
Layer 2: (de)serialization
- Result type: FFI supports no exceptions
- Once this works with JSON,
let's replace it with a binary format like CBOR (or BSON, Msgpack, ...)- significantly more performant
- supports more datatypes (datetimes, dicts with non-string keys, ...)


Layer 3: Exceptions
What is an exception?
- Name
- Message (details, humanly readable)
- Cause (some other exception?)
- Traceback (AKA stack trace, callstack, ...)
- Conceptually* an array
- tblib library: helps manipulating them
* CPython builds them as an intrusive linked list, oh joy!
Layer 3: Exceptions
def lift2to3(self, lower_fun):
def fun(params):
out = lower_fun(params)
if 'Error' in out:
# Parsing failed, rethrow parse error
raise Exception(out['Ok'])
elif 'Ok' in out:
out = out['Ok']
if 'Error' in out:
# Running callback failed, reraise foreign exception
error = out['Error']
serializable_exception.raise_exception_from_value(
error['name'],
error['message'],
error['callstack'],
error['annotations']
)
elif 'Ok' in out:
# Running callback succeeded, return result
return out['Ok']
else:
raise Exception(f"Unexpected format returned from FFI call: {out}")
return fun
def lower3to2(self, higher_fun):
def fun(params_result):
if 'Error' in params_result:
raise Exception(params_result['Error'])
elif 'Ok' in params_result:
try:
out = higher_fun(params_result['Ok'])
return {'Ok': out}
except Exception as ex:
exception_info = sys.exc_info()
out = serializable_exception.exception_to_value(exception_info)
return {'Error': out}
else:
raise Exception(f"Value not in expected format; expected dict with 'Left' or 'Right' key but got: {params_result}")
return funLayer 4: (Un)currying
def lift3To4(self, lower_fun):
def fun(*params):
return lower_fun(params)
return fun
def lower4To3(self, higher_fun):
def fun(params):
return higher_fun(*params)
return funlayer 3: Any -> Any
layer 4:
- () -> Any,
- Any -> Any,
- (Any, Any) -> Any
- ...
Done, sort of
def lift(self, fun):
return lift3to4(lift2to3(lift1to2(lift0to1(fun))))
def lower(self, fun):
return lower1to0(lower2to1(lower3to2(lower4to3(fun))))
def lift_full(self, fun_name):
return lift(wrap_external_fun(fun_name))Extra: Support callbacks
self.ForeignClosure = ctypes.CFUNCTYPE(None, ctypes.POINTER(self.ByteBox), ctypes.POINTER(self.ByteBox))
...
def lowerFull(self, fun):
return self.ForeignClosure(lower(fun))
# Pass this to your JSON/CBOR/etc. encoder:
def customEncoder(self, encoder, obj: Any):
if isinstance(obj, self.ForeignClosure):
ptr = ctypes.cast(obj, ctypes.c_void_p).value
encoder.encode({'foreignClosureAddr': ptr})
# Pass this to your JSON/CBOR/etc. decoder as object_hook:
def custom_decoder(self, obj):
if 'foreignClosureAddr' in obj:
ptr = ctypes.c_void_p(obj['foreignClosureAddr'])
return ctypes.cast(ptr, self.ForeignClosure)not shown: finalization
Extra: Support callbacks
- The same technique can be used to support other objects that are hard or impossible to serialize
- You chose where you need extra performance

1
2
3
4
extra: callbacks
Closing Thoughts
- If someone else already made a library (e.g. PyO3), use that
- But rolling your own simple FFI to combine two languages:
- can be done in a day
- requires no C
- is reasonably production ready (no segfaults, no memory leaks)
- is reasonably performant (you choose where to extend it)