Outcome in Patients over 70 with Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
Martien Oranje
2012
1728
10
Per 100.000 persons
Hospitalizations
418
2,5
252 < 70y
1,7
166 > 70y
9,0
581 < 65y
21
Sources: 1
Per 100.000 persons
Deaths
So...
Entire SAH population
Case Fatality Rate
Population
Age < 65y with SAH
Age > 65y with SAH
24%
18%
37%
Entire population
Relative Risk (of Death)
Age > 70 compared to
Age < 70y
3,6
5,3
Being old and suffering from SAH is a bad combination
AND YET...
Sources: 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7





Maybe age isn't a very good predictor of clinical outcome?
Methods
Patient characteristics
Logistic regression model
- Elderly and outcome
- Crude and Final
DESIGN
Patients
PERIOD
END
Retrospective cohort
All SAH patients
Nov 2008 - June 2011
Follow-up or Death
Variables
Treatment modality,
DCI, hypertension,
anticoagulant drugs,
rebleeds
Analysis
Outcome
Modified Rankin Scale
SAH Protocol
Sources: iPortal AMC, SAB protocol (2008)

Results
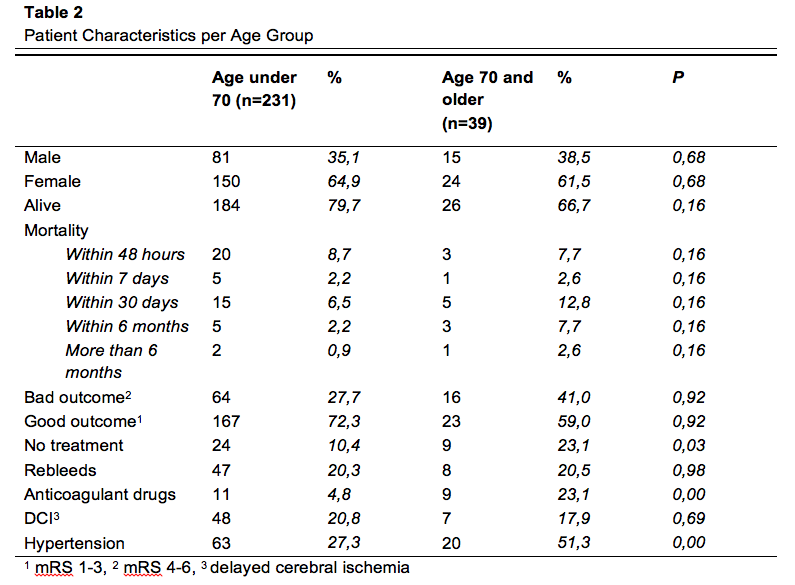
CFR 20,3%
CFR 33,3%
Results
Crude model (mRS vs age)
Final model (MRS VS AGE, INCL. confounders)
Age (70 and older): OR 1,9 CI 0,76 to 5,01
Age (70 and older): OR 1,2 CI 0,41 to 3,65
The relationship between age and clinical outcome was not supported.
Discussion
The elderly did not fare worse than the young
AMC
- Endovascular coiling 6,7,8
- Aggressive and invasive treatment 5,9
Limitations
- Follow-up, selection bias and small sample size
Sources: 5, 6, 7, 8, 9
Sources
-
CBS - Statline
-
Koffijberg H, Buskens E, Rinkel GJE. Aneurysm occlusion in elderly patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage: a cost-utility analysis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011;82(7):718-27.
-
Schöller, K., Massmann, M., Markl, G., Kunz, M., Fesl, G., Brückmann, H., … Schichor, C. (2013). Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in elderly patients: long-term outcome and prognostic factors in an interdisciplinary treatment approach. Journal of Neurology, 260(4), 1052–60.
-
Degos, V., Gourraud, P., & Tursis, V. (2012). Elderly age as a prognostic marker of 1-year poor outcome for subarachnoid hemorrhage patients through its interaction with admission hydrocephalus. Anesthesiology, (6), 1289–1299.
-
Awe, O. O., Gonzalez, L. F., Hasan, D., Maltenfort, M., Rossenwasser, R., & Jabbour, P. (2011). Treatment outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients aged 70 years and older. Neurosurgery, 68(3), 753–8; discussion 758.
-
Shimamura, N., Matsuda, N., Satou, J., Nakano, T., & Ohkuma, H. (2014). Early ambulation produces favorable outcome and nondemential state in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage patients older than 70 years of age. World Neurosurgery, 81(2), 330–4.
-
Connolly, E. S., Rabinstein, A. A., Carhuapoma, J. R., Derdeyn, C. P., Dion, J., Higashida, R. T., … Vespa, P. (2012). Guidelines for the management of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/american Stroke Association. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 43(6), 1711–37.
-
Mutoh, T., Kazumata, K., Terasaka, S., Taki, Y., Suzuki, A., & Ishikawa, T. (2014). Early intensive versus minimally invasive approach to postoperative hemodynamic management after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke; a Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 45(5), 1280–4.
-
Garbossa, D., Panciani, P. P., Fornaro, R., Crobeddu, E., Marengo, N., Fronda, C., … Fontanella, M. (2012). Subarachnoid hemorrhage in elderly: advantages of the endovascular treatment. Geriatrics & Gerontology International, 12(1), 46–9.
The End
Thank you
Special thanks to: Dagmar, David, Jantien en René
QALY
Sources: 2
Text