Vue.js

Martin Janyš
Vue.js
pronounced /vju:/, like view
Simple UI FW
Data binding
Effective
Simple
- Write some HTML,
- grab some JSON,
- create a Vue instance,
- that's it.
Reactive
- Expressions
- computed properties
- dependency tracking.
Components
- Compose your application with decoupled,
- reusable components.
Compact
- ~24kb min+gzip,
- no dependency.
Fast
- Precise and efficient async batch DOM updates.
Examples
Two-way data binding
Rendering a list
Handle user input
All together
Editor
SVG Graph
Transitions
Carousel
And more ...
Vue basics
{
el: '#app',
data: {},
methods: {}
}
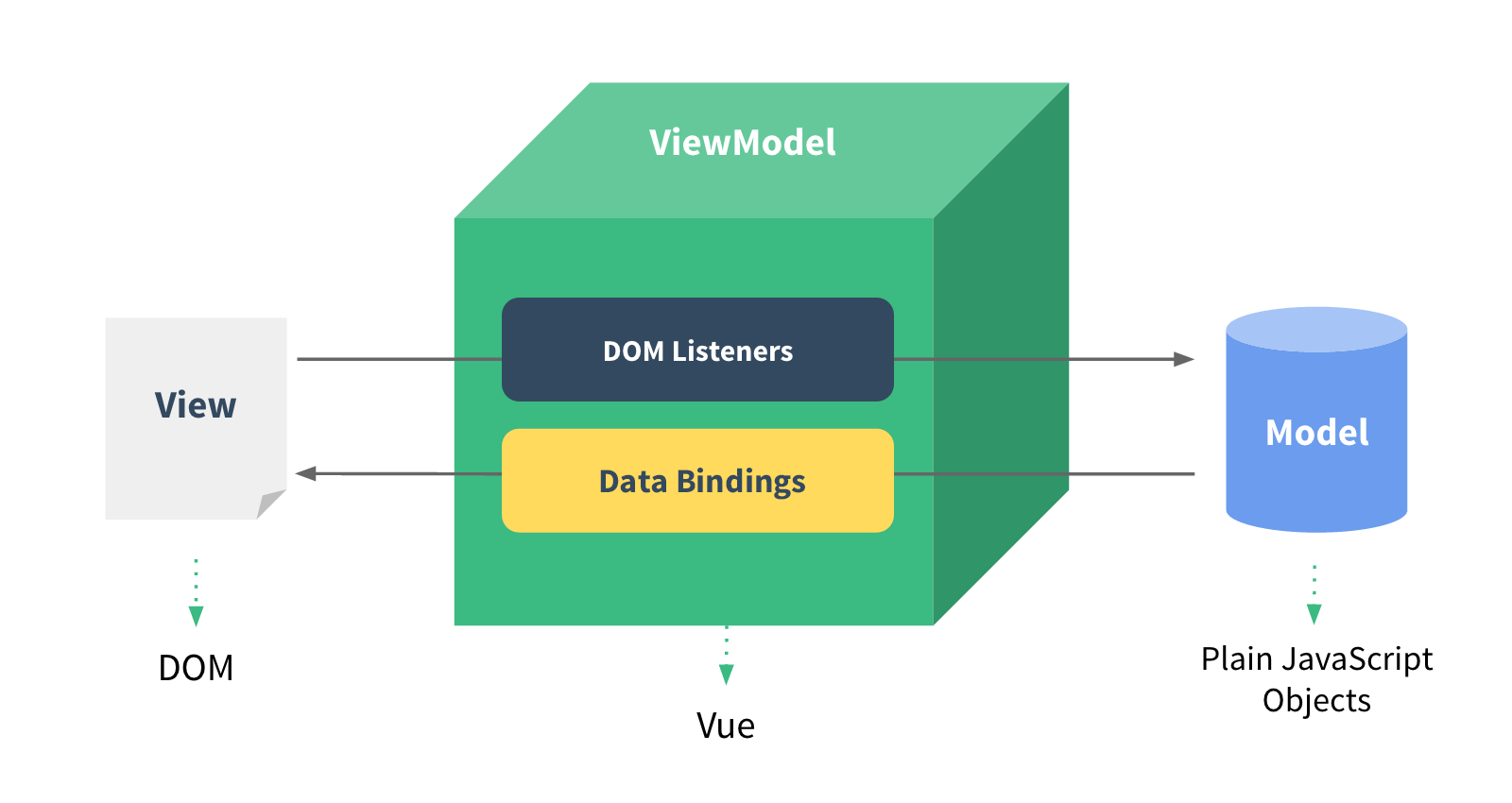
Reactive Data Binding
- Keeps your data and the DOM in sync
- Makes our code easier to write,
- easier to reason about,
- easier to maintain.
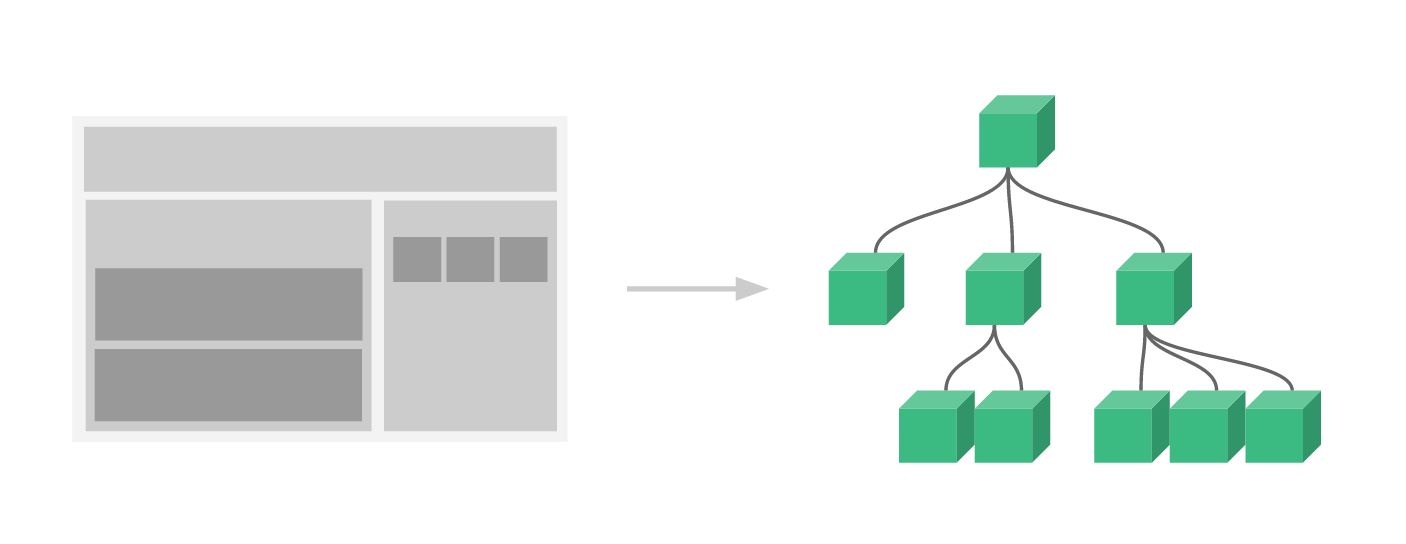
Components
- Module abstration
- to build large-scale applications composed of small, self-contained, and often reusable components
- very similar to Custom Elements, which is part of the Web Components Spec
- Web Components Spec is still very much a work in progress
- Vue.js components provide more features
<div id="app">
<app-nav></app-nav>
<app-view>
<app-sidebar></app-sidebar>
<app-content></app-content>
</app-view>
</div>Data binding syntax
Binding expression
{{ number + 1 }}
{{ ok ? 'YES' : 'NO' }}
{{ message.split('').reverse().join('') }}Filters
{{ message | capitalize }}
{{ message | filterA | filterB }}
{{ message | filterA 'arg1' arg2 }}Text
<span>Message: {{ msg }}</span>
<span>This will never change: {{* msg }}</span>Raw HTML
<div>{{{ raw_html }}}</div>Attributes
<div id="item-{{ id }}"></div>Directives
attributes with the v- prefix
Arguments
<a v-bind:href="url"></a>Arguments
<a v-bind:href="url"></a>
<a v-on:click="doSomething">Modifiers
<a v-bind:href.literal="/a/b/c"></a>v-bind shorthand
<!-- full syntax -->
<a v-bind:href="url"></a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<a :href="url"></a>
or
<!-- full syntax -->
<button v-bind:disabled="someDynamicCondition">
Button
</button>
<!-- shorthand -->
<button :disabled="someDynamicCondition">
Button
</button>v-on shorthand
<!-- full syntax -->
<a v-on:click="doSomething"></a>
<!-- shorthand -->
<a @click="doSomething"></a>All directives
- v-bind
- v-on
- v-model
- v-if
- v-else
- v-show
- v-cloak
- v-for
- v-text
- v-html
- v-ref
- v-el
- v-pre
Computed properties
Computed set & get
// ...
computed: {
fullName: {
// getter
get: function () {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
},
// setter
set: function (newValue) {
var names = newValue.split(' ')
this.firstName = names[0]
this.lastName = names[names.length - 1]
}
}
}
// ...- Computed properties
- cached
- transparency dependency tracking
Classes bindings
Array syntax
Object syntax
<div class="static"
:class="{'class-a':isA, 'class-b':isB}">
</div>
<div v-bind:class="[classA, classB]">data: {
isA: true,
isB: false
}data: {
classA: 'class-a',
classB: 'class-b'
}you can directly bind to an object in data as well
data: {
classes: ['class-a', 'class-b']
}data: {
classes: {
'class-a': true,
'class-b': false
}
}Object syntax
Array syntax
<div v-bind:style="styleObject"></div>
<div v-bind:style="[styleObjectA, styleObjectB]">Styles binding
<div v-bind:style="{ color: activeColor, fontSize: fontSize + 'px' }"></div>Events
- Could be any event (click, keyup, focus, ...)
Events modifiers
<!-- the click event's propagation will be stopped -->
<a v-on:click.stop="doThis"></a>
<!-- the submit event will no longer reload the page -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent="onSubmit"></form>
<!-- modifiers can be chained -->
<a v-on:click.stop.prevent="doThat">
<!-- just the modifier -->
<form v-on:submit.prevent></form>
<!-- only call vm.submit() when the keyCode is 13 -->
<input v-on:keyup.13="submit">
<!-- same as above -->
<input v-on:keyup.enter="submit">Components
Dynamic components
<tr is="my-component"></tr>Carousel component
Modal component
How to write components?
It is up to you!
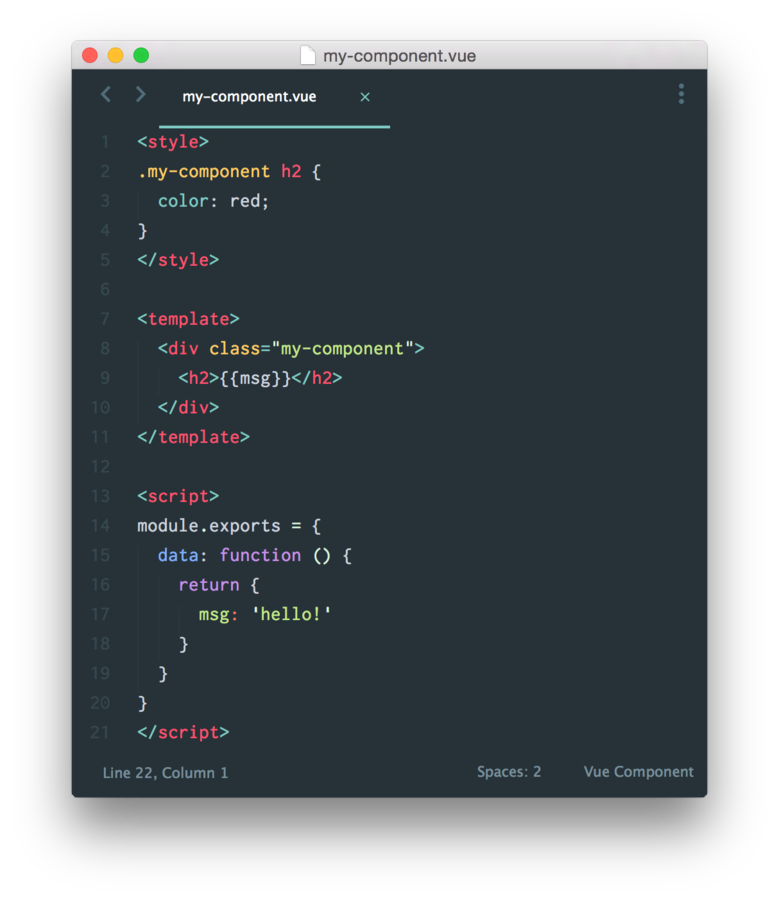
.vue file
- reference style
- style preprocessor
- templating
- html, jade
- scripting
- JS, ES6
- Output: Single JS file
- Webpack + vue-loader
- Browserify + vueify
.html file
- Pure html + css + script
- good IDE support
- No preprocesor nor compiler
- Scoped CSS
-
Include by <link rel="import" href="">
<div>
<template id="myTemplate">
<!-- template -->
</template>
<style type="text/css" scoped>
<!-- css -->
</style>
<script type="text/javascript">
<!-- js -->
</script>
</div>3 files - DIY
- Files for:
- script
- template
- css
- Use whatever you want
- js, ES6, TypeScript
- html, jade, ...
- css, LESS, SASS
- compile & bundle yourself
- maven + grunt, ...
Reactivity in depth
- Model is plain JavaScript Object
- Modified it and view updates
- Every binded property
must be in rective system
How Changes Are Tracked
- all properties is converted to getter/setters using Object.defineProperty
- Property perform dependency-tracking and change-notification
- For every directive/data binding in the template, there will be a corresponding watcher object
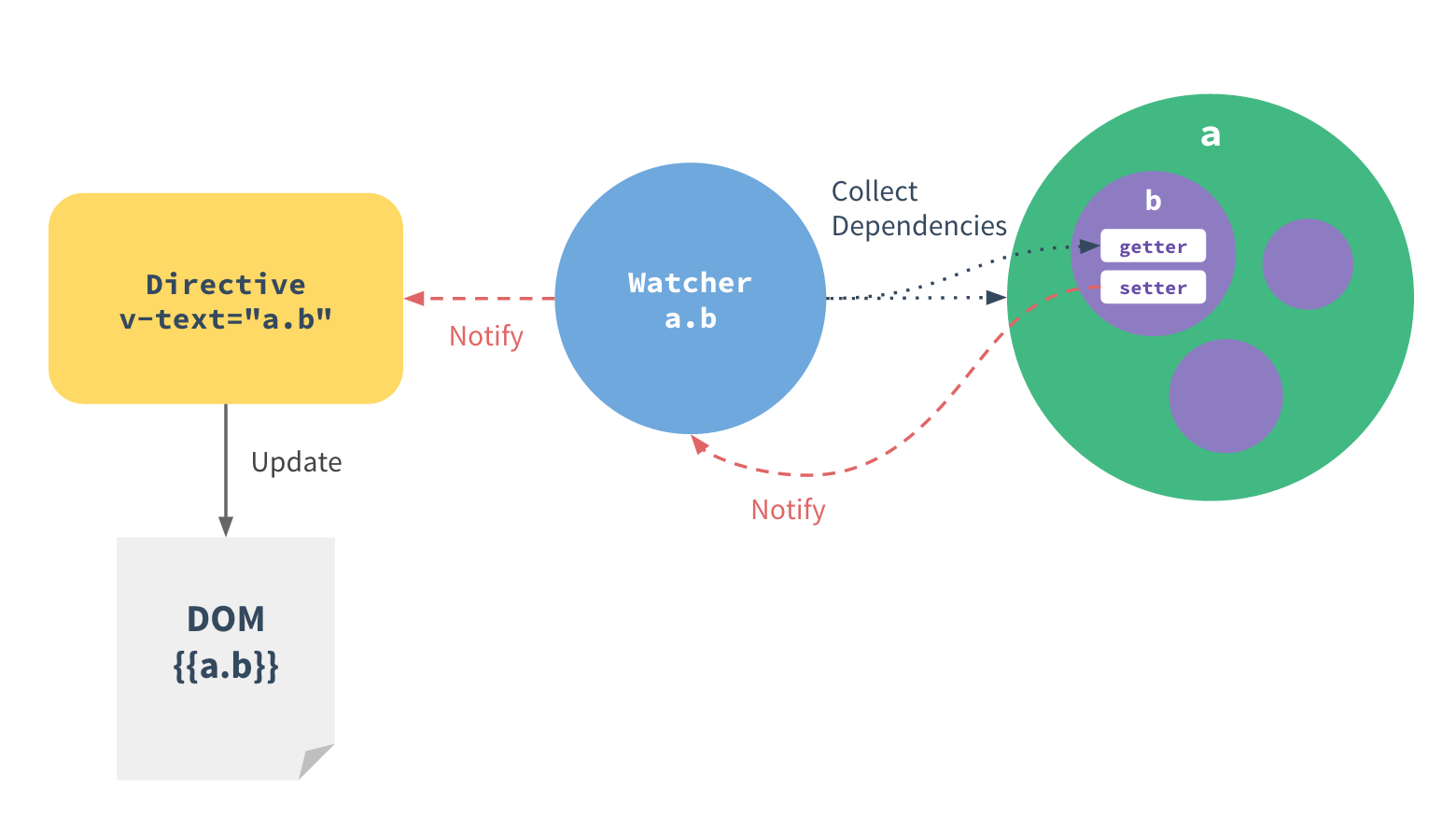
Change detection
- Specify your data object
- Vue cannot detect property addition or deletion
- Bullet Three
var data = { a: 1 }
var vm = new Vue({
data: data
})
// `vm.a` and `data.a` are now reactive
vm.b = 2
// `vm.b` is NOT reactive
data.b = 2
// `data.b` is NOT reactivevm.$set('b', 2)
// `vm.b` and `data.b` are now reactive
Vue.set(data, 'c', 3)
// `vm.c` and `data.c` are now reactive
this.someObject = Object.assign({},
this.someObject,
{ a: 1, b: 2 })Initialize Your Data
var vm = new Vue({
template: '<div>{{msg}}</div>'
})
vm.$set('msg', 'Hello!')var vm = new Vue({
data: {
msg: ''
},
template: '<div>{{msg}}</div>'
})
vm.msg = 'Hello!'Plugins
- official plugin
- to build SPA
var App = Vue.extend({})
var router = new VueRouter()
router.map({
'/foo': {
component: Foo
},
'/bar': {
component: Bar
}
})
router.start(App, '#app')- maintained by the PageKit team
- AJAX
/* HTTP Client */
this.$http({url: '/someUrl', method: 'GET'}).then(function (response) {
// success callback
}, function (response) {
// error callback
});
/* ROSOURCE */
var resource = this.$resource('someItem/{id}');
resource.get({id: 1}).then(function (response) {
this.$set('item', response.item)
});
resource.save({id: 1}, {item: this.item}).then(function (response) {
// success callback
}, function (response) {
// error callback
});
resource.delete({id: 1}).then(function (response) {
// success callback
}, function (response) {
// error callback
});
}- Flux/Redux inspired application architecture
- State management
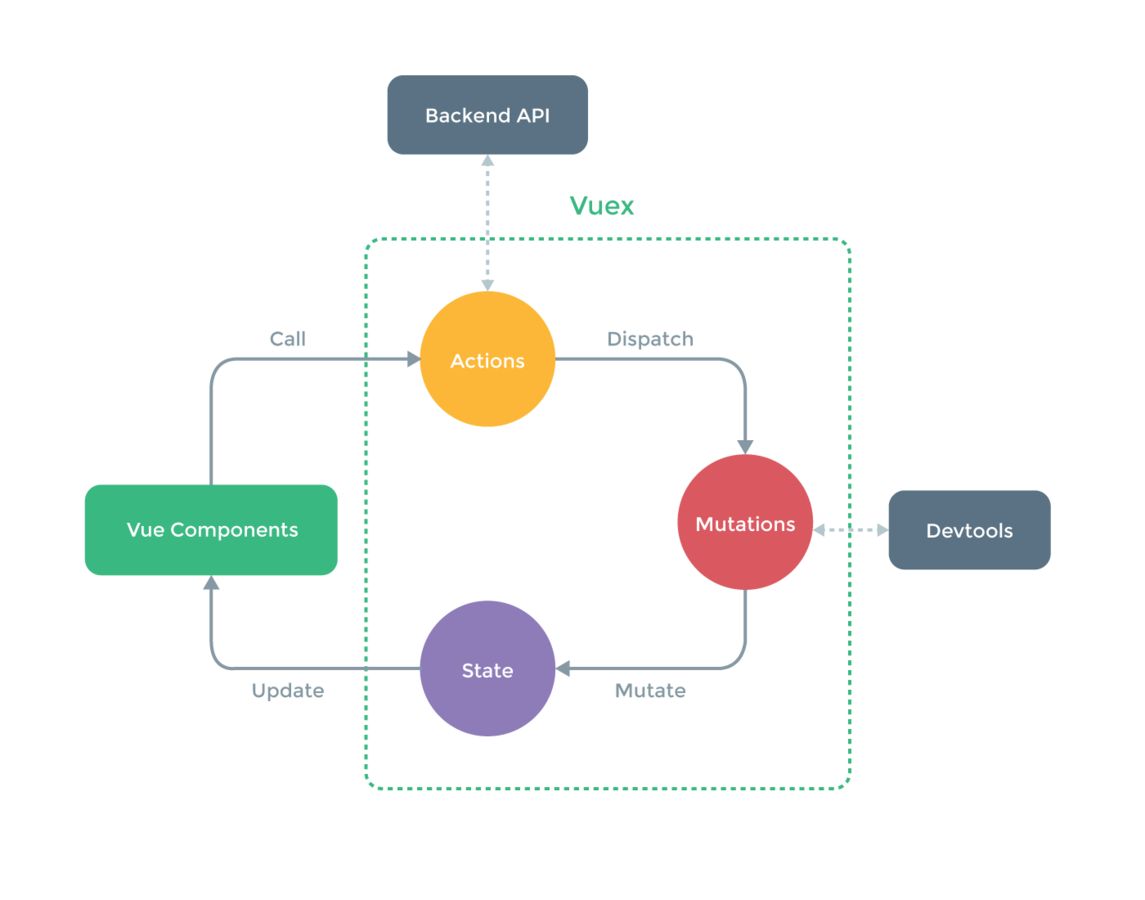
UI Components
- Boostrap
- Material design
- Components
- ... github.com/vuejs/
awesome-vue#ui-components
Other
Comparison with Other Frameworks

AngularJS 1.x
- Vue is simplier
- API, design, to learn
- Vue is a more flexible,
less opinionated solution - Vue use one-way binding between
parent-child component - Vue has a clearer separation
between directives and components - Vue has better performance
and is much, much easier to optimize
React
- both provide reactive &
composable View components - React uses virtual DOM
- React has higher learning barrier
- React - everything in JavaScript
- Vue.js actually outperforms React
when it comes to hot updates
Ember.js
- Ember's learning curve is high
- Vue outperforms Ember
- Templating and object model layer
- Vue provides reactivity on plain JS objects,
and fully automatic computed properties - Ember you need to wrap everything
in Ember Objects
- Vue provides reactivity on plain JS objects,
Polymer
- In fact was a source of inspiration for Vue as well
- Vue's components can be loosely
compared to Polymer's custom elements - Polymer's Web Components features must be native or emulated with degraded performance
- Vue works without any dependencies down to IE9
- The only expressions supported in Polymer templates are the boolean negation and single method calls (performance restriction)
- Polymer elements need to be bundled via Vulcanizer
References:
Workshop
Computed properties
Modal component
Prerequisites
Modal component
-
index.html structure
- Static minized modal (with slot)
- Static modal dialog (with slot)
- Overlay
- Title + body
- Dynamic behaviors
- click - close button, overlay
- esc key
- Transitions