SQL Two

Database Relationships, Foreign Keys, Joins, & Sub-Queries

DATA INTENSIFIES
Altering Tables
In SQL, ALTER TABLE statements can be used to:
Add/Remove Columns
Alter Column Data Types
Rename Columns
Change Table Name
Adding/Removing Tables
To add a table use the following syntax:
ALTER TABLE racers
ADD COLUMN team TEXT;Table being altered
How table is being altered
Column name and data type
Syntax for removing, or dropping, column is the following:
ALTER TABLE racers
DROP COLUMN team;Altering Data Types
The syntax for altering data types is the following:
ALTER TABLE racers
ALTER team
SET DATA TYPE VARCHAR(100);Table being altered
This can also be done in a shorter syntax:
ALTER TABLE racers
ALTER team
TYPE VARCHAR(100);Column being altered
New data type
Renaming Columns/Table
The syntax for renaming a column is the following:
ALTER TABLE racers
RENAME COLUMN team
TO "group";The syntax for renaming a table is the following:
ALTER TABLE racers
RENAME TO bike_racers;Table Relationships
When working with relational databases, one table's data will often relate to another table's data.
There are three main categories of table relationships:
One to One
One to Many
Many to Many
Examples:
1 Husband, 1 Wife
1 Mother, Many Children
Many Books, Many Authors
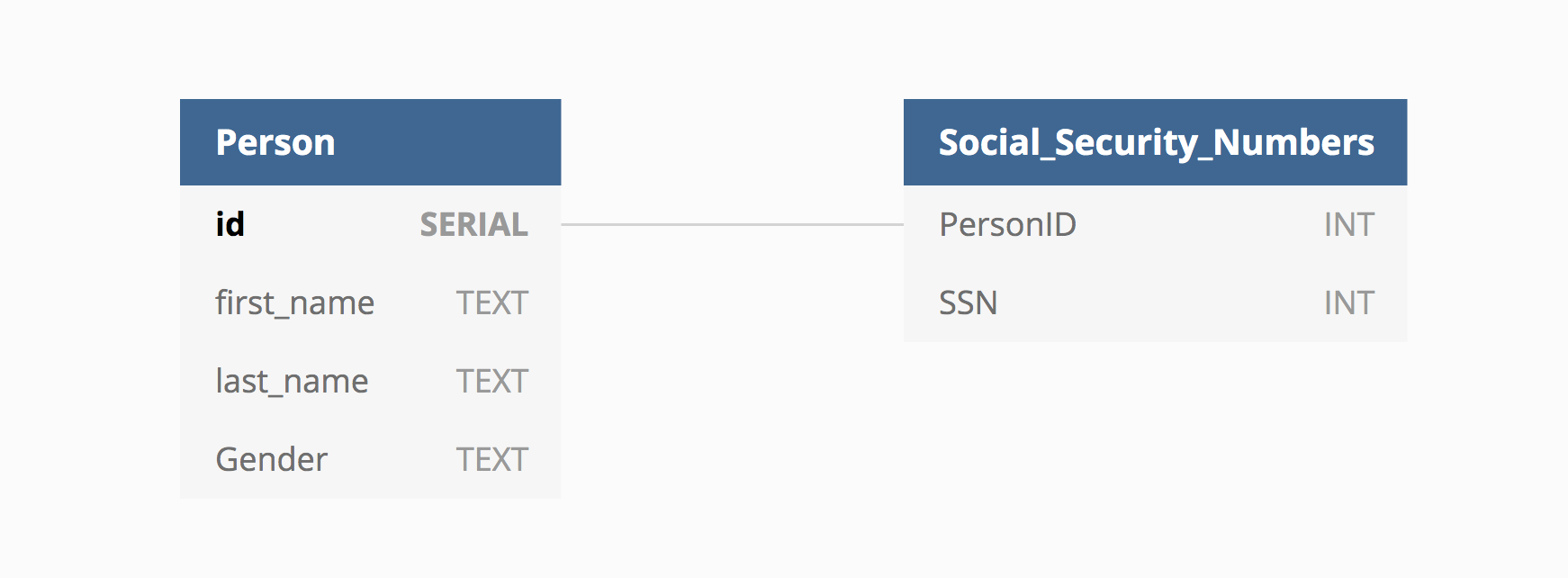
One to One
One to One relationships mean one row in one table relates to one row in another table.
One to Many
One to Many relationships mean that one row in one table can relate to many rows in another table.

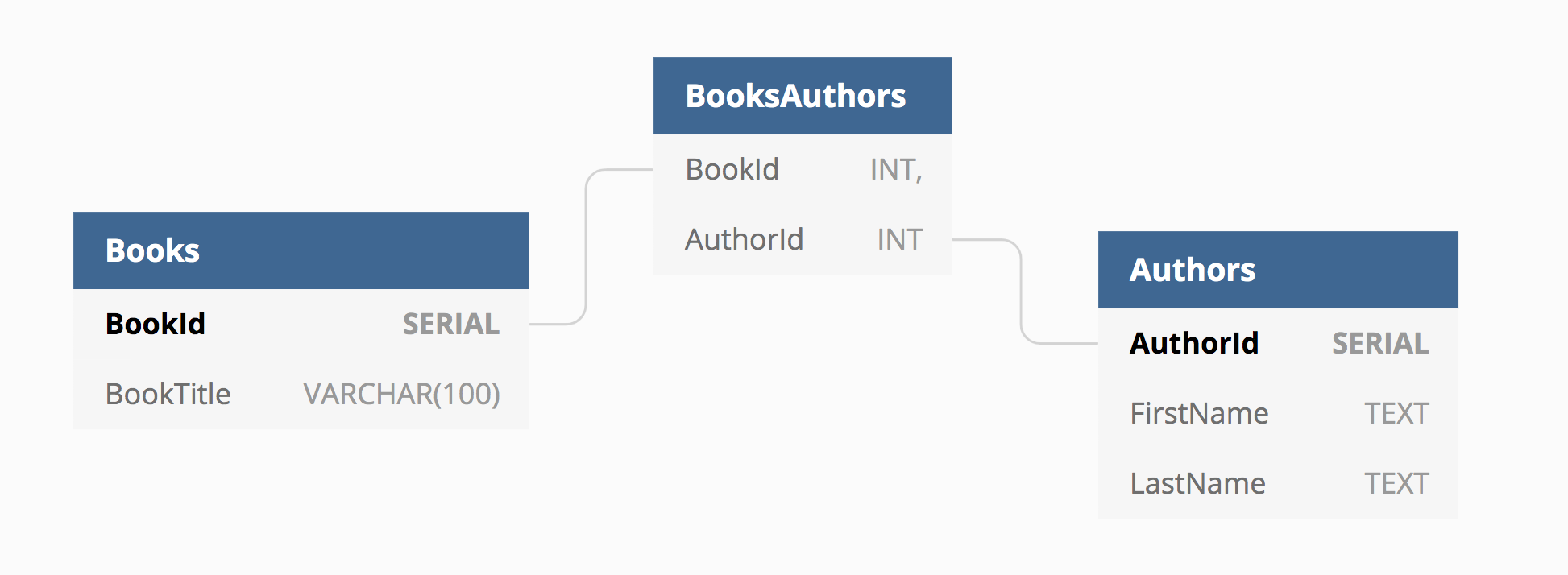
Many to Many
Many to Many means many rows from one table can relate to many rows from another table.
Joins and/or junction tables are a common approach to handling many to many relationships.
Foreign Keys
So how do we create these table relationships?
Through constraints known as foreign keys.
Foreign keys allow us to reference another table's column, typically a column with a primary key.
CREATE TABLE bikes (
bikeId SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
racerId INTEGER REFERENCES racers(racerId),
type TEXT,
color TEXT
);Table being referenced
Column being referenced
Join Statements
Once table relationships have been created, join statements can be used to collect data from tables that relate to each other.
SELECT *
FROM racers
JOIN bikes ON racers.racer_id = bikes.racer_id;First table to join
How the tables are joining
Second table to join
Subqueries
Subqueries are a queries that rely on an outer query.
A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved.
They are created by nesting a query within another query like so:
SELECT *
FROM racers
WHERE racerid IN (
SELECT racerid
FROM bikes
WHERE type = 'fezzari'
AND age >= 25
)