Matt Soria
matt.m.soria@gmail.com
F I R E B E L L Y
Why?
- Anyone can do it.
- Fun & exciting.
- Flexible & open-minded.
- Pays the bills.
Who does it benefit?
EVERYBODY.
What?
A website is a collection of documents stored on a server that can be accessed on the internet via a unique address (its location).
A website only requires a single HTML document, but is typically comprised of documents written in other languages and technologies as well (CSS, JavaScript, php, Ruby, etc.)
How?
HTML = HyperText Markup Language
+
CSS = Cascading StyleSheet
HTML = Content/structure
CSS = Style
HTML - CSS = BORING
CSS - HTML = NOTHING
HTML BASICS
made up of elements (or tags)
that are the name of the element enclosed in angle brackets:
<img>most of which have opening AND closing tags:
<h1>I am a header!</h1>
<p>I am a paragraph!</p>
Element Structure

Common Attributes
<p class="example">Class</p>
<p id="example">ID</p>
<a href="http://example.com">href</a>
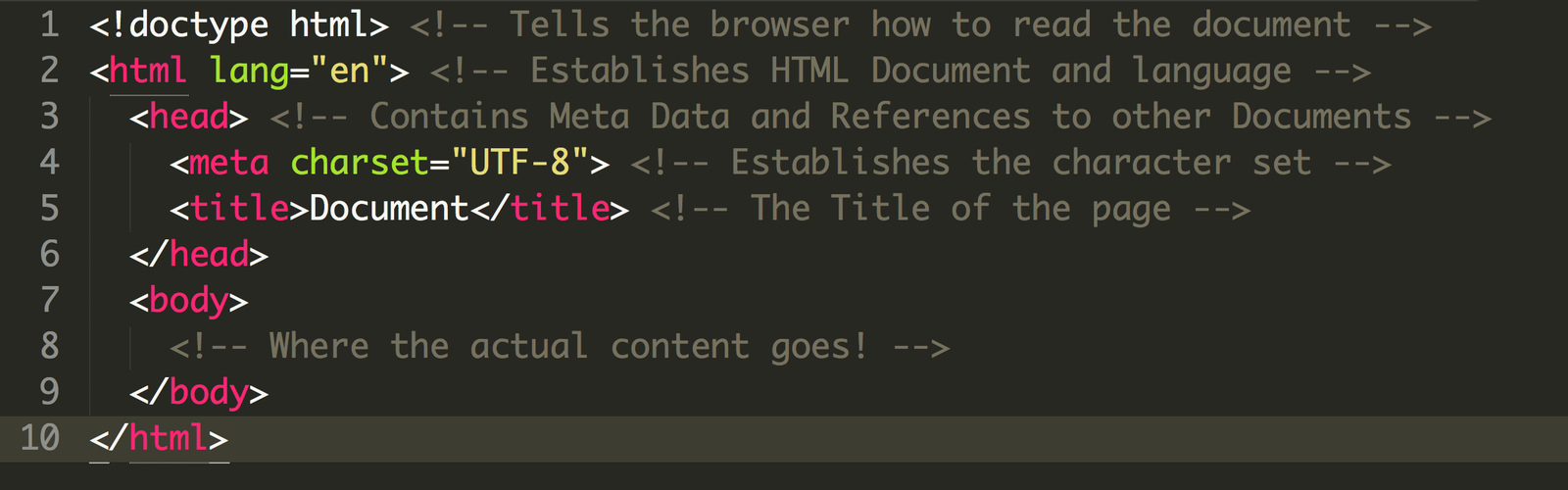
Basic HTML Structure
Common Elements:
<h1>The main Heading element</h1>
<h2>A second-level Heading</h2>
<h3>A third-level Heading</h3><div> A div is a generic block-level element used to contain other elements. </div><p>The paragraph element.</p><!-- This is a comment, it won't be "rendered" by the browser! -->
HTML5 Elements
There have been different iterations of HTML as a language, and we are currently in the middle of the 5th iteration, aptly called HTML5
HTML5 introduces some new elements:
<header>
The header is used to contain the "header" content of a page or section
<nav>
The nav element is used to contain the site's navigation
</nav>
</header>
<main>
The main element is used to contain the main content section of a site
<section>
The section element is used to contain a specific section of a page, typically an area that could live on its own, with its own heading element (<h1> or <h2>)
</section>
</main>
<footer>
The footer typically contains "background"-type information about the page or section
</footer>
CSS BASICS
CSS syntax:

Elements are styled in CSS by targeting them by:
1. Their name
p {
color: #6CC;
}
.example {
color: #6CC;
}#example {
color: #6CC;
} <p id="example" class="example">The styled paragraph</p>elements can be targeted more or less specifically:
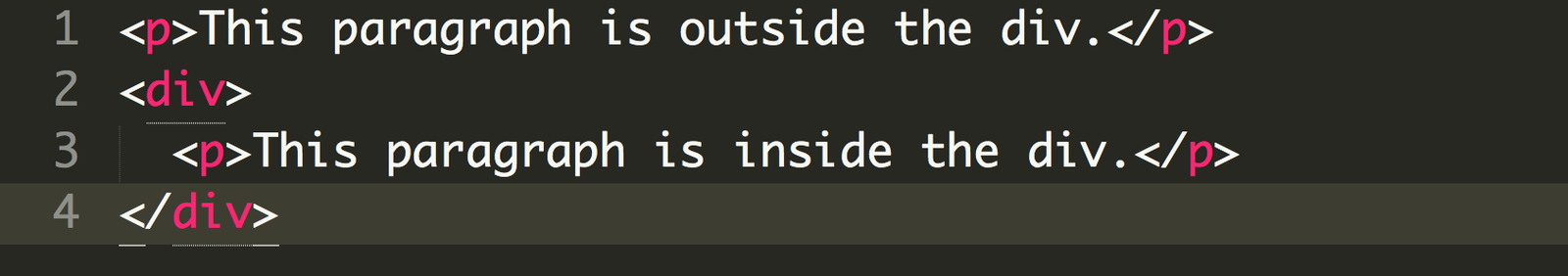
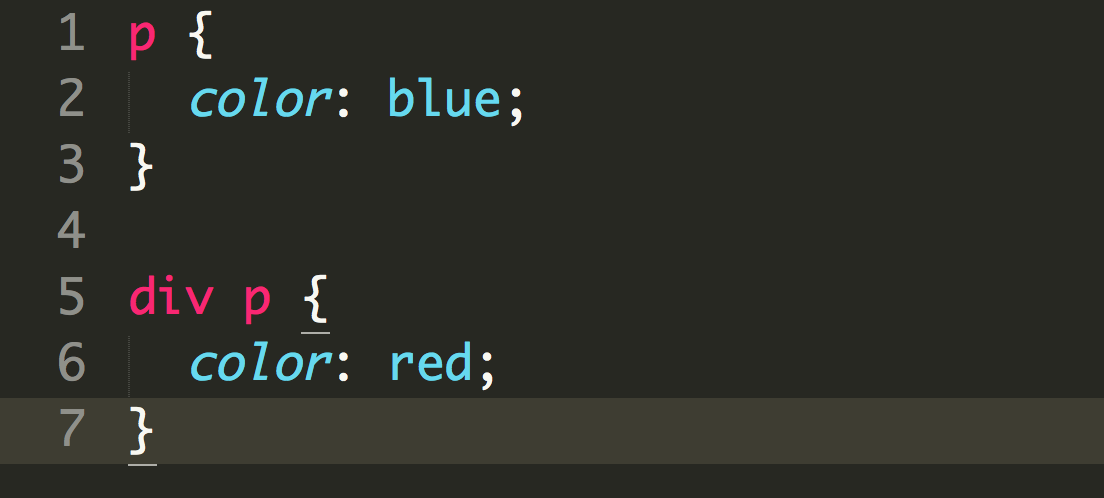
This paragraph is outside the div.
This paragraph is inside the div.
This paragraph is inside the div.
ids are more specific than classes, classes are more specific than just names:

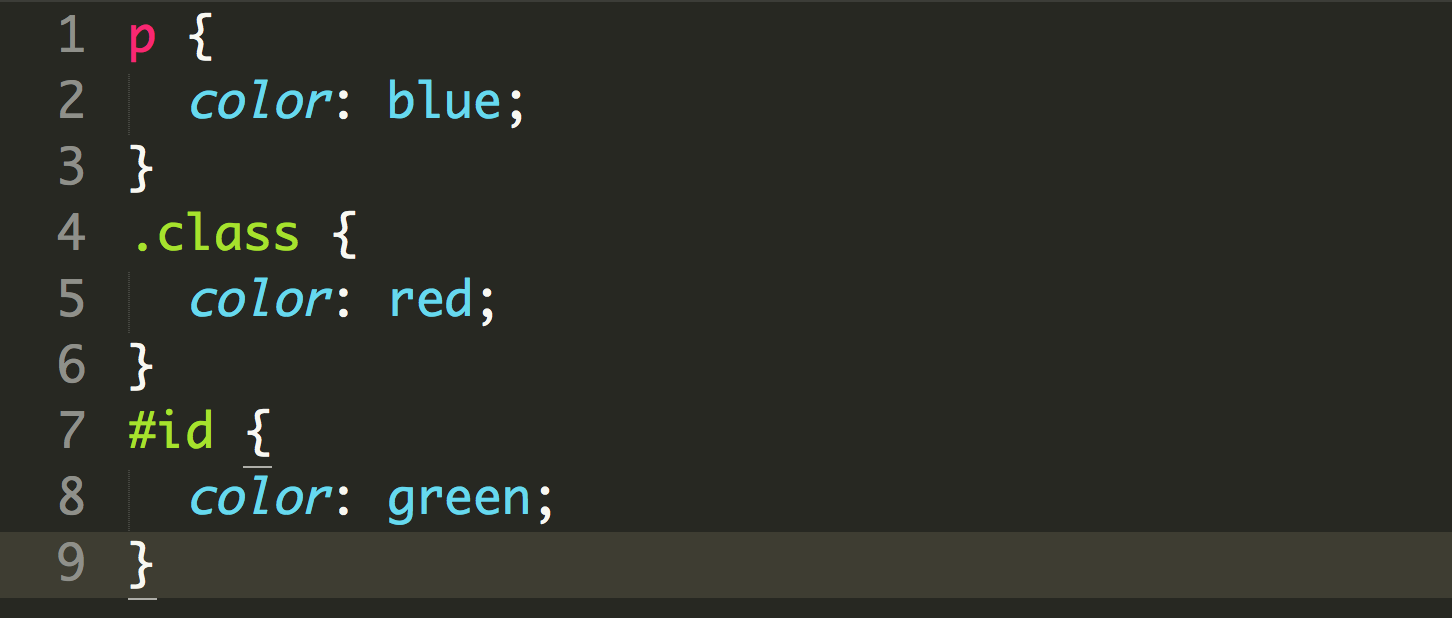
Just a paragraph.
A paragraph with a class.
A paragraph with a class and id!
A paragraph with a class.
A paragraph with a class and id!
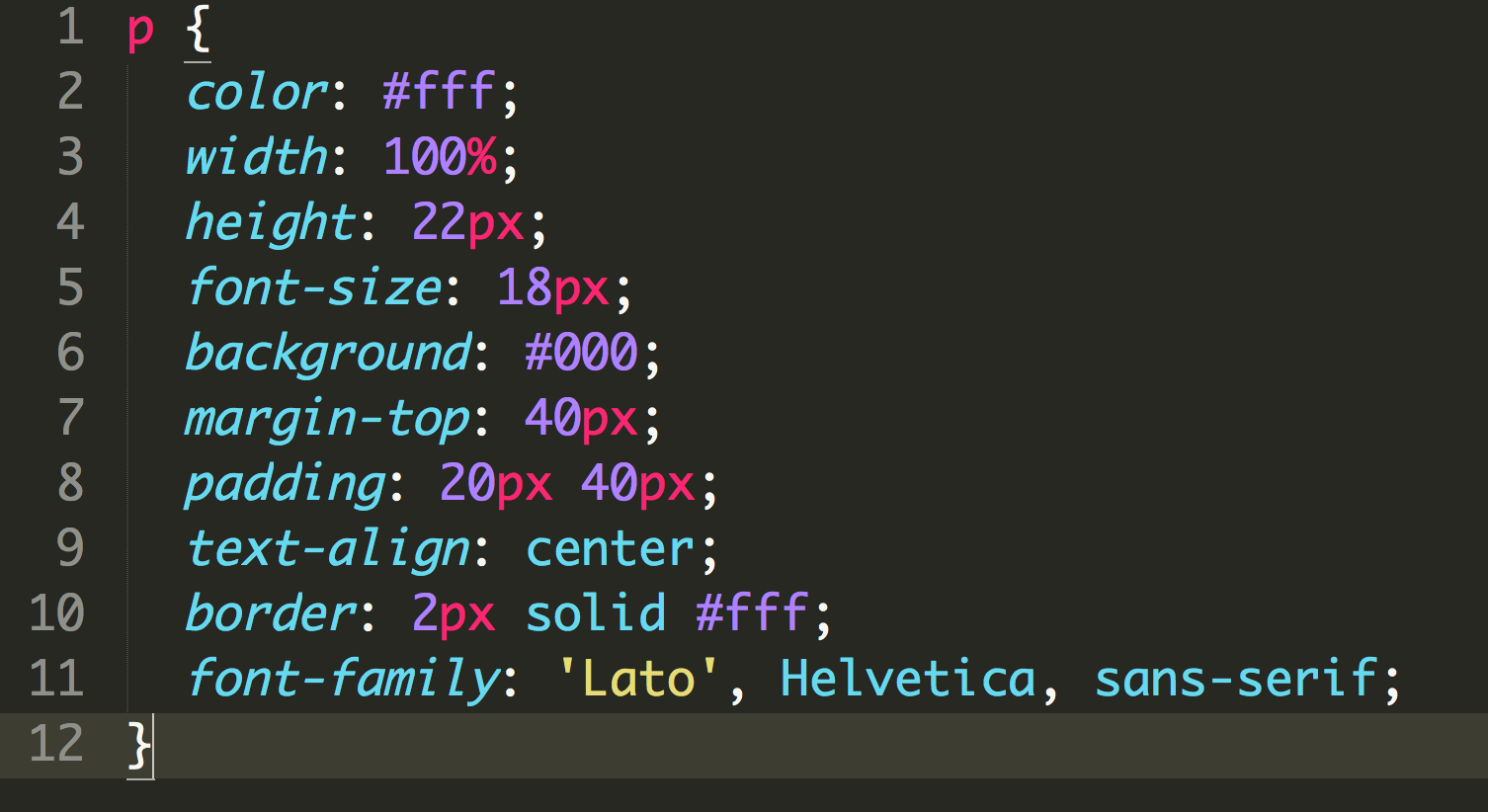
Common properties & values:
The Box Model 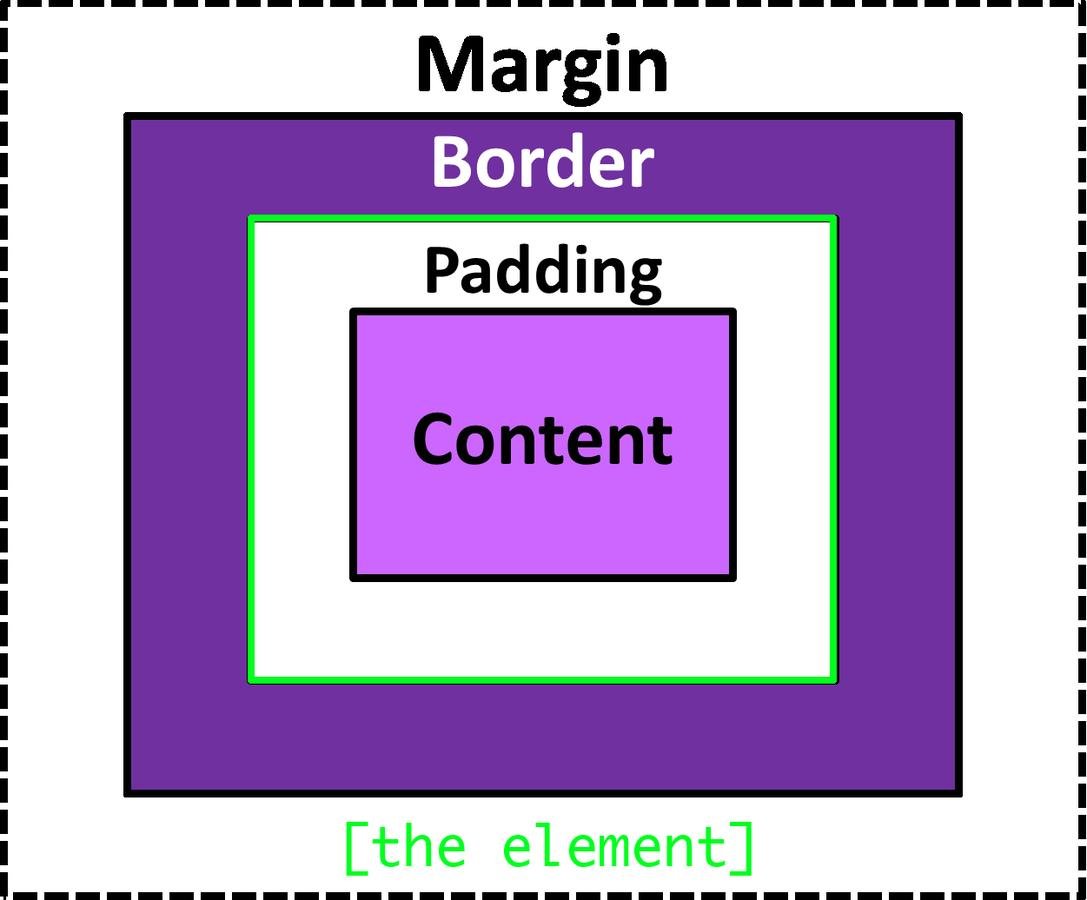

www.fredsbackpack.com
Let's build a website!
Our website:
http://fredsbackpack.com/backpack/freds-first-website.zip
Or on Codepen.io:
http://codepen.io/poopsplat/pen/bNrevo
WE DID IT!
WE MADE A WEBSITE!
Now what?
- Continue to learn and practice
- Make more websites
-
Repeat
Check out:
for more info and resources about what we learned tonight,
as well as what comes next.