COMP2511
Tutorial 5
Today
- Overview
- Strategy Pattern
- Observer Pattern
- State Pattern
Reminders
- Assignment 1 is due this Friday
- Remember to submit via
give
- Remember to submit via
- Assignment 2 has been released
- Get in contact with your partner if you haven't already
- Lab 05 is due Week 7, Monday 1pm
Review of the term
- Introduction to Java and its syntax
- Classes, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism
- Design by contract and unit testing
- Design principles (coupling, LOD, LSP, ...)
What's next?
Going Forward
- Design patterns are useful tools that you can use solve problems
- They are typical solutions to common problems in software
- They are developed upon the OOP principles we've seen so far
- Don't use any design patterns if you don't need to (KISS)
- Design patterns are mostly language agnostic
- Not limited to just Java
Design patterns will be the primary focus from now on!

Strategy Pattern
Strategy Pattern
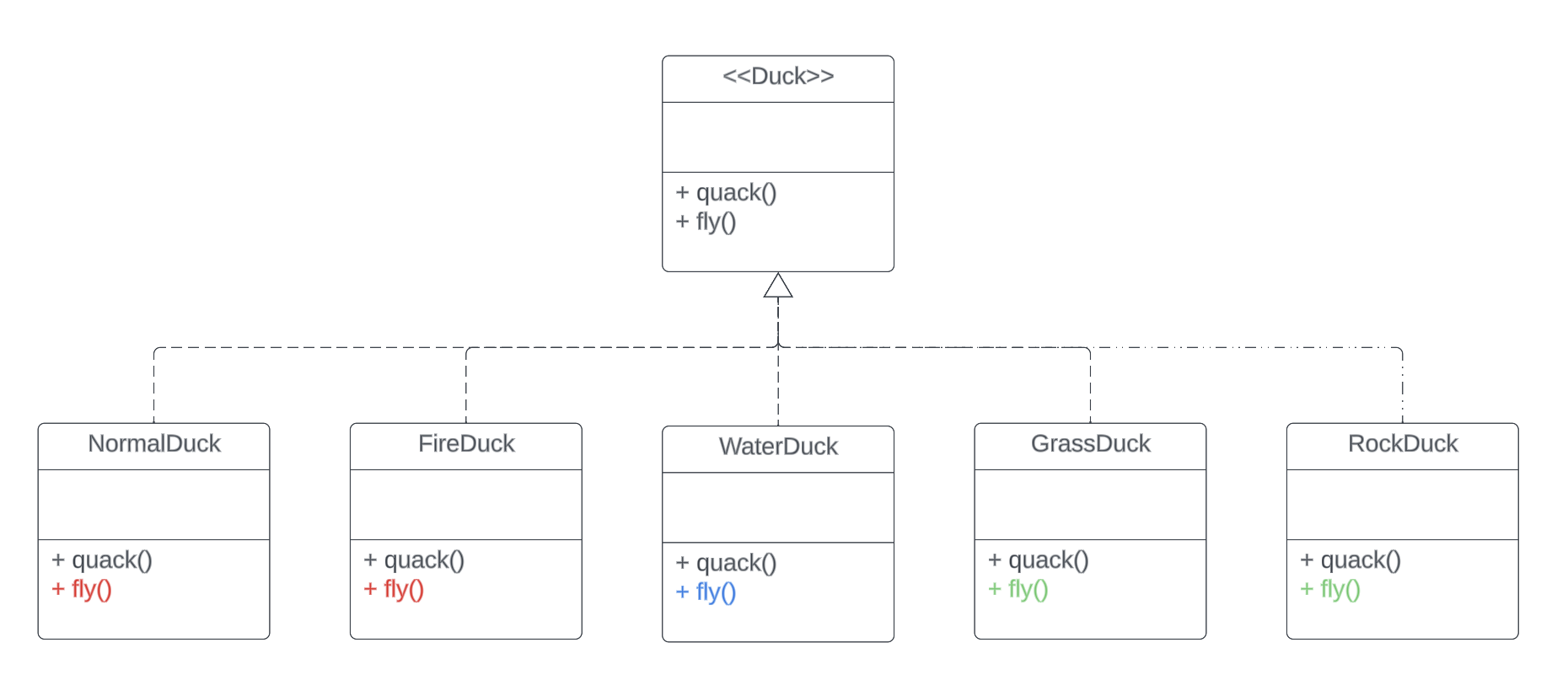
Suppose some of the subclasses implement the fly method in the same way
What changes do we need to make to implement this feature without duplicating code?
Strategy Pattern
Suppose only some of the subclasses implement the fly method in the same way.
Attempt:
Since some subclasses share the same implementation, let's introduce two new abstract classes in between Duck and our existing subclasses to maximise code re-use.
What changes do we need to make to implement this feature?
Strategy Pattern
Attempt: introduce two new abstract classes
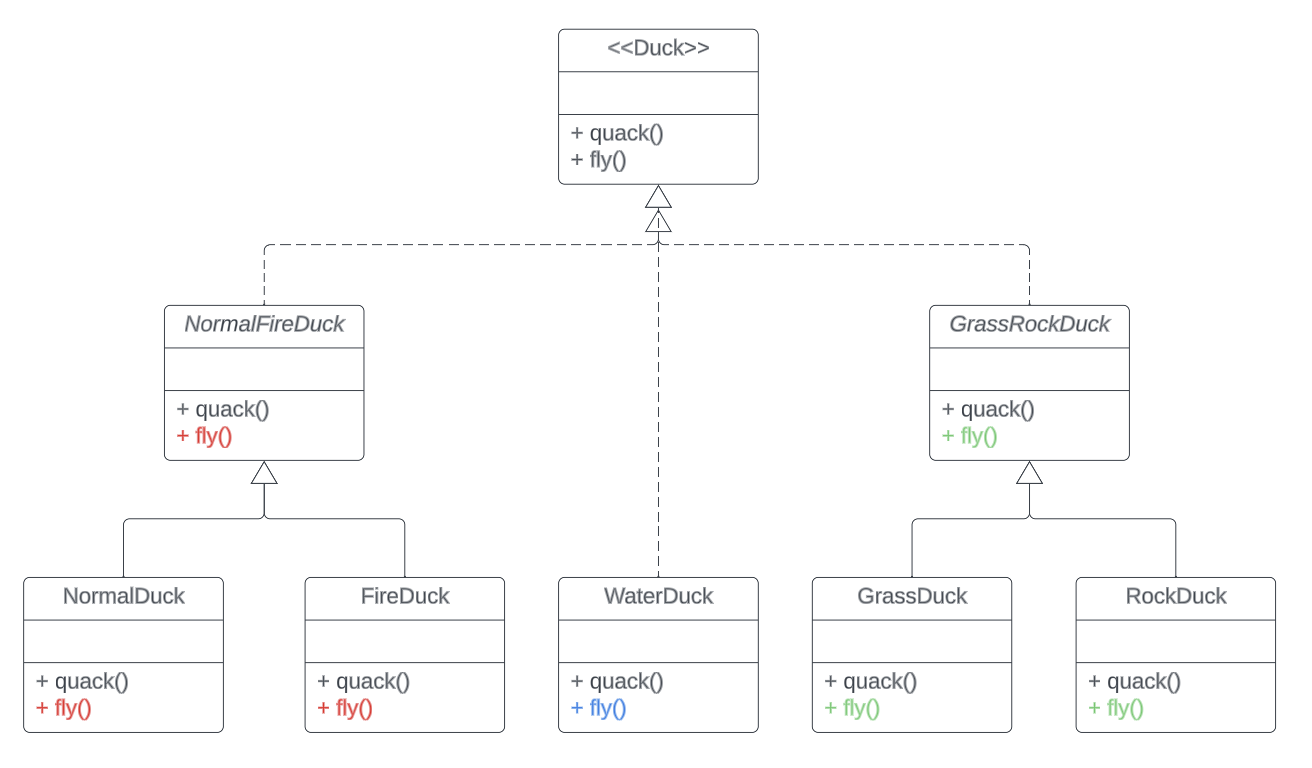
Requirements update:

GrassDuck and FireDuck share the same implementation for Quack
Strategy Pattern

Requirement update: Suppose now given an instance of any type of Duck, we need to be able to change the way it flies at runtime
How would we implement this feature?
We currently don't have any tools that can achieve this :(

Strategy Pattern
Solution: extract each implementation of flying into a separate class and let the Duck class compose it
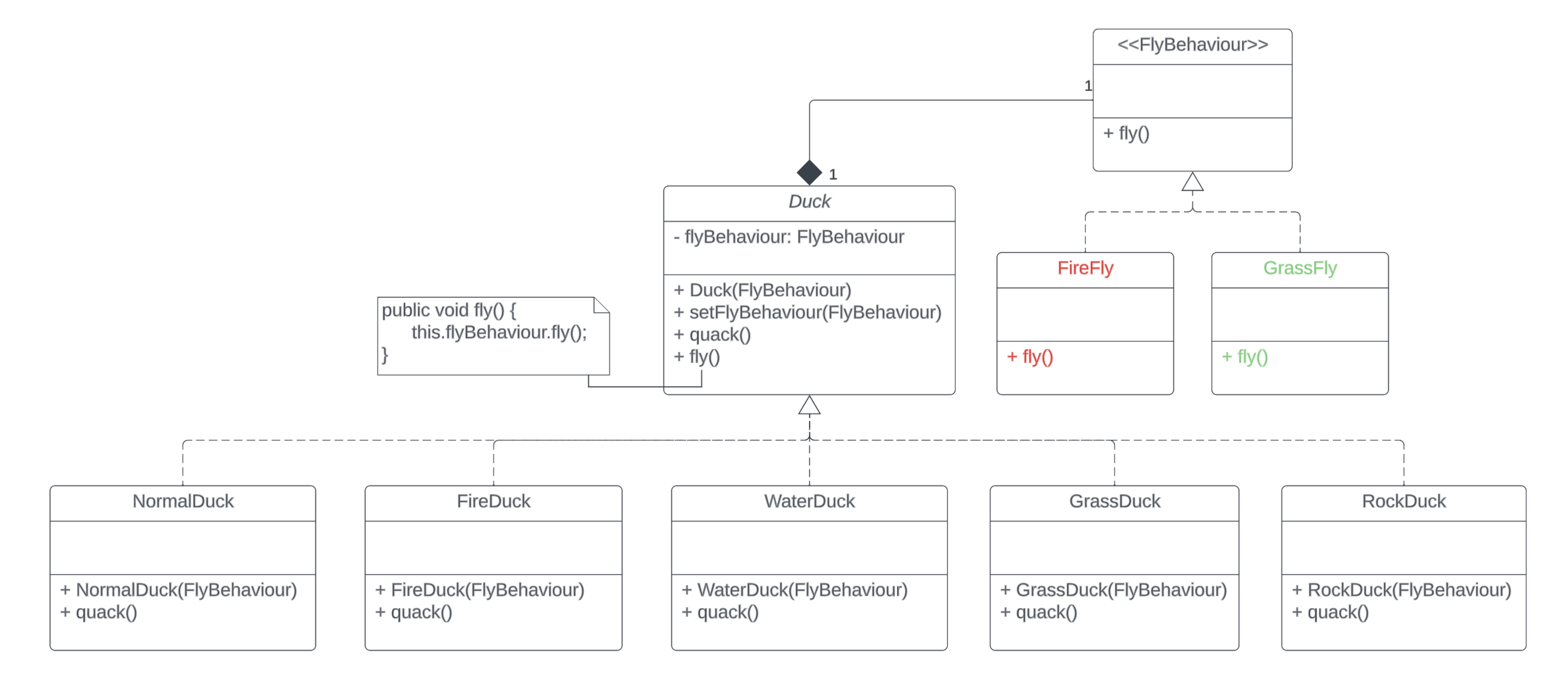

What is it?
Strategy Pattern
- Use composition instead of inheritance (more flexibility)
-
Allow behaviour to change at runtime (dependency injection)
- Encapsulate interchangeable behaviours into classes
-
Introduce new behaviours without violating the Open-Closed principle
-
Allow behaviour to be re-used without duplication
Why use it?
Behavioural Design pattern that lets you define a family of methods that are interchangeable at runtime

Strategy Pattern
How does the code violate the open/closed principle?
- Not closed for modification / open for extension.
- Each new case requires a new
switchstatement.
Strategy Pattern
Let's refactor it!
Currently, the code uses switch statements to handle each of the different cases.
Strategy Pattern
public interface ChargingStrategy {
// Calculate the cost of their order.
public double cost(List<Meal> order, boolean isMember);
// Modifying factors of charges for customers.
public double standardChargeModifier();
}Strategy Pattern
Find out more at Strategy (refactoring.guru)
Observer Pattern
Observer Pattern
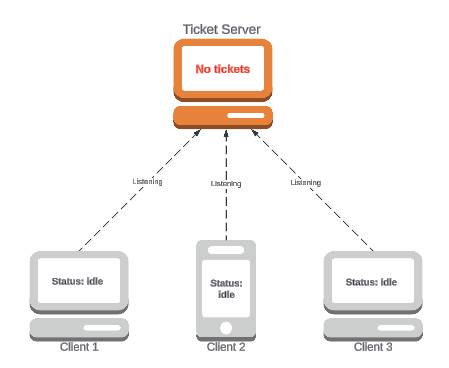
Suppose we have:
- A
TicketServerthat will periodically release tickets for a concert- It will inform all clients when tickets are available
- Some
Clientslistening to theTicketServer, buying tickets as soon as they become available
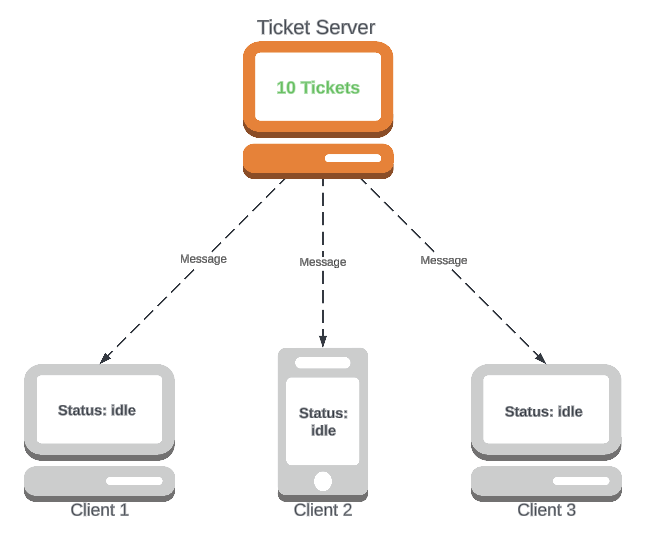
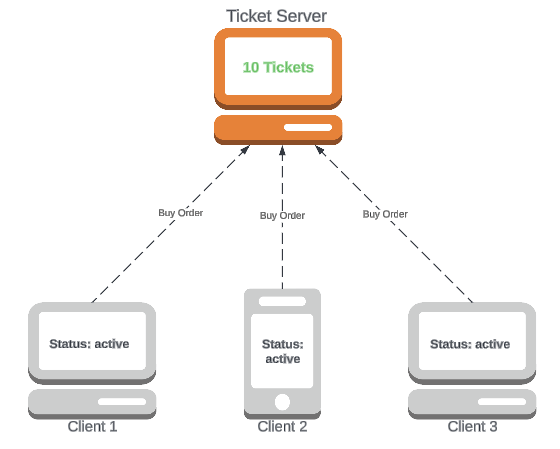
It's a subscription system!
Observer Pattern
Why do we need to use it?
- Modelling a push system with a one-to-many relationship can easily lead to tight coupling
- The observer pattern is a convenient tool that can be used to simplify the problem
What is it?
Behavioural design pattern to model a push-based subscription mechanism between observers and a subject
- Subject: notify observers of any changes (i.e. broadcast available tickets)
- Observers: receive updates from the subject and perform some action (i.e. buying tickets)
Observer Pattern
UML Diagram
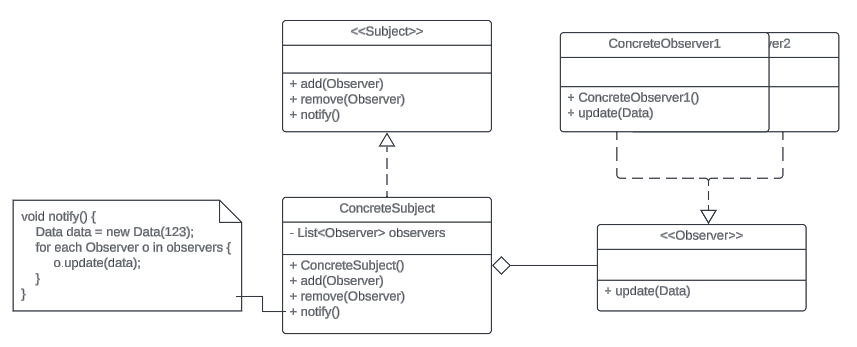
Model the system in Java!

Observer Pattern
Observer Pattern
public class Producer implements Subject {
private List<Observer> subscribers = new ArrayList<>();
private String name;
public Producer(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void addSubscriber(Observer subscriber) {
this.subscribers.add(subscriber);
}
@Override
public void upload(Video video) {
for (Observer subscriber : this.subscribers) {
subscriber.alertNewVideo(video);
}
}
}
public interface Subject {
public void upload(Video video);
public void addSubscriber(Observer subscriber);
}
public interface Observer {
public void subscribe(Subject producer);
public void alertNewVideo(Video video);
}
Implementation of interfaces and the Producer
Observer Pattern
public class User implements Observer {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
@Override
public void subscribe(Subject producer) {
producer.addSubscriber(this);
}
@Override
public void alertNewVideo(Video video) {
System.out.println("Video: " + video.getName() + "was posted");
}
}
Implementation of the User
State Pattern
State Pattern
Suppose we have:
- A
VideoPlayerwith a play and lock button - If we press play while the status is ready,
then we play a video - If we press play while the status is playing, then we pause the video
- If we press lock in either state, we turn off the screen
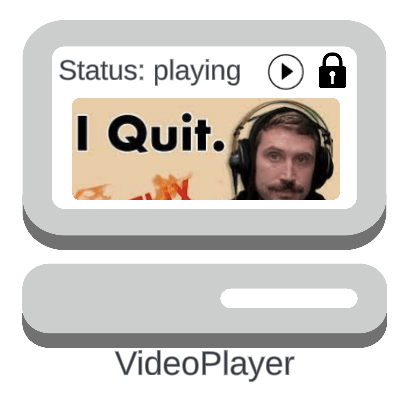


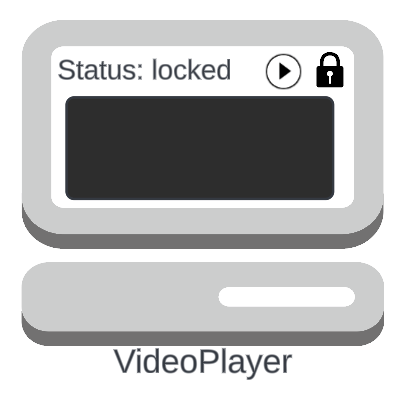
It's a state machine!
What is it?
State Pattern
- Each state and its associated behaviour is encapsulated into a separate class
- Delegation (i.e. method calls) is used to switch between states (and behaviours)
- Reduce conditional complexity by minimising the use of
if/switchstatements (i.e. if state isadob, else if state iscdod, etc) - Functionality cannot be added at run-time, only switched
Behavioural design pattern to model a state machine where the behaviour of an object changes depending on its internal state
State Pattern

Transition Diagram
State Pattern
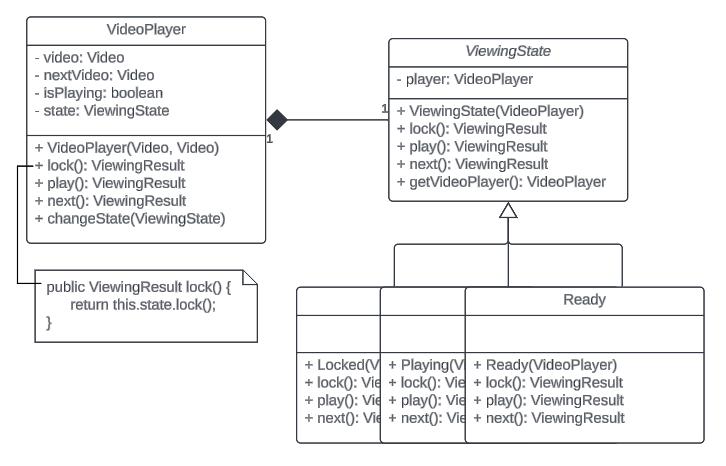
UML Diagram
State Pattern
Find out more at State (refactoring.guru)
The End
"Composition over inheritance"