COMP2511
Tutorial 2
Some material by Alvin Cherk (z5311001)
Today
- VSCode and GitLab
- Classes, inheritance & Interface
- Commenting & Documentation
- Access Modifiers
Assignment I is out, please have a read of the spec and start early!
VSCode Tips
VSCode Tips
Ensure that you open the correct folder
example: cs2511-project
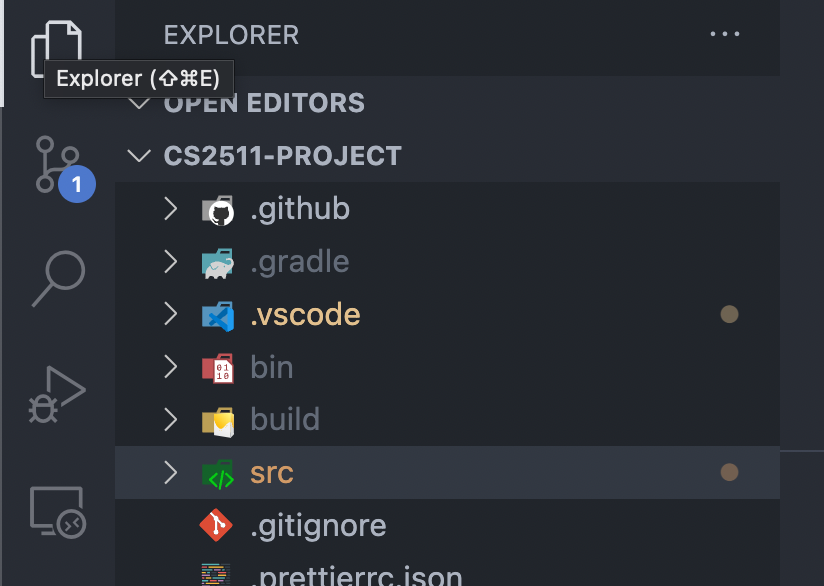
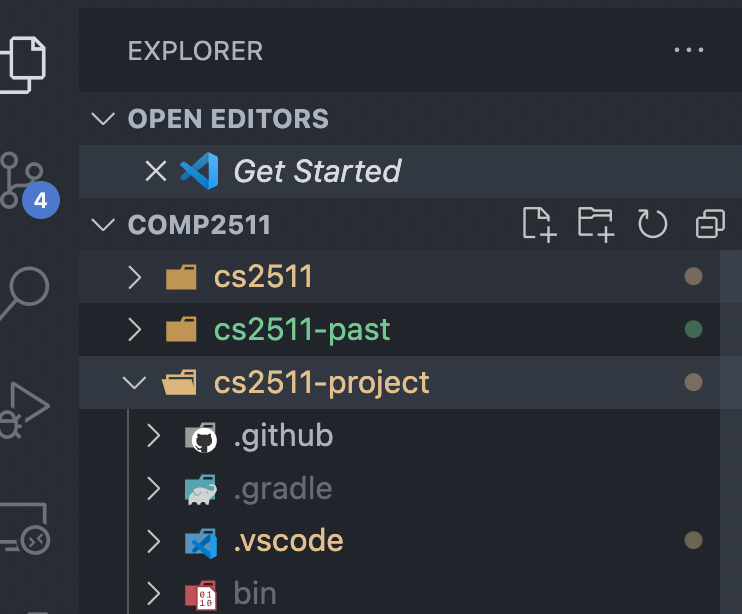
Good
Bad
Name of folder open
The folder I want to actually open
GitLab Pipelines
GitLab Pipelines
How to view pipeline output?
GitLab Pipelines
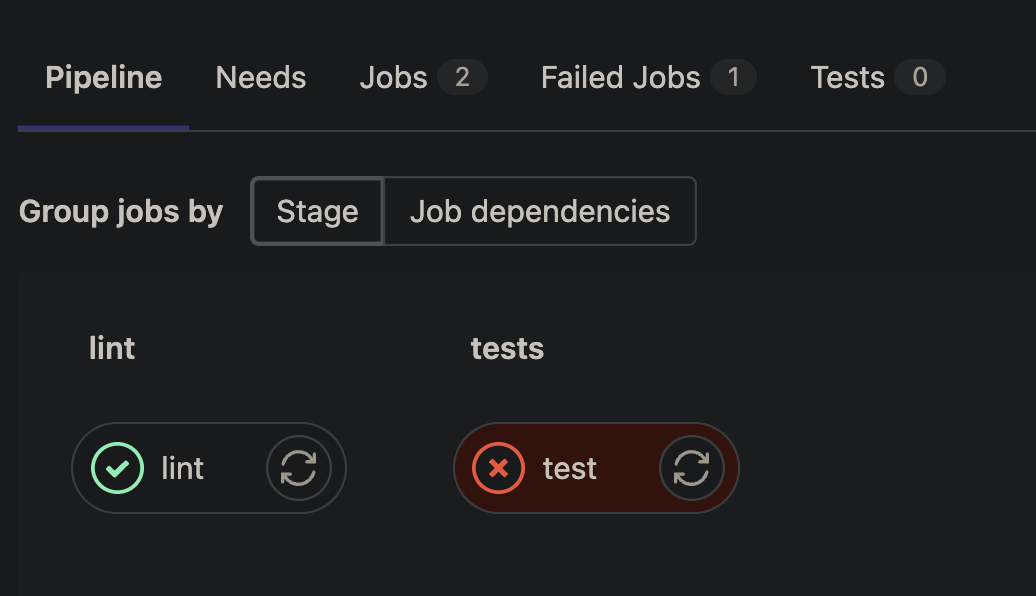
View linting output
View tests output
GitLab Pipelines
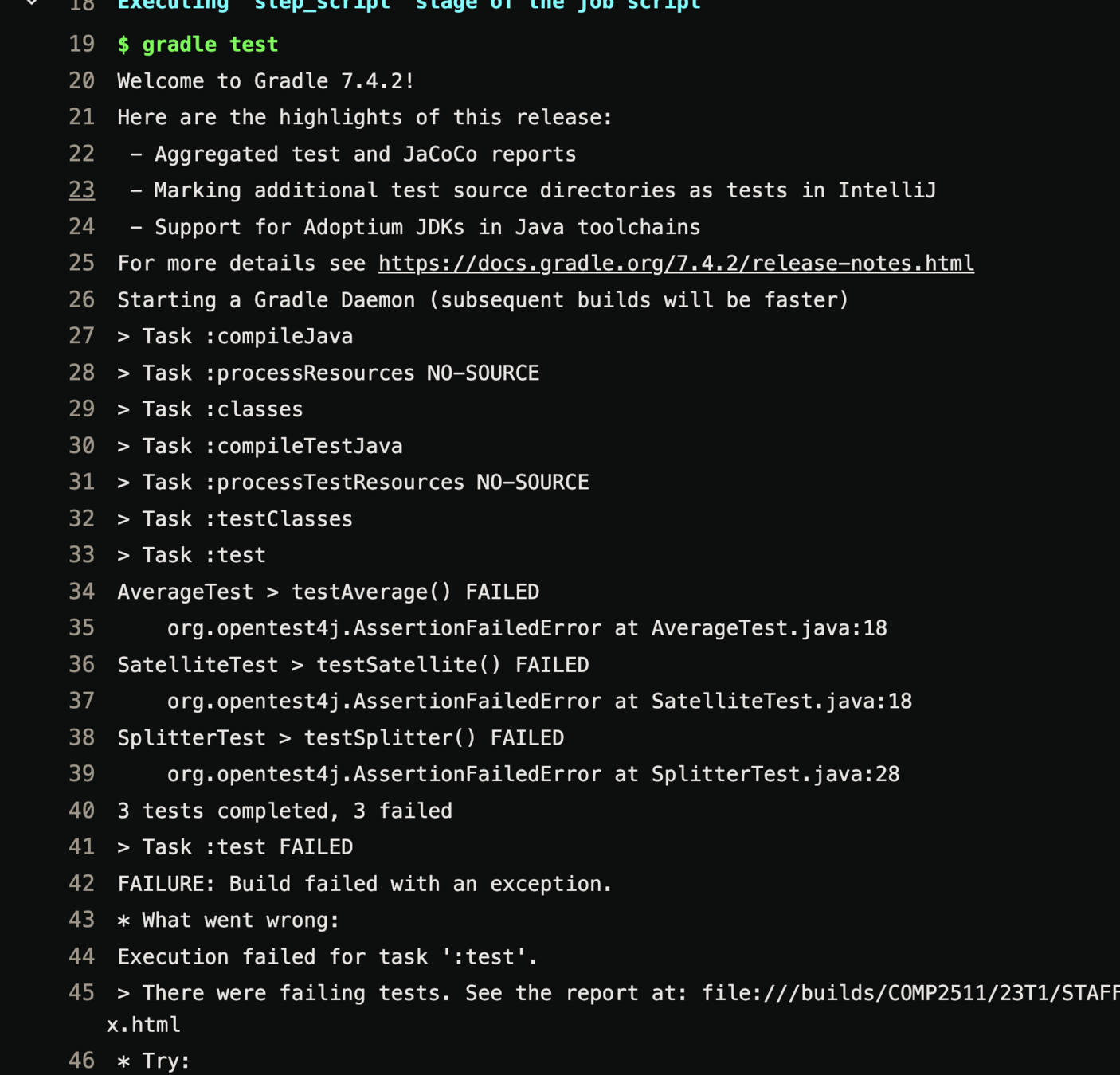
Lines of code that caused the code to fail the test
Inheritance
Bonus: interface & abstract classes
Inheritance
What is it?
In object-oriented languages like Java, a class can inherit attributes and methods from another class
- The class that inherits the properties is the sub-class or the child class.
- The class from which the properties are inherited is the superclass or the parent class.
Inheritance represents a "is-a" relationship
Inheritance
Example
Animal
Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
- A
Tigeris anAnimal, aDogis anAnimal, ... - A
Tigershould have all the properties and functionalities of an Animal - We shouldn't have to copy the code from
Animalwhen creating a class likeDogbecause this has obvious problems
Solution: make Dog a subclass of Animal using
the extends keyword in Java ✅
Superclass: Animal
Subclasses: Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
Inheritance
Example
Animal
Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
Change in requirements
Solution: make Animal into an abstract class ✅
Superclass: Animal
Subclasses: Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
- All subclasses of
Animalmust implement a method calledmakeSound - Prevent users from constructing instances of
Animal
Inheritance
Example
Animal
Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
Whoops, another change in requirements
Solution:
- Create an interface for the ability to play Catch
- Implement the interface for the
Dogclass
Superclass: Animal
Subclasses: Tiger, Dog, Cat, ...
Some subclasses of Animal (i.e. Dog) can play Catch with its owner
Code Review
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color);
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String name, int width, int height) {
this(name);
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}- What is the difference between
superandthis?-
superrefers to the immediate parent class -
thisrefers to the current class
-
- What about
super(...)andthis(...)?-
super(...)is a constructor from the parent class and should be the first line in a child class constructor -
this(...)acts as a current class constructor (can be used for overloading)
-
Code Review
package shapes;
public class Shape {
public String color;
public Shape(String color) {
System.out.println("Inside Shape constructor");
this.color = color;
}
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape {
public int height;
public int width;
public Rectangle(String color) {
super(color); // => Calling constructor of parent `Shape(String color)`
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with one argument");
}
public Rectangle(String name, int width, int height) {
this(name); // => Calling constructor `Rectangle(String color)`
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle constructor with three arguments");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Rectangle(3 arguments) => Rectangle(1 argument) => Shape(1 argument)
Rectangle r = new Rectangle("red", 10, 20);
System.out.println(r.color);
System.out.println(r.width);
System.out.println(r.height);
}
}- What is the difference between
superandthis?-
superrefers to the immediate parent class -
thisrefers to the current class
-
- What about
super(...)andthis(...)?-
super()is a constructor from the parent class and should be the first line in a child class constructor -
this()acts as a current class constructor (can be used for method overloading)
-
Code Review
package circle;
public class Circle extends Object {
// Every class extends Object, it is not needed though
private static final double pi = 3.14159;
private int x, y;
private int r;
// Only 1 variable for all Circle objects
static int no_circles = 0;
public Circle() {
super(); // not needed
no_circles++;
}
public double circumference() {
return 2 * pi * r;
}
}What are static fields and methods?
Static fields: variables that are common and available to all instances of a class
They belong to the class, rather than a particular instance
Documentation
JavaDoc
Documentation
- Why is documentation important? When should you use it
- What does the term "self-documenting" code mean?
- Code that documents itself. It is inherently readable. Usually accomplished through variable name and function names
- Can commends be bad (code smell)? If so, when?
- Comments become stale & does not get updated with new changes
- Possibly hinting that your design/code is too complex
Documentation
Single Line
// Single line commentMulti-line comment
/**
* This is multi-line
* documentation
*/JavaDoc Documentation
/**
* Constructor used to create a file
* @param fileName the name of the file
* @param content contents of the file
*/JavaDoc
- JavaDoc is one way of documenting in Java.
- JavaDoc is a way of writing your comments
- It mainly targets class definitions and method/function definitions.
- In COMP2511, you will not have to use JavaDoc documentation unless asked. Though, it is a good idea to do it anyway in assignments.
JavaDoc
/**
* File class that stores content under a file name
*/
public class File {
/**
* Constructor used to create a file
* @param fileName the name of the file
* @param content contents of the file
*/
public File(String fileName, String content) {}
/**
* Constructor used to make a partial file when receiving a new file
* I.e., content.length() != fileSize with no compression
* @param fileName
* @param fileSize
*/
protected File(String fileName, int fileSize) {}
/**
* Checks if transfer has been completed
* @return true if it has been completed
*/
public boolean hasTransferBeenCompleted() {}
}Code Demo
Employee.java & Manager.java
Code Demo
- Create a Employee class with a name and salary
- Create setters & getters with JavaDoc
- Create a Manager class that inherits Employee with a hireDate
- Override toString() method
- Write equals() method
Code Demo
The java extension packs come with some features you can use to generate boilerplate code
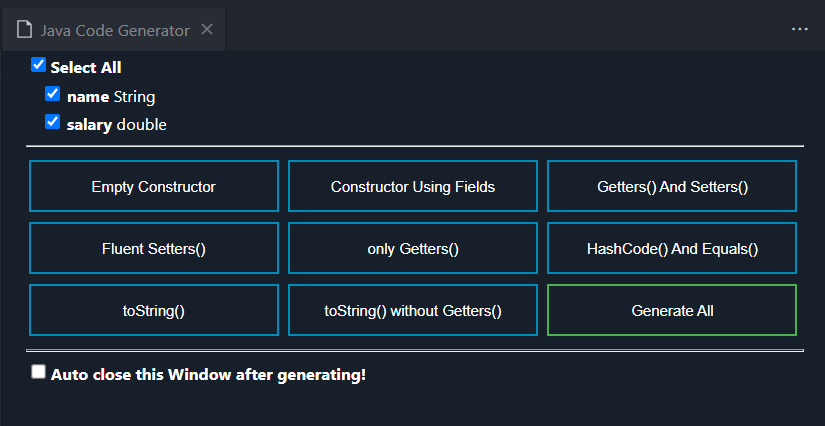
Please do not generate the equals method. Write it yourself. This applies for Lab02 marking.
Code Demo
How do you write a sound equals method?
Since we are overriding an existing method (in the super most class called Object), we must follow its conditions
The conditions can be found in the Java Docs

The semantics of this was explored in a recent exam
Access Modifiers
Private
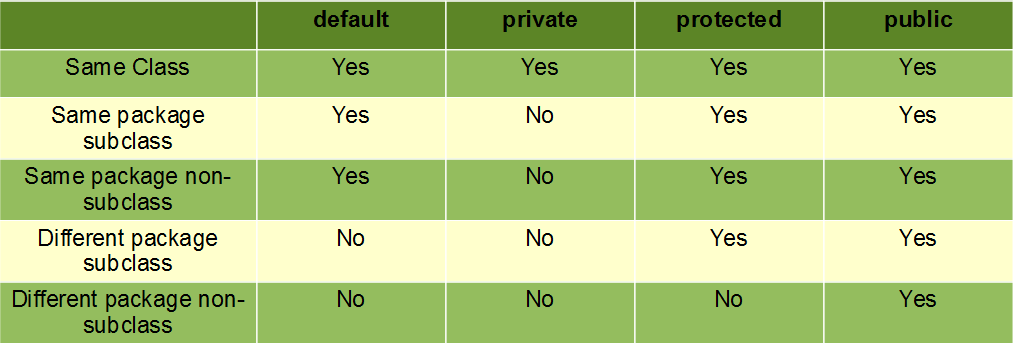
- If a member variable / method is private then it's accessible only within the same class
- The most restrictive access modifier
Public

- If a member variable / method is public then it's accessible anywhere
- The least restrictive access modifier
Protected

- If a member variable / method is protect then it's accessible only in itself or subclasses
- Typically breaks encapsulation, generally only used for methods
Rule of Thumb
-
All member variables MUST be private
- Except
staticconstants that are to be shared
- Except
- Most methods should be private or public
- Private if it's only called from within the class
- Public if it can be called from everywhere
- Be wary when making methods protected