COMP2511
Tutorial 3
Today
- Polymorphism / Inheritance
- Domain Modelling (UML Diagrams)
- Exceptions
- JUnit testing
Important Notices
- Assignment-i is out, please start early
- Go to help sessions if you need help (they get busier towards the due date)
-
No auto-generated UMLs. You will get 0 :(
- If you use programs that generate it based on text, please commit this text as a file in your repo.
-
Assignment-ii pair preferences are out
- Please fill in this form: https://forms.gle/HoVWHffKJbs99WSH6

scan the QR code to access the preference form
Preference form only for H11A
Polymorphism
Polymorphism
An object's ability to decide what method to call, depending on where it is in the inheritance hierarchy
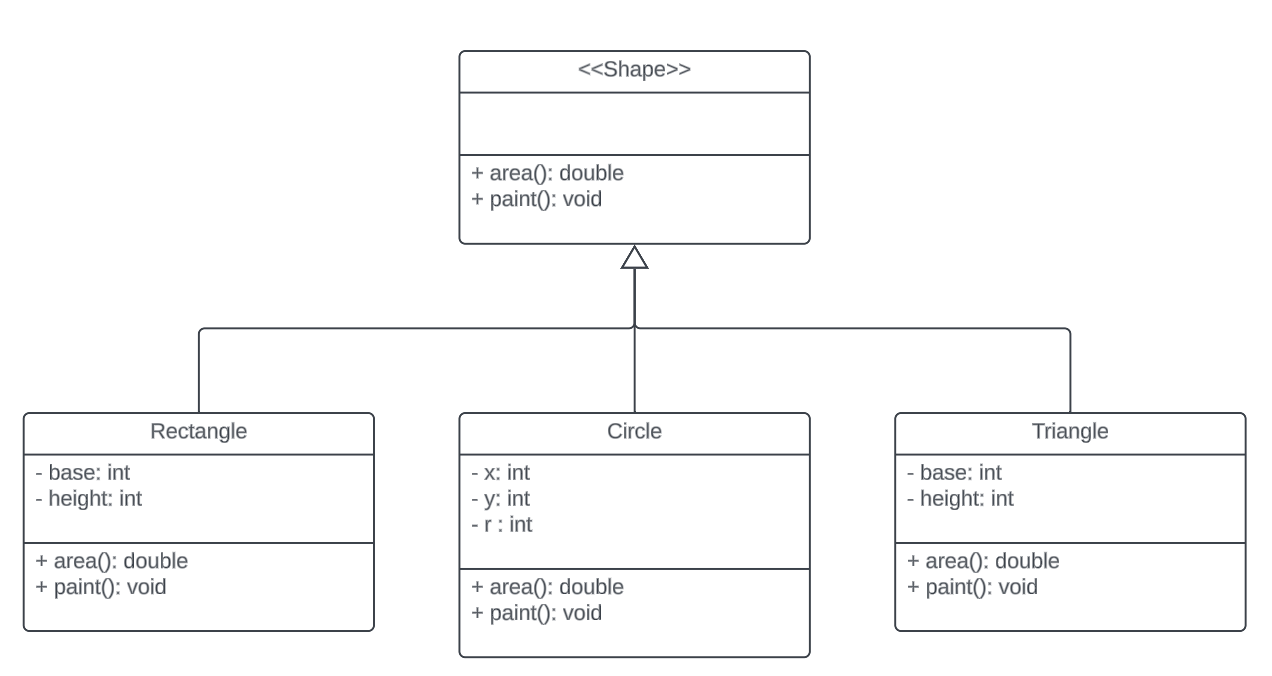
The arrow represents the subclass relationship
Polymorphism also apply with the implements relationship
Domain Modelling
UML Diagrams
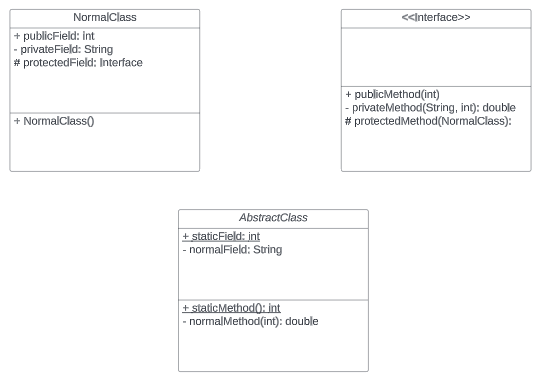
UML Classes
UML Relationships
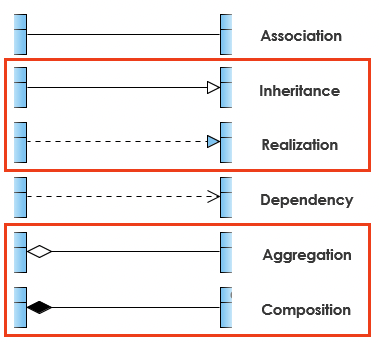
1. Inheritance: "is-a" relationship
- Denotes subclass → superclass
2. Realisation: "implements" relationship
- Denotes class → interface
3. Aggregation: "part-of" relationship
- Class A aggregates an instance of B and an instance of A is destroyed
- Instance of B can still exist
4. Composition: "has-a" relationship
- Class A composes of an instance of B and an instance of A is destroyed
- Instance of B can no longer exist
UML Cardinality
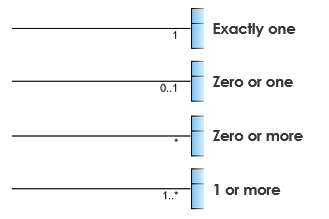
Types of cardinality
- one to one
- one to many
- many to meny
Domain Modelling
Create an OO domain model for a system with the following requirements.
A Car has one or more engines and a producer. The producer is a manufacturing company who has a brand name. Engines are produced by a manufacturer and have a speed. There are only two types of engines within UNSW's cars:
- Thermal Engines, which have a default max speed of 114, although they can be produced with a different max speed, and the max speed can change to any value between 100 and 250.
- Electrical Engines, which have a default max speed of 180. This is the speed at which they are produced, and the max speed can change to any value that is divisible by 6.
Cars are able to drive to a particular location x, y.
Since UNSW is a world-leader in technology innovation, they want you to be able to model the behaviour of Time Travelling for any vehicle, and to model a time travelling car. A vehicle that travels in time stays in the same location but travels to a LocalDateTime.
Domain Modelling
Create an OO domain model for a system with the following requirements.
A Car has one or more engines and a producer. The producer is a manufacturing company who has a brand name. Engines are produced by a manufacturer and have a speed. There are only two types of engines within UNSW's cars:
- Thermal Engines: which have a default max speed of 114, although they can be produced with a different max speed, and the max speed can change to any value between 100 and 250.
- Electrical Engines: which have a default max speed of 180. This is the speed at which they are produced, and the max speed can change to any value that is divisible by 6.
Cars are able to drive to a particular location x, y.
Since UNSW is a world-leader in technology innovation, they want you to be able to model the behaviour of Time Travelling for any vehicle, and to model a time travelling car. A vehicle that travels in time stays in the same location but travels to a LocalDateTime.
LucidCharts
A generally good diagram maker software that is free*
*if you sign up with an .edu account
Code Demo
Wondrous.java
The Wondrous Sequence is generated by the simple rule:
- If the current term is even, the next term is half the current term.
- If the current term is odd, the next term is three times the current term, plus 1
Wondrous Sequence
JUnit Testing
JUnit Testing
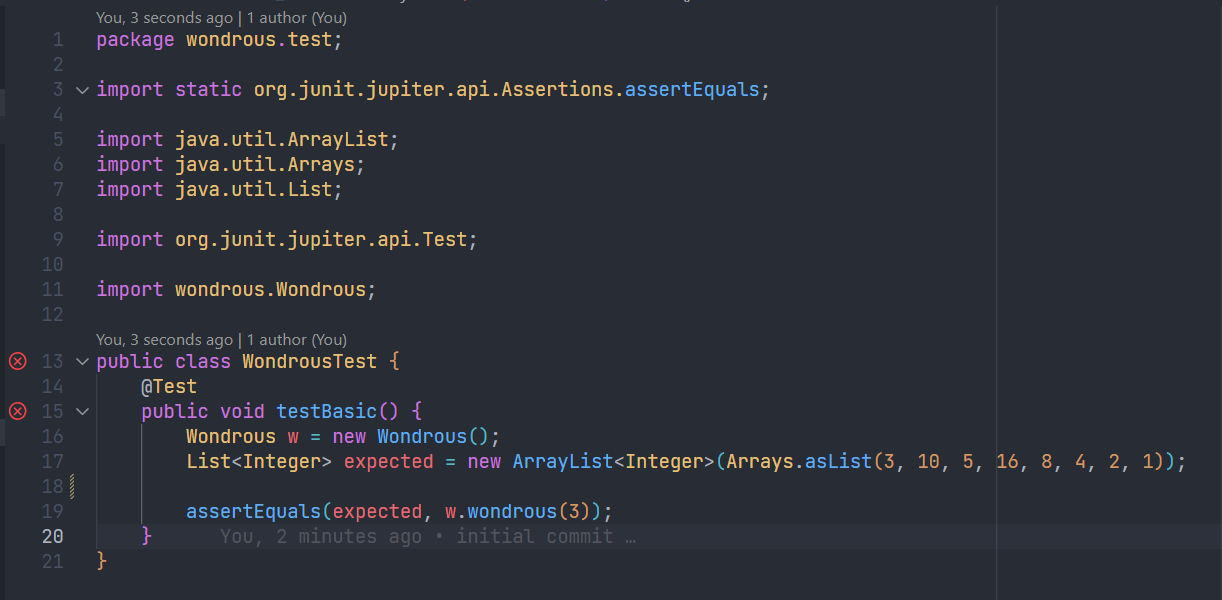
Make sure your VSCode is open in the correct folder, otherwise, these buttons wont appear
JUnit Testing
Make sure your VSCode is open in the correct folder, otherwise, these buttons won't appear
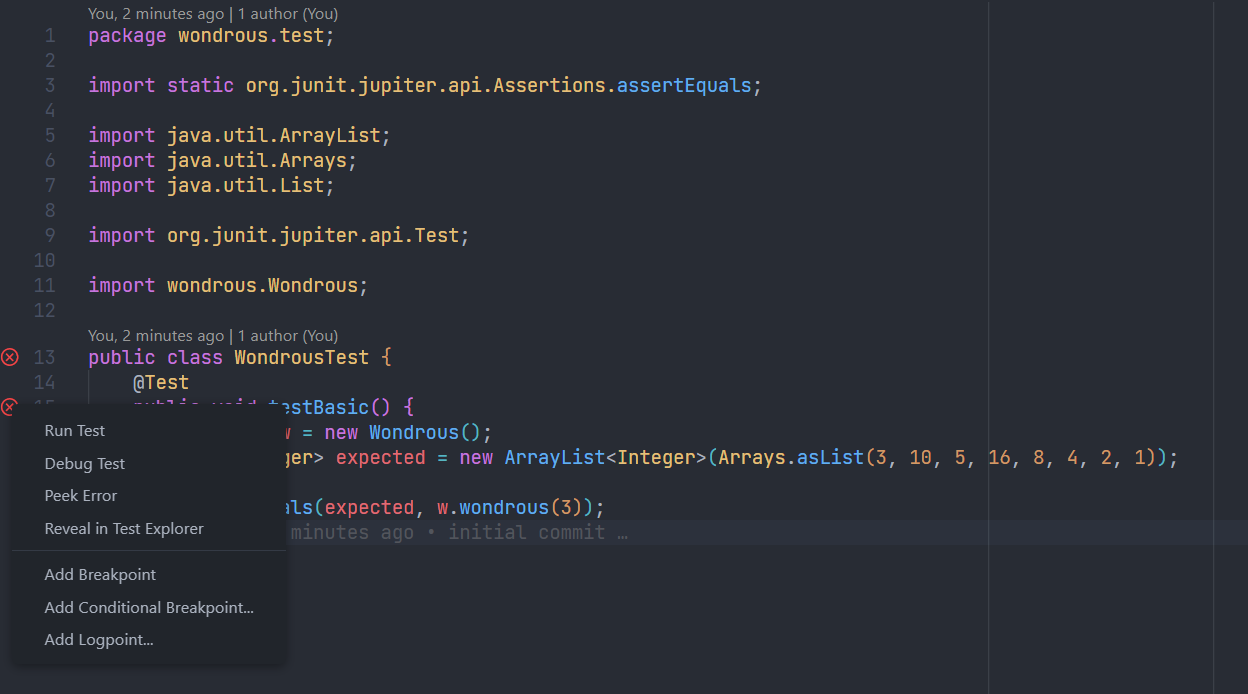
JUnit Testing
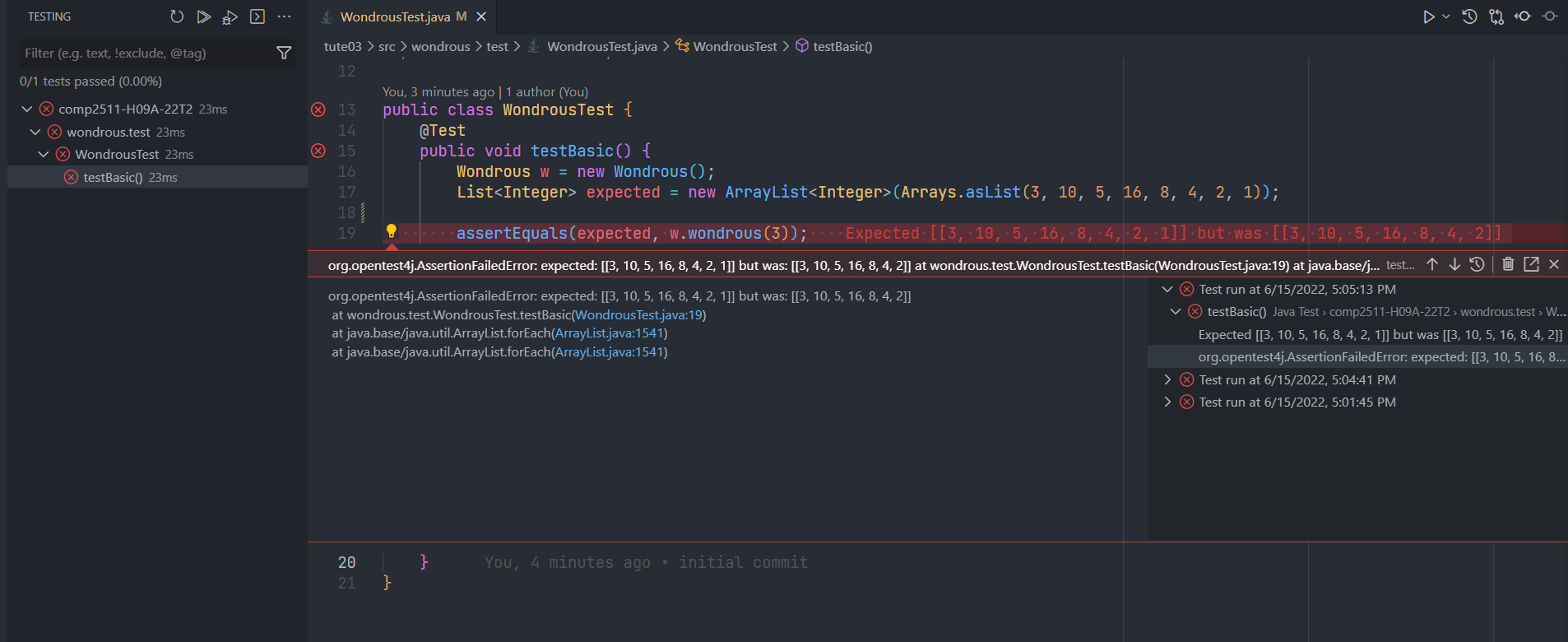
- Failed test output
- See past history
Debug Mode
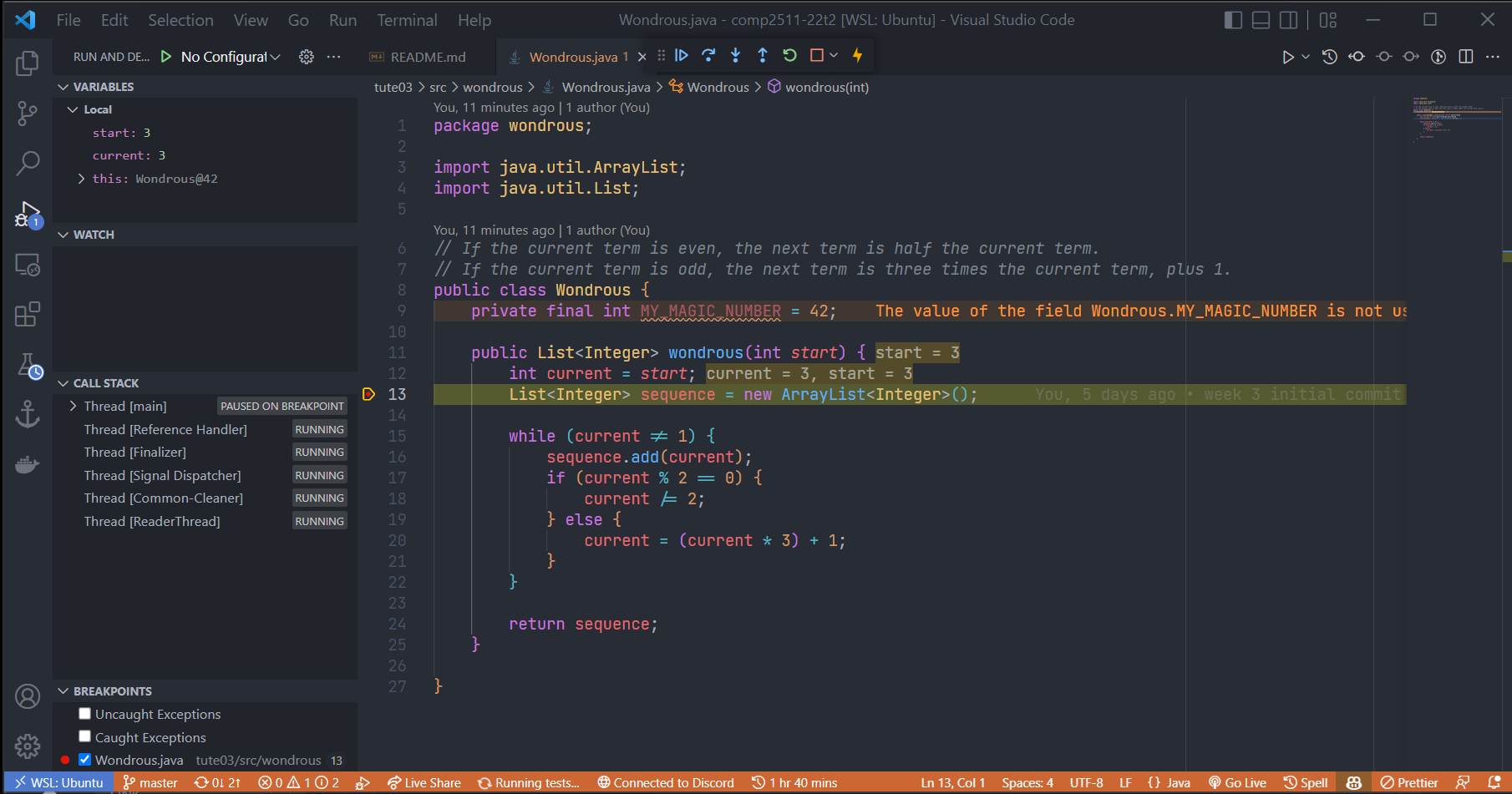
- Set a breakpoint, run the test in debug mode
- Stops at a breakpoint it encounters
- See variable values, call stack
Debug Mode
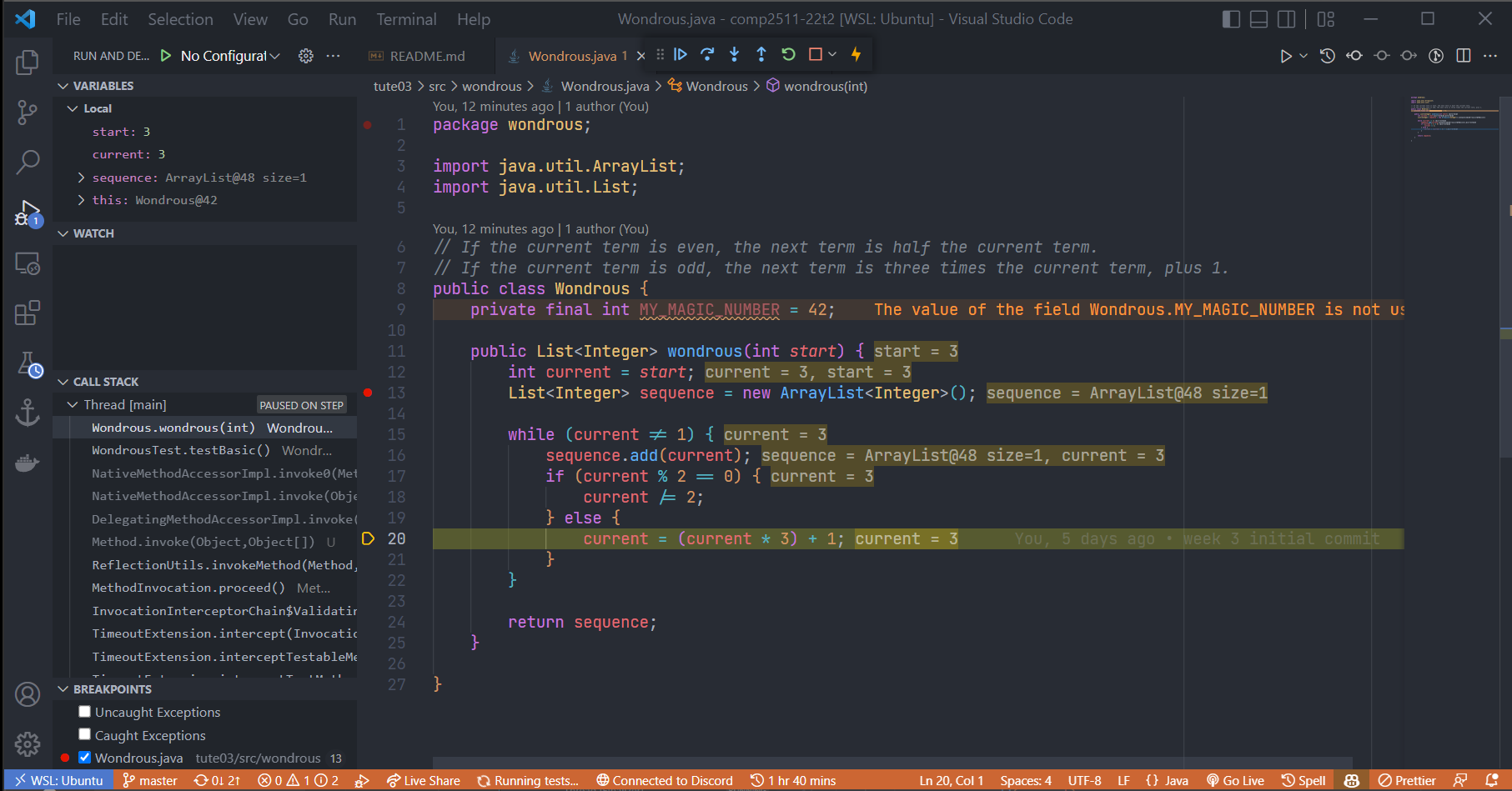
Now lets fix it
package wondrous;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
// If the current term is even, the next term is half the current term.
// If the current term is odd, the next term is three times the current term, plus 1.
public class Wondrous {
public List<Integer> wondrous(int start) {
int current = start;
List<Integer> sequence = new ArrayList<Integer>();
while (true) {
sequence.add(current);
if (current == 1) {
break;
} else if (current % 2 == 0) {
// Even
current /= 2;
} else {
// odd
current = (current * 3) + 1;
}
}
return sequence;
}
}Exceptions
Exceptions
An exception is an undesirable event that can occur during the execution of a program and it can disrupt the normal flow of the program.
What happens when an error occur
- Exception object is created and given to the runtime system. This is called throwing an exception.
- Execution of the program is paused and the Java runtime will search in the call stack for a method that can handle the exception.
- The exception handler chosen is said to catch the exception.
Exceptions
Checked vs Unchecked
- Checked: must be manually checked, will result in compilation error if not handled
- Any class that inherits from `Exception` is a checked exception.
- E.g., IOException, SQLException
- Unchecked: genuine errors that occur at run time
- Any class that inherits from `RuntimeException` is unchecked
- E.g., ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptions, ArithmeticException
Exceptions - Wondrous
Exceptions - Wondrous
package wondrous;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Wondrous {
public List<Integer> wondrous(int start) {
int current = start;
List<Integer> sequence = new ArrayList<Integer>();
if (start < 1) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("wondrous start must be >= 1");
}
while (true) {
sequence.add(current);
if (current == 1) {
break;
} else if (current % 2 == 0) {
current /= 2;
} else {
current = (current * 3) + 1;
}
}
return sequence;
}
}A non-positive starting value cannot produce a valid
wondrous sequence
Let's throw an exception!
Exceptions - Wondrous
JUnit Testing
More tests
package wondrous.test;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertThrows;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import wondrous.Wondrous;
public class WondrousTest {
@Test
public void testBasic() {
Wondrous w = new Wondrous();
List<Integer> expected = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(3, 10, 5, 16, 8, 4, 2, 1));
assertEquals(expected, w.wondrous(3));
}
@Test
public void testOne() {
Wondrous w = new Wondrous();
List<Integer> expected = new ArrayList<Integer>(Arrays.asList(1));
assertEquals(expected, w.wondrous(1));
}
@Test
public void testInvalid() {
Wondrous w = new Wondrous();
assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
w.wondrous(0);
});
}
}