Breve introducción a la manipulación de datos georeferenciados con GeoDjango
Quién soy?
- Soy desarrolladora en Nearsoft
- Organizadora y fundadora de PythonDay México
- Organizadora de PyCon Charlas
- Directora de Women Who Code Ciudad de México
- Líder de Women Who Code Python
- También organizo RustMX :P
Sistema de coordenadas
Sistema que utiliza uno o más números para determinar la posición de un punto u objeto.
Un ejemplo es el sistema de latitud, longitud para localizar coordenadas geográficas.

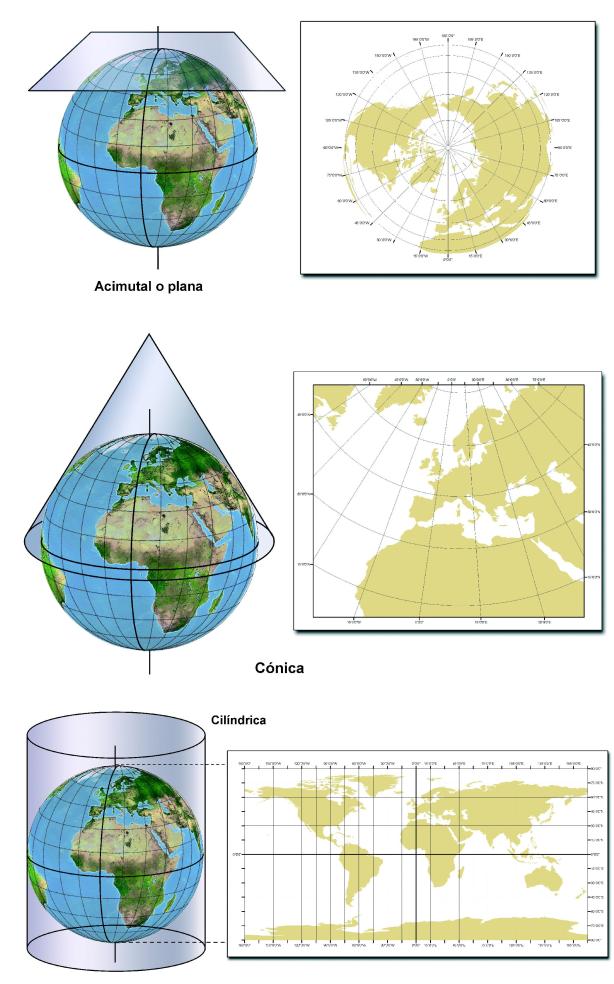
Proyecciones
Sistema de representación gráfica que establece una relación ordenada entre los puntos de la superficie curva de la Tierra y los de una superficie plana.
PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL es un sistema de gestión de bases de datos relacional orientado a objetos y de código abierto

PostGIS
- Tipos de datos espaciales,
- Índices espaciales
- Funciones que operan sobre ellos

Requerimientos extra
- GEOS
- GDAL
- PROJ.4
GeoDjango
ORM que abstrae las funcionalidades de la una base de datos con datos geo referenciados.
from django.contrib.gis.db import models
class WorldBorder(models.Model):
# Regular Django fields corresponding to the attributes in the
# world borders shapefile.
name = models.CharField(max_length=50)
area = models.IntegerField()
pop2005 = models.IntegerField('Population 2005')
fips = models.CharField('FIPS Code', max_length=2)
iso2 = models.CharField('2 Digit ISO', max_length=2)
iso3 = models.CharField('3 Digit ISO', max_length=3)
un = models.IntegerField('United Nations Code')
region = models.IntegerField('Region Code')
subregion = models.IntegerField('Sub-Region Code')
lon = models.FloatField()
lat = models.FloatField()
# GeoDjango-specific: a geometry field (MultiPolygonField)
mpoly = models.MultiPolygonField()
# Returns the string representation of the model.
def __str__(self):
return self.namefrom django.db import models
from owners.models import Owner
class Animal(models.Model):
name = models.CharField('Pet name', max_length=50)
breed = models.CharField('Breed',max_length=30)
age = models.IntegerField('Age', default=0)
sound = models.CharField('Sound',max_length=10)
owner = models.ForeignKey(Owner, models.SET_NULL, blank=True, null=True,)
def __str__(self):
return f"The {self.name} says {self.sound}"pets/models.py
import uuid
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.db import models
class Owner(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
membership = models.UUIDField(default=uuid.uuid4, editable=False)
def __str__(self):
return self.user.get_full_name()owners/models.py
import uuid
from django.contrib.auth.models import User
from django.db import models
class Vet(models.Model):
user = models.OneToOneField(User, on_delete=models.CASCADE)
certification = models.UUIDField(default=uuid.uuid4, editable=False)
def __str__(self):
return self.user.get_full_name()vets/models.py
import uuid
from django.contrib.gis.db import models
from vets.models import Vet
class Hospital(models.Model):
chief_vet = models.ForeignKey(Vet, models.SET_NULL, blank=True, null=True)
name = models.CharField('Name', max_length=255)
address = models.CharField('Address', max_length=255)
location = models.PointField()
license = models.UUIDField(default=uuid.uuid4, editable=False)
def __str__(self):
return self.namehospitals/models.py
from rest_framework import serializers
from rest_framework_gis.serializers import GeoFeatureModelSerializer
from hospitals.models import Hospital
class HospitalSerializer(GeoFeatureModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = Hospital
geo_field = "location"
fields = ('name', 'address', 'license')hospitals/serializers.py
from django.contrib.gis.geos import GEOSGeometry
from django.contrib.gis.measure import D
from hospitals.models import Hospital
def closest_hospitals_by_location(latitude, longitude, distance=5):
point_wkt = 'POINT({} {})'.format(longitude, latitude)
point = GEOSGeometry(point_wkt, srid=4326)
hospitals = Hospital.objects.filter(
location__distance_lte=(
point,
D(km=distance)
)
)
return hospitalshospitals/utils.py
Código demo
https://github.com/mayela/geodjango-demo

@mayela0x14