Building custom web administrators for geographic data driven websites with Django

Marc Compte
University of Girona (SIGTE)


Django


Talks @ GeoPython
by Paolo Melchiorre
in Room 2
on 23rd april @ 11:45
Maps with Django
by Megan Luisa White
in Room 1
on 23rd april @ 21:00
Cal ToxTrack
GeoDjango
Use case

Django


Django makes it easier to build better Web apps more quickly and with less code.e.
Django is a high-level Python Web framework that encourages rapid development and clean, pragmatic design. Built by experienced developers, it takes care of much of the hassle of Web development, so you can focus on writing your app without needing to reinvent the wheel. It’s free and open source.
What is it?

Django



Why Django?

Django


Features (some)
- MVC paradigm
- HTML Templates (jinja2 like)
- Integrated web server
- i18n and l10n ready
- Caching & Logging
- URL management (routing)
- CLI custom commands
- Backup&restore
- Admin!!
- Object-Relational Mapping!!

+ Loads of third-party modules
Django Admin


What is it?
It’s not just scaffolding – it’s the whole house.e.
It’s the backend templates, the views, forms, controllers and even some models out-of-the-box without typing a single line.

Django Admin


0 lines of code
$ pip install django $ django-admin startproject demo $ django-admin startapp app $ python manage.py migrate $ python manage.py createsuperuser $ python manage.py runserver
+

Django Admin


0 lines of code
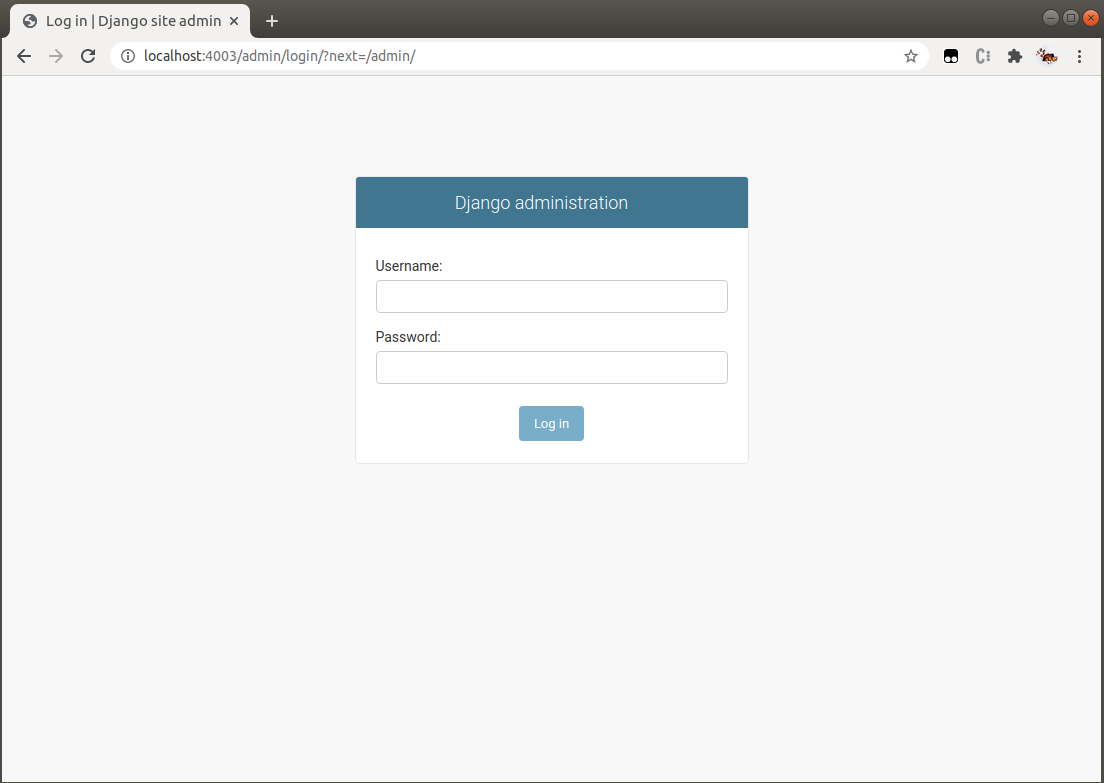

Django Admin


0 lines of code
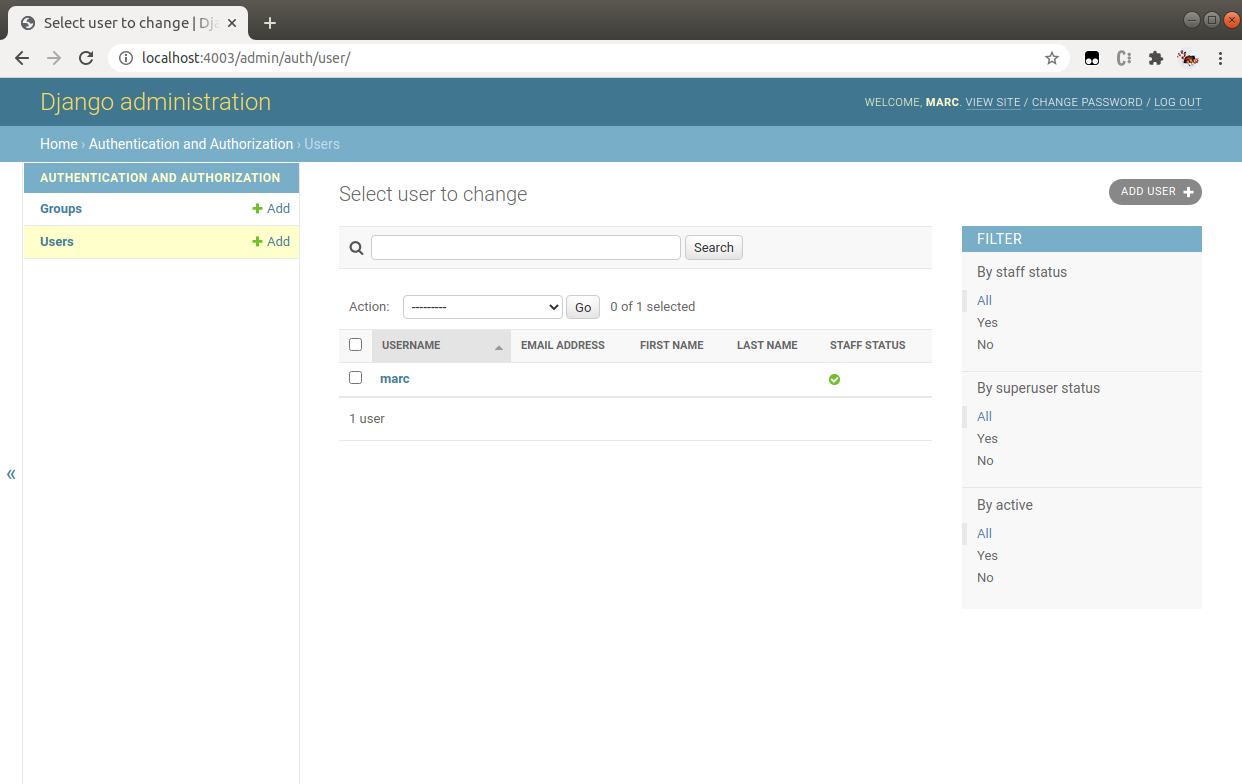

Django Admin


Adding new models (tables)

Django Admin


Adding new models (tables)
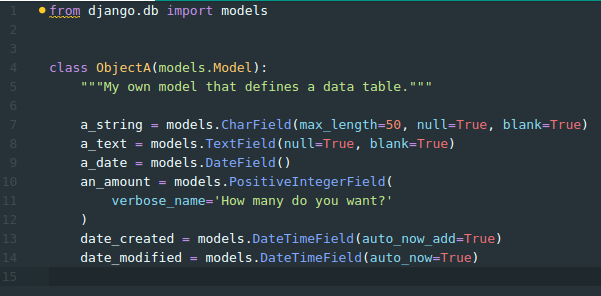

$ python manage.py makemigrations
$ python manage.py migrate
+
+

Django Admin


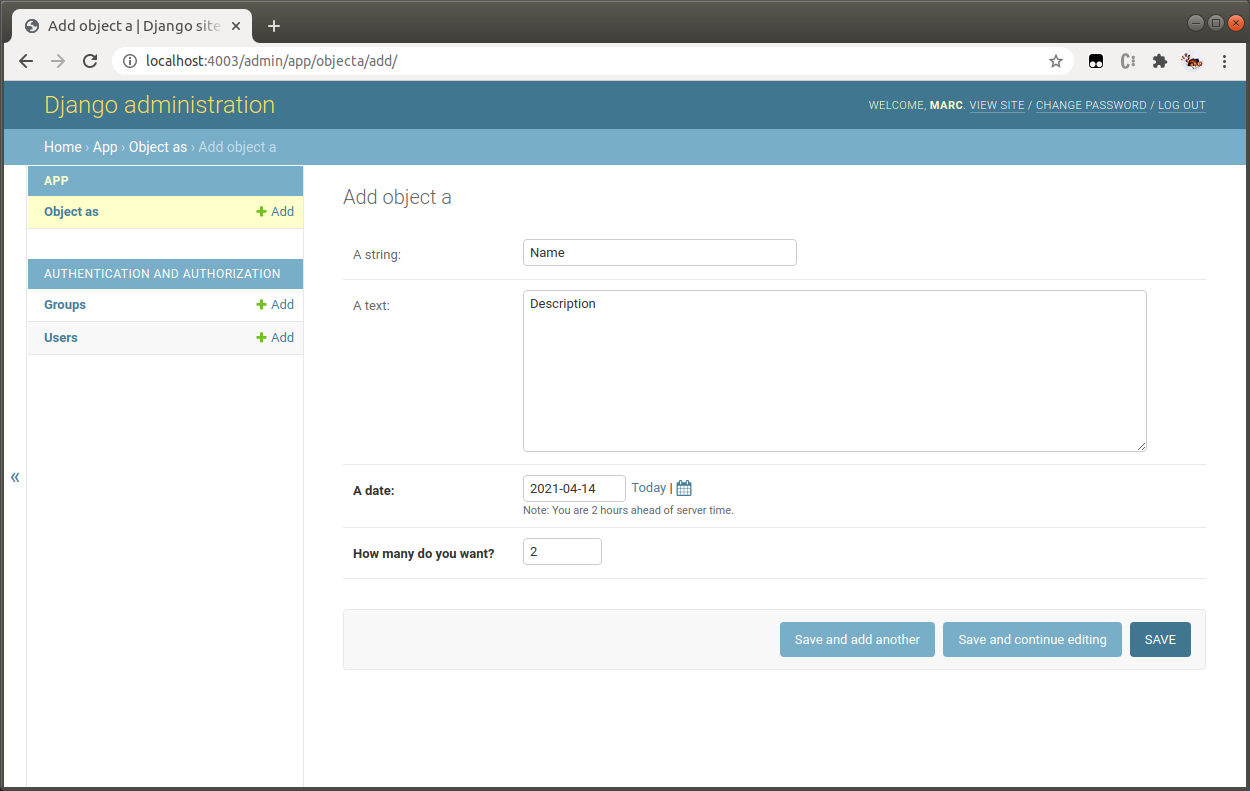
Adding new models (tables)

Django Admin


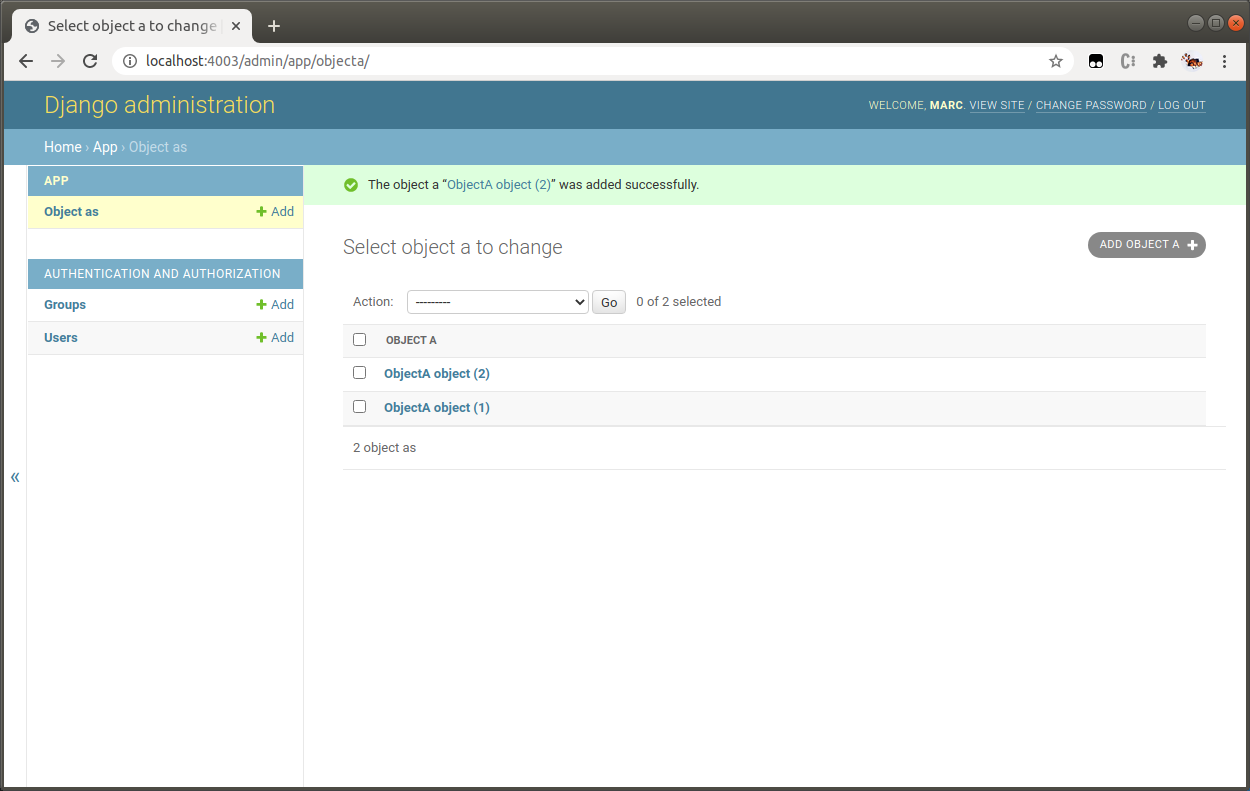
Adding new models (tables)

Django Admin


Tune up with one-liners

Django Admin


Tune up with one-liners
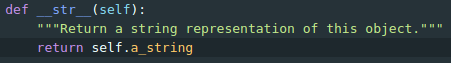
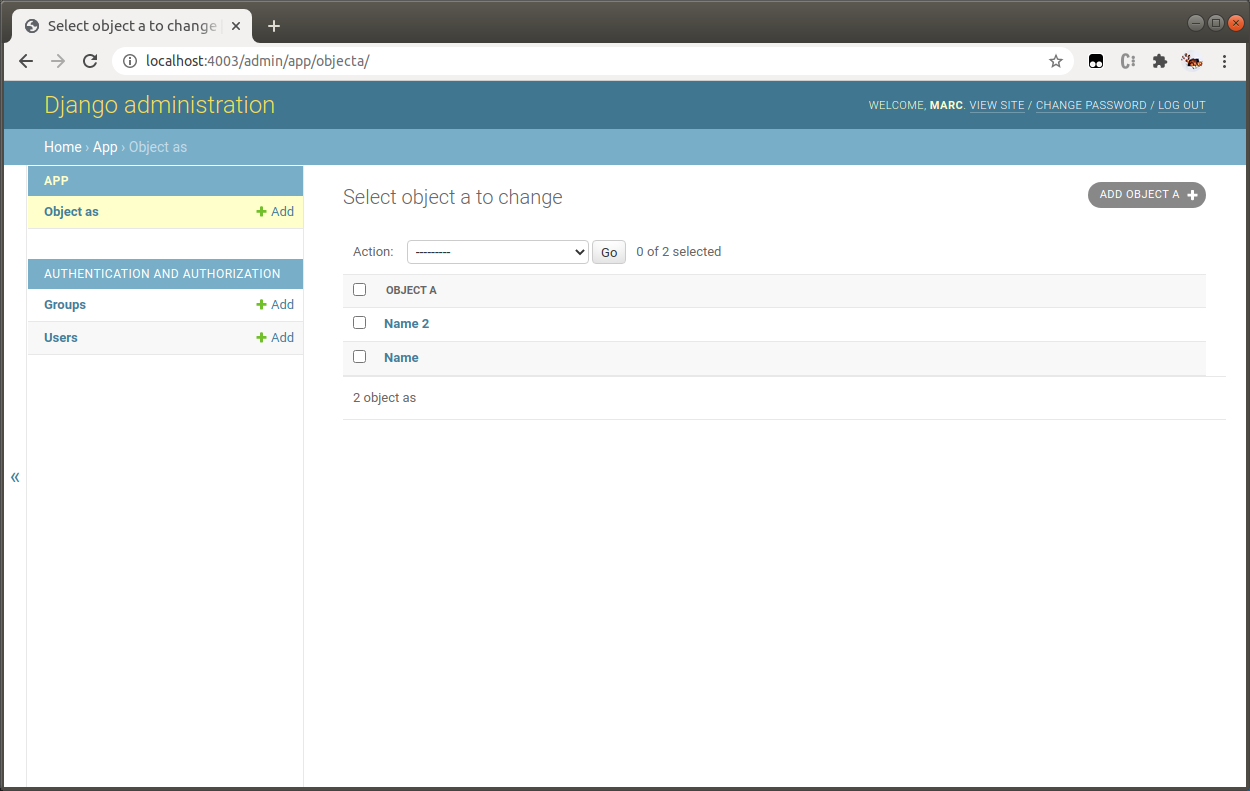

Django Admin


Tune up with one-liners
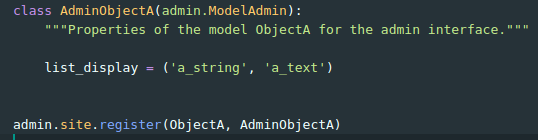


Django Admin


Tune up with one-liners
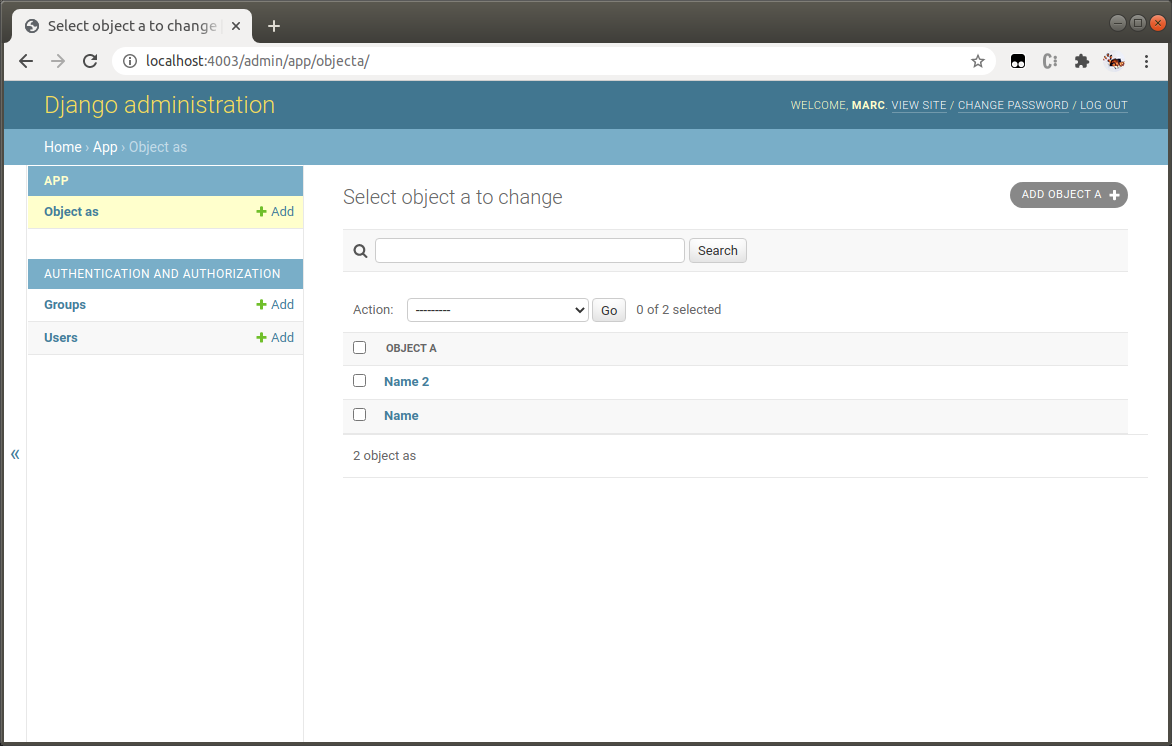
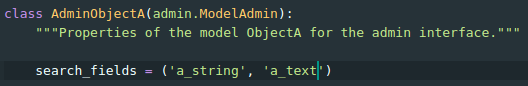

Django Admin


Tune up with one-liners
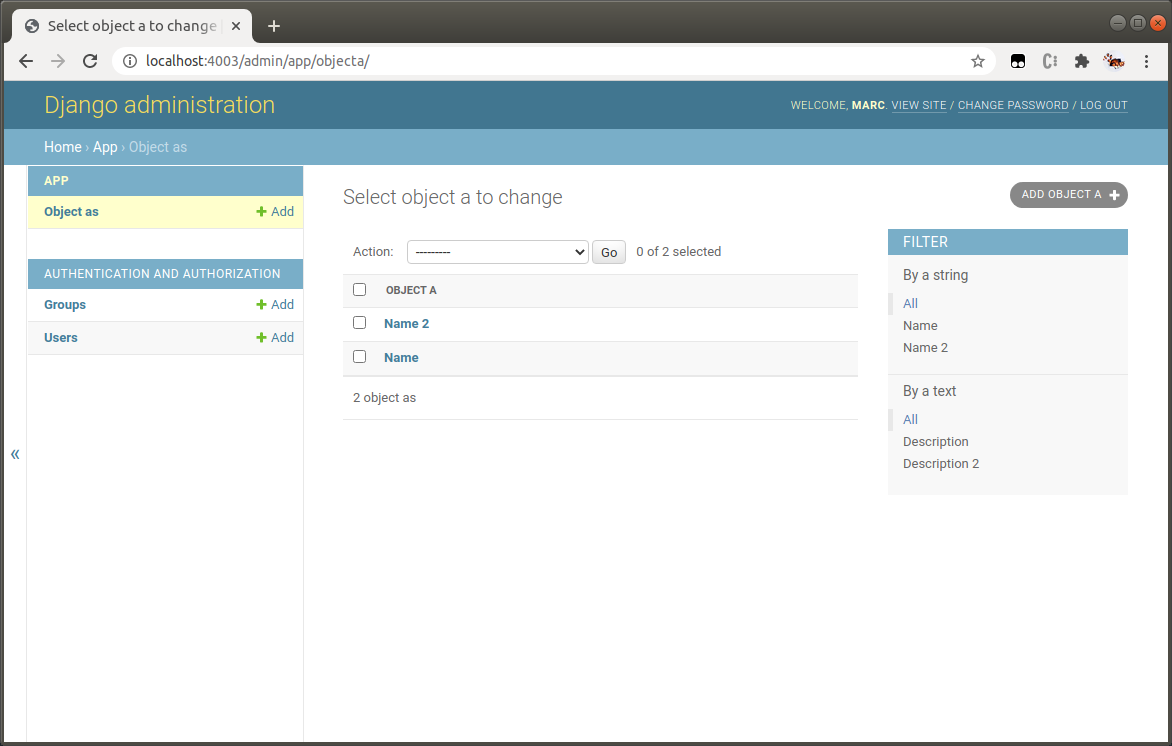
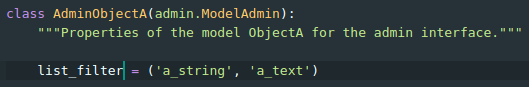

Django Admin


Other tune-ups: inlines
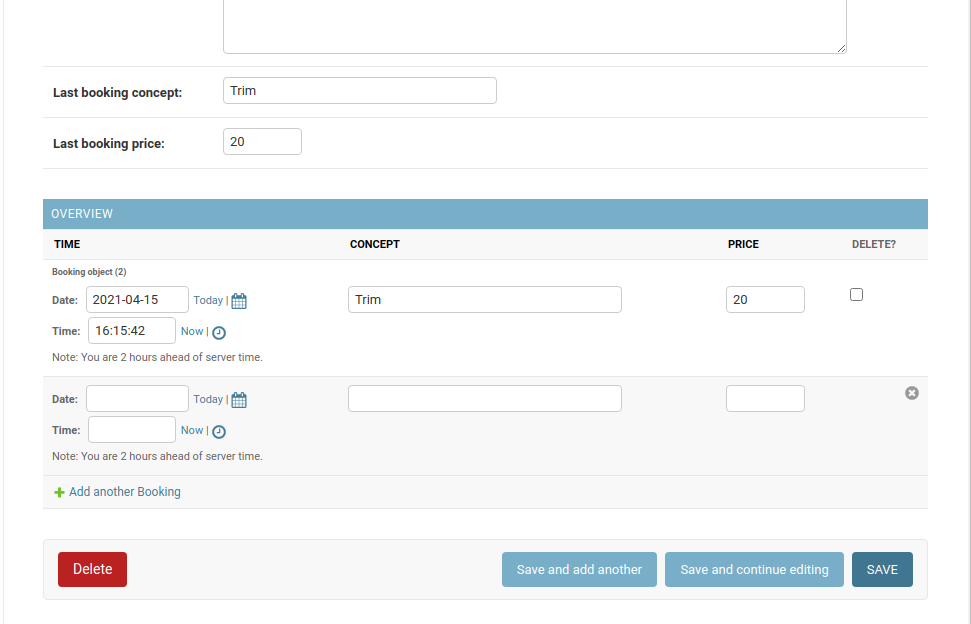

Django Admin


Adding geometries
GeoDjango
django-geojson + django-leaflet
Spatial databases
Non-spatial databases

Django Admin


Adding geometries
| GeoDjango | GeoJSON+Leaflet | |
|---|---|---|
| Database | Spatial | Non-spatial |
| Field | Geometry | JSON |
| Spatial operations | Included | Requires modules |
| ORM integration | Yes | No |
| Spatial indexing | Yes | No |

Django Admin


Adding geometries as JSON fields
(env)$ pip install django-geojson jsonfields django-leaflet

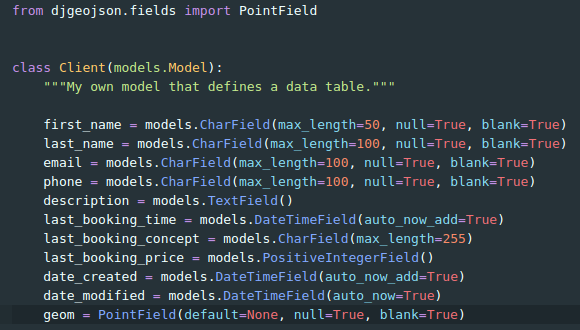
Add geom field to model
Django Admin


Adding geometries as JSON fields
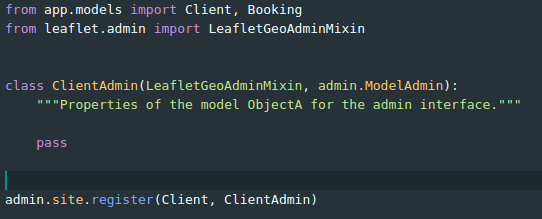

Add leaflet map widget to the ModelAdmin
Django Admin


Creating geometries from the admin
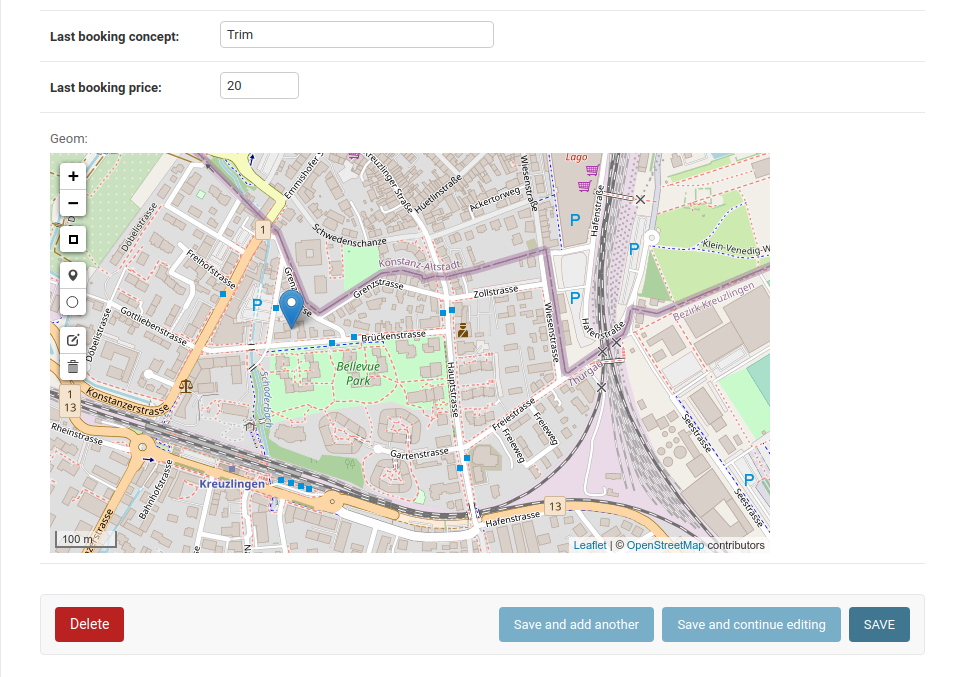

Django Admin


Legacy databases

(env)$ python manage.py inspectdb > app/models.py
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.postgresql_psycopg2',
'NAME': 'my_db_name',
'USER': 'my_user',
'PASSWORD': 'my_password',
'HOST': 'my_server',
'PORT': '5432',
}
}
settings.py
Django ORM


SQL is an English-like language
>>> from .models import ObjectA
>>> all_as = ObjectA.objects.all()
SELECT * FROM ObjectA;
>>> filtered = ObjectA.objects.filter( ... a_string='Test' ... )
>>> filtered2 = ObjectA.objects.filter( ... a_number__gte=10 ... )
SELECT * FROM ObjectA WHERE ...;

Django ORM


>>> filtered = ObjectA.objects.filter( ... objectb__field1='Test' ... )
SELECT ObjectA.* FROM ObjectA, ObjectB WHERE ObjectA.objectb = ObjectB.id AND ObjectB.field1 = 'Test';
Is SQL an English-like language?

Django ORM


>>> filtered = Publication.objects.select_related(
... 'country', 'country_state', 'city'
... ).values(
... 'id', 'title', 'country__country_name',
... 'countrystate__name', 'city__name'
... )
SELECT publication.id, publication.title, country.country_name, countrystate.name, city.name
FROM publication
INNER JOIN country ON ( publication.country_id = country.id )
INNER JOIN countrystate ON ( publication.countrystate_id = countrystate.id )
INNER JOIN city ON ( publication.city_id = city.id );
This is not an Enligsh-like sentence any more

Django ORM


>>> filtered = Publication.objects.all() >>> for item in filtered: ... print(item.id, item.title, ... item.country.country_name, ...)
SELECT publication.id, publication.title, country.country_name, countrystate.name, city.name
FROM publication
INNER JOIN country ON ( publication.country_id = country.id )
INNER JOIN countrystate ON ( publication.countrystate_id = countrystate.id )
INNER JOIN city ON ( publication.city_id = city.id );
Caveats

Django ORM


>>> filtered = ObjectA.objects.exclude( ... a_string__contains='Test' ... ) >>> for item in filtered: ... # do something >>> filtered2 = filtered.filter( ... a_number__gte=10, ... a_date__gte=date,
... a_date__lte=another_date, ... geom__intersects=geometry ... )
>>> for item in filtered2: ... # do something
Reusing queries
Other benefits

Django ORM


Versatility
Why it is better
Security
Readability

Questions?


