Exploring ES6 Classes in AngularJS
Michael Bromley
What is ES6?
EcmaScript version 6
AKA The New JavaScript
Browser / Transpiler support:
An ES6 Class
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}!`);
}
}
var bruce = new Person('Bruce');
bruce.greet(); // Hi, I'm Bruce!Full syntax:
http://www.2ality.com/2015/02/es6-classes-final.html
Why ES6 Classes With AngularJS?
Readability
class Person {
constructor(name) {
this.name = name;
}
greet() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}!`);
}
}
// versus
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.greet = function() {
console.log(`Hi, I'm ${this.name}!`);
};Enforces the Naming of Functions
// No
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('AppController', function() {
// ... code
});
// Yes
class AppController {
// ... code
}
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('AppController', AppController);The Future

// An example Angular 2 directive
@ComponentDirective
class SantaTodoApp {
constructor() {
this.newTodoTitle = '';
}
addTodo: function() { ... }
removeTodo: function(todo) { ... }
todosOf: function(filter) { ... }
}
// An example Angular 2 service
class TodoStore {
constructor(win:Window) {
this.win = win;
}
add(todo) {
// access this.win.localStorage ...
}
remove(todo) { ... }
todosOf(filter) { ... }
}TypeScript
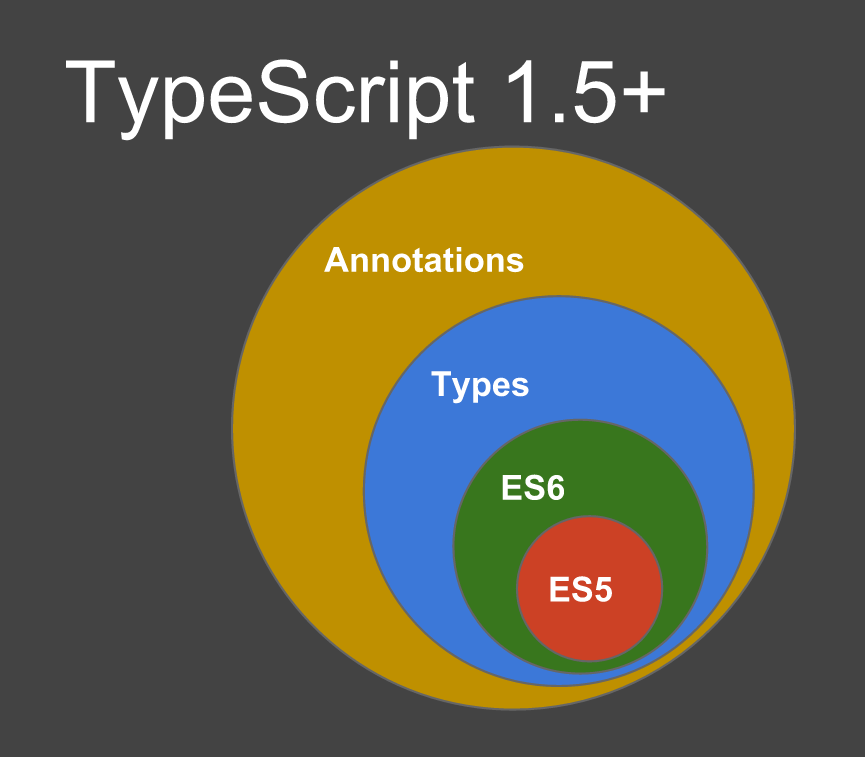
Where Can We Use Them?
Controllers
Services
Factories
Directives
- "components"
A Brief Review of angular.Module
controller(name, constructor);
function AppController(someDependency) {
this.stuff = someDependency.getTheStuff();
// etc.
}
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('AppController', AppController);service(name, constructor);
function MyService($http) {
this.getStuff = $http.get('api/stuff');
// etc.
}
angular.module('myApp')
.service('myService', MyService);factory(name, providerFunction);
function stuffFactory($http) {
function getStuff() {
$http.get('api/stuff');
}
// etc.
return {
getStuff: getStuff
}
}
angular.module('myApp')
.factory('stuffFactory', stuffFactory);directive(name, directiveFactory);
function myDirective() {
return {
restrict: 'E',
template: 'path/to/template.html',
scope: {
list: '='
},
// lots more to configure...
link: function(scope, element, attrs) {
//.. code
}
};
}
angular.module('myApp')
.directive('myDirective', myDirective);Controllers
class PersonController {
constructor(userService) {
this.userService = userService;
this.userService.getFullName()
.then(result => this.userName = result.fullName);
this.likes = 0;
}
like() {
this.userService.addLike();
this.likes ++;
}
}
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('PersonController', PersonController);<div ng-controller="PersonController as vm">
{{ vm.userName }} <i class="icon-like" ng-click="vm.like()"></i>
</div>A Note on Annotation
// array notation
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('PersonController', ['userService', PersonController]);// $inject property
PersonController.$inject = ['userService'];
angular.module('myApp')
.controller('PersonController', PersonController);
// ngAnnotate
class PersonController {
/* @ngInject */
constructor(userService) {
// ...
}
}// TypeScript
class PersonController {
public static $inject = ['userService'];
constructor(userService) {
// ...
}
}Services
class UserService {
/* @ngInject */
constructor(config, $http) {
this.userId = config.userId;
this.$http = $http;
}
getFullName() {
this._doRequest(`api/user/${this.userId}/fullname`);
}
addLike() {
this._doRequest(`api/user/${this.userId}/like`);
}
_doRequest(url) {
return this.$http.get(url);
}
}
angular.module('myApp')
.service('userService', UserService);
Factories

"Don't do it!"
- Pete Bacon Darwin (paraphrase)
class ThingFactory {
constructor($timeout) {
this.$timeout = $timeout;
}
newThing() {
console.log('Getting a new Thing...');
return this.$timeout(() => new Thing(), 1000);
}
}
// nope
angular.module('myApp')
.factory('thingFactory', ThingFactory);// A working method, but too much repetition!
angular.module('app')
.factory('thingFactory', ['$timeout', ($timeout) => new ThingFactory($timeout)]);// Pass a factory function that returns an instance of the class
angular.module('app')
.factory('thingFactory', () => new ThingFactory());// Goal: turn `ThingFactory` into
// ['$timeout', ($timeout) => new ThingFactory($timeout)]
var constructorFn = ThingFactory;
var args = constructorFn.$inject; // args = ['$timeout']
var factoryFunction = (...args) => {
return new constructorFn(...args);
}
var factoryArray = args.push(factoryFunction);
// factoryArray = ['$timeout', factoryFunction]function makeFactoryArray(constructorFn) {
var args = constructorFn.$inject,
factoryFunction = (...args) => new constructorFn(...args);
return args.push(factoryFunction);
}
Directives
class MyDirective {
/* @ngInject */
constructor($interval) {
this.template = '<div>I\'m a directive!</div>';
this.restrict = 'E';
this.scope = {}
// etc. for the usual config options
this.$interval = $interval;
}
// optional compile function
compile(tElement) {
tElement.css('position', 'absolute');
}
// optional link function
link(scope, element) {
this.$interval(() => this.move(element), 1000);
}
move(element) {
element.css('left', (Math.random() * 500) + 'px');
element.css('top', (Math.random() * 500) + 'px');
}
}Compile/Link Problems
compile() {
// do stuff
return this.link;
}Nope: `link` method called in context of global scope. i.e. `this` == `window`
compile() {
// do stuff
return (scope, element ) => {
this.$interval(() => this.move(element), 1000);
};
}compile() {
// do stuff
return this.link.bind(this);
}Better, but less clear & ugly
Better, still too much to remember
var constructorFn = MyDirective;
if (!constructorFn.prototype.compile) {
// create an empty compile function if none exists
constructorFn.prototype.compile = () => {};
}
var originalCompileFn = _cloneFunction(constructorFn.prototype.compile);
// the _override helper function replaces the 'compile' property on
// constructorFn.prototype with a new function defined by the third argument.
_override(constructorFn.prototype, 'compile', function () {
return function () {
originalCompileFn.apply(this, arguments);
if (constructorFn.prototype.link) {
return constructorFn.prototype.link.bind(this);
}
};
});Encapsulate
class MyAngularComponent {
/*@ngInject*/
constructor(dependency1, dependency2) {
this.dependency1 = dependency1;
// stuff happens here
}
someMethods() {
this.dependency1.doThatThing();
// more stuff here
}
}
register('app')
.controller('MyController', MyAngularComponent)
.service('myService', MyAngularComponent)
.provider('myOtherService', MyAngularComponent)
.factory('myFactory', MyAngularComponent)
.directive('myDirective', MyAngularComponent);Resources
Article: Exploring ES6 Classes In AngularJS 1.x
Demo App
Thank you