SSR
created by Apptension
Kaj Białas
Daniel Capeletti
Artur Kudeł
Michał Przyszczypkowski
What is Single Page App?
How SPA works?
A web application that fits on a single web page with the goal of providing a user experience similar to that of a desktop application. In an SPA, either all necessary code – HTML, JavaScript, and CSS – is retrieved with a single page load or the appropriate resources are dynamically loaded and added to the page as necessary, usually in response to user actions.
What problem this has?
- problems with SEO
- sharing single pages/urls
- performance in big applications
- large application size
- long loading time
Posible ways to solve problems?
- problems with SEO
- problem only with special search engines (asian markets etc.)
- pre-rendering
- sharing single pages/urls
- performance in big applications
- code optimization and asynchronous loading of resources
Probably the best way to solve problems?
Server Side Rendering
What SSR gives us?
What SSR gives us?
- SEO
- Sharing
- Speed
- Cache
- Additional layer
How?
A bit of history...
Fully server side rendering
SPA
(without server side rendering)
How bots see SPA

Users happy
but sad bots...
A bit of history...
Fully server side rendering
SPA
(without server side rendering)
Server Side Rendering
+
SPA
=
problem solved?
people and robots are happy

but how does it exactly work?
BROWSER
PROXY (RENDERING) SERVER
API SERVER
URL
API
requests
responses
Generated html
CDN
GET
STATIC
ASSETS
- main.min.js
- main.min.css
- ...
non-interactive
time
What we need?
on server side:
But in our example will be

-
python-react
-
React.NET
-
react-php-v8js
-
and more...
On client side?
- React
- Angular 2+
- Vue.js
- and probably some more frameworks...

SSR in React + Redux
App
switch (action.type) {
case PREPARE_NUMBER:
return Object.assign({}, state, { number: action.number * 10 });
default:
return state;
}export class App extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Switch>
<Route exact={true} path="/:id" component={StaticContainer} />
<Route component={NotFound} />
</Switch>
)
}
}constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.props.prepareNumber(this.props.match.params.id);
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h1>Static number: {this.props.number} </h1>
</div>
)
}Server side code
import Express from 'express';
import React from 'react';
import { renderToString } from 'react-dom/server';
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import { App } from './app/App';
import createReducer from './app/reducers/app.redux';
import { StaticRouter } from 'react-router';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
const app = Express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(Express.static('public'));
app.use(handleRender);
function handleRender(req, res) {
let store = createStore(createReducer());
const context = {};
renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter context={context} location={req.url}>
<App/>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
);
const preloadedState = store.getState();
store = createStore(createReducer(), preloadedState);
const html = renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<StaticRouter context={context} location={req.url}>
<App/>
</StaticRouter>
</Provider>
);
res.send(`
<!doctype html>
<html>
<header>
<title>Simple SSR in React</title>
</header>
<body>
<script>window.__PRELOADED_STATE__ = ${JSON.stringify(preloadedState).replace(/</g, '\\u003c')}</script>
<div id='app'>${html}</div>
<script src='bundle.js'></script>
</body>
</html>
`)
}
app.listen(port);Client side code
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import {App} from './App';
import createReducer from './reducers/app.redux';
const preloadedState = window.__PRELOADED_STATE__;
delete window.__PRELOADED_STATE__;
const store = createStore(createReducer(), preloadedState);
export default class Main extends React.Component {
render() {
return (
<Provider store={store}>
<BrowserRouter>
<App/>
</BrowserRouter>
</Provider>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render((
<Main/>
), document.getElementById('app'));
React checksum
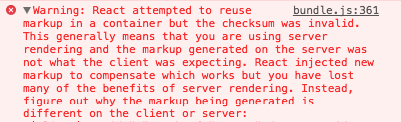
Problems?
Fetching data
- server needs to wait for all API calls if data is needed to render the page
- it may overload server if there is a lot of API calls for each request
- use caching when possible
- only load data that is required to render the page
- don't load same data twice (don't requst on client if it is already loaded by server)
Different JS environment
- node.js vs browser
- some objects are not available on server side (document, window etc.)
- don't run any code that need browser-specific objects on server
- measuring window / orientation
- initializing iScroll etc.
- checking browser compatibility
React Lifecycle
- componentWillMount & contructor are run on server
- anything else is run on client only
Caching strategies
- cache API calls
- cache whole server requests
- cache components instances
- https://github.com/walmartlabs/react-ssr-optimization
SSR in practice (Apptension Boilerplate)
First things first
We need a NodeJS server
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
.
.
.
// Start your app.
app.listen(port, host, (err) => {
if (err) {
return logger.error(err.message);
}
// Connect to ngrok in dev mode
if (ngrok) {
ngrok.connect(port, (innerErr, url) => {
if (innerErr) {
return logger.error(innerErr);
}
logger.appStarted(port, prettyHost, url);
});
} else {
logger.appStarted(port, prettyHost);
}
});Let's handle a connection
//Somewhere in the server:
const handleSSR = require('./middlewares/handleSSR');
app.get('*', handleSSR);
/* --------- */
const app = express();
app.use(handleSSR);
/* --------- */
module.exports = function handleSSR(req, res) {
const options = {
assets,
webpackDllNames: extractWebpackDllNamesFromPackage(),
lang: req.acceptsLanguages(appLocales),
};
renderAppToStringAtLocation(req.url, options, (response) => {
if (response.error) {
res.status(500).send(response.error.message);
printError(response.error);
} else if (response.redirectLocation) {
res.redirect(302, response.redirectLocation);
} else if (response.notFound) {
res.status(404).send(response.html);
} else {
res.status(200).send(response.html);
}
});
};What do we need to render a react application on backend? (in a nutshell)
// In a nutshell
import { renderToStaticMarkup } from 'react-dom/server';
const doc = renderToStaticMarkup(
<HtmlDocument
appMarkup={appMarkup}
lang={state.locales.language}
state={state}
head={Helmet.rewind()}
assets={assets}
/>
);Well... we need a bit more than that
import 'babel-polyfill';
import React from 'react';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { renderToString, renderToStaticMarkup } from 'react-dom/server';
import { createMemoryHistory, match, RouterContext } from 'react-router';
import { syncHistoryWithStore } from 'react-router-redux';
import Helmet from 'react-helmet';
import configureStore from './modules/store';
import routes from './routes';
import HtmlDocument from './htmlDocument';
import { selectLocationState } from './modules/router/router.selectors';
function renderAppToString(store, renderProps) {
return renderToString(
<Provider store={store}>
<RouterContext {...renderProps} />
</Provider>
);
}
function renderAppToStringAtLocation(url, { webpackDllNames = [], assets, lang }, callback) {
const memoryHistory = createMemoryHistory(url);
const store = configureStore({}, memoryHistory);
syncHistoryWithStore(memoryHistory, store, {
selectLocationState: selectLocationState(),
});
match({ routes, location: url }, (error, redirectLocation, renderProps) => {
if (error) {
callback({ error });
} else if (redirectLocation) {
callback({ redirectLocation: redirectLocation.pathname + redirectLocation.search });
} else if (renderProps) {
store.rootSaga.done.then(() => {
const state = store.getState().toJS();
const appMarkup = renderAppToString(store, renderProps);
const doc = renderToStaticMarkup(
<HtmlDocument
appMarkup={appMarkup}
lang={state.locales.language}
state={state}
head={Helmet.rewind()}
assets={assets}
webpackDllNames={webpackDllNames}
/>
);
const html = `<!DOCTYPE html>\n${doc}`;
callback({ html });
}).catch((e) => {
callback({ e });
});
renderAppToString(store, renderProps);
store.close();
} else {
callback({ error: new Error('Unknown error') });
}
});
}
export {
renderAppToStringAtLocation,
};
Let's break this down a bit
React router match
function renderAppToStringAtLocation(url, { webpackDllNames = [], assets, lang }, callback) {
match({ routes, location: url }, (error, redirectLocation, renderProps) => {
if (error) {
callback({ error });
} else if (redirectLocation) {
callback({ redirectLocation: redirectLocation.pathname + redirectLocation.search });
} else if (renderProps) {
//Rest of code goes here This function is to be used for server-side rendering. It matches a set of routes to a location, without rendering, and calls a callback(error, redirectLocation, renderProps) when it's done.
http://knowbody.github.io/react-router-docs/api/match.html
After we match the route
.
.
} else if (renderProps) {
//Stuff going on here, will get back in a minute ;)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
renderAppToString(store, renderProps);
store.close();We call renderApptoString
here
This will render the application, trigger the sagas, make the API calls and so on!
Next, we gonna stop the sagas
store.close = () => store.dispatch(END);Why do we stop sagas?
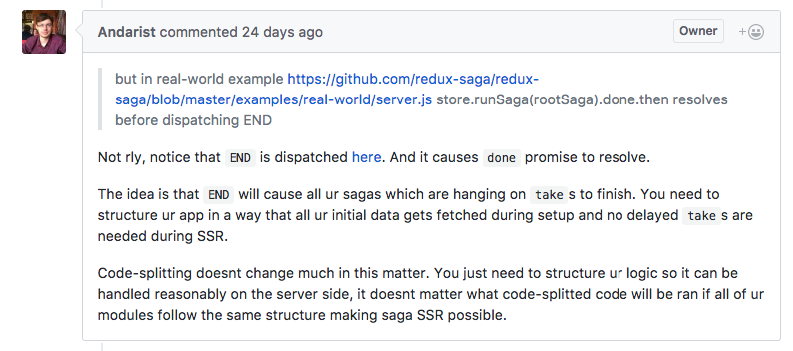
After we stop sagas
store.rootSaga = sagaMiddleware.run(rootSaga);
store.rootSaga.done.then(() => {
const state = store.getState().toJS();
const appMarkup = renderAppToString(store, renderProps);
const doc = renderToStaticMarkup(
<HtmlDocument
appMarkup={appMarkup}
lang={state.locales.language}
state={state}
head={Helmet.rewind()}
assets={assets}
webpackDllNames={webpackDllNames}
/>
);
const html = `<!DOCTYPE html>\n${doc}`;
callback({ html });
}).catch((e) => {
callback({ e });
});
renderAppToString(store, renderProps);
store.close();So, when our sagas finishes
We render the app again with new state
Render to static markup (html)
Respond our rendered html :)
Curious about HtmlDocument?
render() {
const { lang, head, appMarkup, state, assets, webpackDllNames } = this.props;
const attrs = head.htmlAttributes.toComponent();
return (
<html lang={lang} {...attrs}>
<head>
<meta charSet="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1" />
<meta name="mobile-web-app-capable" content="yes" />
{head.title.toComponent()}
{head.meta.toComponent()}
<link href="https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Open+Sans:400,700" rel="stylesheet" />
<link href={assets.main.css} rel="stylesheet" />
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
If you are seeing this message, that means <strong>JavaScript has been disabled on your browser</strong>
, please <strong>enable JS</strong> to make this app work.
</noscript>
<div id="app">
<div dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: appMarkup }} />
</div>
<script dangerouslySetInnerHTML={{ __html: `APP_STATE = ${htmlescape(state)}` }} />
{(webpackDllNames || []).map((dllName) =>
<script data-dll key={dllName} src={`/${dllName}.dll.js`}></script>
)}
<script type="text/javascript" src={assets.main.js}></script>
</body>
</html>
);
}Webpack
module.exports = {
name: 'server',
target: 'web',
externals: [
nodeExternals(),
],
entry: [
path.join(process.cwd(), 'app/server.js'),
],
output: {
path: outputPath,
filename: 'server.js',
publicPath: '/',
libraryTarget: 'commonjs2',
},Webpack - Server side
new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV),
},
'__SERVER__': false,
'__CLIENT__': true,
}), new webpack.DefinePlugin({
'process.env': {
NODE_ENV: JSON.stringify(process.env.NODE_ENV),
},
'__CLIENT__': false,
'__SERVER__': true,
}),Webpack - Frontend side
So you could..
if (__SERVER__) {
//do server-specific code
}
if (__CLIENT__) {
//do client-specific code
//i.e. window.location = 'http://google.com'
}Problems and Optimizations
We have a problem with routing, when using /en, /pt and so on
App dispatches the redux actions on Backend and Frontend
The code deserves a refactoring
Currently hosted at https://github.com/cpBurn/redux-saga-ssr