Are all programming languages in English?
Michele Riva
Senior Software Architect @NearForm
Michele Riva
Senior Software Architect @NearForm
Google Developer Expert
Microsoft MVP
Creator of Lyra (lyrajs.io)

MicheleRivaCode

MicheleRivaCode

I'm a huge programming languages nerd

var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var evenNumbers = [];
for (var i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
var current = numbers[i]
if (current % 2 === 0) {
evenNumbers.push(current)
}
}
console.log(evenNumbers);const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const evenNumbers = numbers
.filter((number) => number % 2 === 0);
console.log(evenNumbers);Until ES5
Starting with ES6
MicheleRivaCode

Filter
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
var sum = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
sum += numbers[i];
}
console.log(sum);const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const sum = numbers
.reduce(
(acc, current) => acc + current,
0);
console.log(sum);Until ES5
Starting with ES6
MicheleRivaCode

Reduce
var numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
for (var i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
numbers[i] = numbers[i] * 2;
}
console.log(numbers);const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const multiplied = numbers
.map((number) => number * 2);
console.log(multiplied);Until ES5
Starting with ES6
MicheleRivaCode

Map
MicheleRivaCode

Why calling it .map?
MicheleRivaCode



MicheleRivaCode

"In mathematics, specifically category theory, a functor is a mapping between categories"
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functor
MicheleRivaCode

"In mathematics, specifically category theory, a functor is a mapping between categories"
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functor
MicheleRivaCode


MicheleRivaCode

Category theory can be helpful in understanding Haskell's type system. There exists a "Haskell category", of which the objects are Haskell types, and the morphisms from types a to b are Haskell functions of type a -> b.
MicheleRivaCode


Category theory can be helpful in understanding Haskell's type system. There exists a "Haskell category", of which the objects are Haskell types, and the morphisms from types a to b are Haskell functions of type a -> b.
MicheleRivaCode


"We can picture a map as collection of arrows that go from elements of one set to element of another set:"
https://markkarpov.com/post/category-theory-part-1.html
MicheleRivaCode

const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];const multiplied = [2, 4, 6, 8];const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const evenNumbers = numbers
.filter((number) => number % 2 === 0);
console.log(evenNumbers);MicheleRivaCode

Ok but where is category theory here?
MicheleRivaCode

MicheleRivaCode

Keywords and jargon can be a problem
MicheleRivaCode

Is there a programming language that doesn't use English-based keywords?
MicheleRivaCode

Let's go down the rabbit hole
MicheleRivaCode

A bit of history
MicheleRivaCode

Konrad Zuse

MicheleRivaCode

R1.1(V0[:sig]) => R0
R1.2(V0[:m x sig]) => R0
0 => i | m + 1 => j
[W [ i < j -> [ R1.1(V0[i: m x sig]) => R0 | i + 1 => i ] ] ]
END
R1.3() => R0
'H';'e';'l';'l';'o';',';' ','w';'o';'r';'l';'d';'!' => Z0[: m x sig] R1.2(Z0) => R0
ENDPlankalkül
MicheleRivaCode


Flow-Matic
1955 circa
MicheleRivaCode

Flow-Matic
(0) INPUT INVENTORY FILE-A PRICE FILE-B ; OUTPUT PRICED-INV FILE-C UNPRICED-INV
FILE-D ; HSP D .
(1) COMPARE PRODUCT-NO (A) WITH PRODUCT-NO (B) ; IF GREATER GO TO OPERATION 10 ;
IF EQUAL GO TO OPERATION 5 ; OTHERWISE GO TO OPERATION 2 .
(2) TRANSFER A TO D .
(3) WRITE-ITEM D .
(4) JUMP TO OPERATION 8 .
(5) TRANSFER A TO C .
(6) MOVE UNIT-PRICE (B) TO UNIT-PRICE (C) .
(7) WRITE-ITEM C .
(8) READ-ITEM A ; IF END OF DATA GO TO OPERATION 14 .
(9) JUMP TO OPERATION 1 .
(10) READ-ITEM B ; IF END OF DATA GO TO OPERATION 12 .
(11) JUMP TO OPERATION 1 .
(12) SET OPERATION 9 TO GO TO OPERATION 2 .
(13) JUMP TO OPERATION 2 .
(14) TEST PRODUCT-NO (B) AGAINST ; IF EQUAL GO TO OPERATION 16 ;
OTHERWISE GO TO OPERATION 15 .
(15) REWIND B .
(16) CLOSE-OUT FILES C ; D .
(17) STOP . (END)MicheleRivaCode


COBOL
1957 circa
MicheleRivaCode

COBOL
//COBUCLG JOB (001),'COBOL BASE TEST', 00010000
// CLASS=A,MSGCLASS=A,MSGLEVEL=(1,1) 00020000
//BASETEST EXEC COBUCLG 00030000
//COB.SYSIN DD * 00040000
00000* VALIDATION OF BASE COBOL INSTALL 00050000
01000 IDENTIFICATION DIVISION. 00060000
01100 PROGRAM-ID. 'HELLO'. 00070000
02000 ENVIRONMENT DIVISION. 00080000
02100 CONFIGURATION SECTION. 00090000
02110 SOURCE-COMPUTER. GNULINUX. 00100000
02120 OBJECT-COMPUTER. HERCULES. 00110000
02200 SPECIAL-NAMES. 00120000
02210 CONSOLE IS CONSL. 00130000
03000 DATA DIVISION. 00140000
04000 PROCEDURE DIVISION. 00150000
04100 00-MAIN. 00160000
04110 DISPLAY 'HELLO, WORLD' UPON CONSL. 00170000
04900 STOP RUN. 00180000
//LKED.SYSLIB DD DSNAME=SYS1.COBLIB,DISP=SHR 00190000
// DD DSNAME=SYS1.LINKLIB,DISP=SHR 00200000
//GO.SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=A 00210000
// 00220000MicheleRivaCode


Fortran
1957 circa
MicheleRivaCode

Fortran
program average
implicit none
real, dimension(:), allocatable :: points
integer :: number_of_points
real :: average_points, positive_average, negative_average
average_points = 0.0
positive_average = 0.0
negative_average = 0.0
write (*,*) "Input number of points to average:"
read (*,*) number_of_points
allocate (points(number_of_points))
write (*,*) "Enter the points to average:"
read (*,*) points
if (number_of_points > 0) average_points = sum(points) / number_of_points
if (count(points > 0.) > 0) positive_average = sum(points, points > 0.) / count(points > 0.)
if (count(points < 0.) > 0) negative_average = sum(points, points < 0.) / count(points < 0.)
write (*,'(a,g12.4)') 'Average = ', average_points
write (*,'(a,g12.4)') 'Average of positive points = ', positive_average
write (*,'(a,g12.4)') 'Average of negative points = ', negative_average
end program averageMicheleRivaCode


LISP
1958 circa
MicheleRivaCode

LISP
(defun qsort (L)
(cond
((null L) nil)
(t
(append
(qsort (list< (car L) (cdr L)))
(cons (car L) nil)
(qsort (list>= (car L) (cdr L)))))))
(defun list< (a b)
(cond
((or (null a) (null b)) nil)
((< a (car b)) (list< a (cdr b)))
(t (cons (car b) (list< a (cdr b))))))
(defun list>= (a b)
(cond
((or (null a) (null b)) nil)
((>= a (car b)) (list>= a (cdr b)))
(t (cons (car b) (list>= a (cdr b))))))MicheleRivaCode


ALGOL
1958 circa
MicheleRivaCode

Edsger Dijkstra
1972
Niklaus Wirth
1984
Peter Naur
2005



Turing awards
MicheleRivaCode

Algol
procedure Absmax(a) Size:(n, m) Result:(y) Subscripts:(i, k);
value n, m; array a; integer n, m, i, k; real y;
comment The absolute greatest element of the matrix a, of size n by m
is transferred to y, and the subscripts of this element to i and k;
begin integer p, q;
y := 0; i := k := 1;
for p:=1 step 1 until n do
for q:=1 step 1 until m do
if abs(a[p, q]) > y then
begin y := abs(a[p, q]);
i := p; k := q
end
end AbsmaxMicheleRivaCode

Other important languages
MicheleRivaCode

L←(Lι':')↓L←,L ⍝ drop To:
L←LJUST VTOM',',L ⍝ mat with one entry per row
S←¯1++/∧\L≠'(' ⍝ length of address
X←0⌈⌈/S
L←S⌽(−(⍴L)+0,X)↑L ⍝ align the (names)
A←((1↑⍴L),X)↑L ⍝ address
N←0 1↓DLTB(0,X)↓L ⍝ (names)
N←,'⍺',N
N[(N='_')/ι⍴N]←' ' ⍝ change _ to blank
N←0 ¯1↓RJUST VTOM N ⍝ names
S←+/∧\' '≠⌽N ⍝ length of last word in nameAPL
1962
MicheleRivaCode

Begin
Procedure RightText(T, N, FitsIn); Text T; Integer N;
Name FitsIn; Boolean FitsIn;
Begin
Integer I;
FitsIn := N >= T.Length;
For i:=1 step 1 until N-T.Length do OutText(" ");
OutText(T)
End of RightText;
RightText("Short", 30); OutImage;
RightText("And the long one", 30);
End of Program;Simula
1962
MicheleRivaCode

Max(Items, ValueFunction) = value of
§ (Best, BestVal) = (NIL, -∞)
while Items do §
(Item, Val) = (Head(Items), ValueFunction(Head(Items)))
if Val > BestVal then (Best, BestVal) := (Item, Val)
Items := Rest(Items) §⃒
result is Best §⃒CPL
1963
MicheleRivaCode

05 HOME : TEXT : REM Fibonacci numbers
10 LET MAX = 5000
20 LET X = 1 : LET Y = 1
30 IF (X > MAX) GOTO 100
40 PRINT X
50 X = X + Y
60 IF (Y > MAX) GOTO 100
70 PRINT Y
80 Y = X + Y
90 GOTO 30
100 ENDBASIC
1964
MicheleRivaCode

main() {
extrn putchar, n, v;
auto i, c, col, a;
i = col = 0;
while(i<n)
v[i++] = 1;
while(col<2*n) {
a = n+1;
c = i = 0;
while (i<n) {
c =+ v[i] *10;
v[i++] = c%a;
c =/ a--;
}
putchar(c+'0');
if(!(++col%5))
putchar(col%50?' ': '*n');
}
putchar('*n*n');
}
v[2000];
n 2000;B
1969
MicheleRivaCode

What makes these languages so important?
MicheleRivaCode

CPL + B =
The C programming language
1972
MicheleRivaCode

C influence
C
1972
C++
1985
Java
1995
C#
2000
MicheleRivaCode

Scheme
1975
Caml
1985
Racket
1995
Clojure
2007
ML
1973
LISP influence
MicheleRivaCode

Pascal
1985
Simula
1962
Delphi
1995
ALGOL influence
MicheleRivaCode

Non-american languages
MicheleRivaCode

Simula 🇳🇴
Ole-Johan Dahl
Kristen Nygaard


MicheleRivaCode

Pascal 🇨🇭
Niklaus Wirth

MicheleRivaCode

Python 🇳🇱

Guido Van Rossum
MicheleRivaCode

Ruby 🇯🇵

Yukihiro Matsumoto
MicheleRivaCode

Elixir 🇧🇷

José Valim
MicheleRivaCode

ML 🇫🇷




MicheleRivaCode

Online Historical Encyclopaedia of Programming Languages
8.900+ known programming languages
~2.500 🇺🇸
MicheleRivaCode

Online Historical Encyclopaedia of Programming Languages
8.900+ known programming languages
~2.500 🇺🇸
~600 🇬🇧
MicheleRivaCode

Online Historical Encyclopaedia of Programming Languages
8.900+ known programming languages
~2.500 🇺🇸
~600 🇬🇧
~160 🇨🇦
MicheleRivaCode

Online Historical Encyclopaedia of Programming Languages
8.900+ known programming languages
~2.500 🇺🇸
~600 🇬🇧
~160 🇨🇦
~75 🇦🇺
MicheleRivaCode

Symbolic programming languages
MicheleRivaCode

APL
'Hello, world'MicheleRivaCode

APL
(~R∊R∘.×R)/R←1↓ιRMicheleRivaCode

K
2_&{&/x!/:2_!x}'!RMicheleRivaCode

J
quicksort=: (($:@(<#[), (=#[), $:@(>#[)) ({~ ?@#)) ^: (1<#)MicheleRivaCode

Lambda Calculus
λf.(λx.(f(xx))λx.(f(xx)))MicheleRivaCode

Prolog
partition([], _, [], []).
partition([X|Xs], Pivot, Smalls, Bigs) :-
( X @< Pivot ->
Smalls = [X|Rest],
partition(Xs, Pivot, Rest, Bigs)
; Bigs = [X|Rest],
partition(Xs, Pivot, Smalls, Rest)
).
quicksort([]) --> [].
quicksort([X|Xs]) -->
{ partition(Xs, X, Smaller, Bigger) },
quicksort(Smaller), [X], quicksort(Bigger).MicheleRivaCode

Esoteric Programming Languages
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
+[-[<<[+[--->]-[<<<]]]>>>-]>-.---.>..>.<<<<-.<+.>>>>>.>.<<.<-.
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
> = increases memory pointer, or moves the pointer to the right 1 block.
< = decreases memory pointer, or moves the pointer to the left 1 block.
+ = increases value stored at the block pointed to by the memory pointer
- = decreases value stored at the block pointed to by the memory pointer
[ = like c while(cur_block_value != 0) loop.
] = if block currently pointed to's value is not zero, jump back to [
, = like c getchar(). input 1 character.
. = like c putchar(). print 1 character to the console0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: >
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: +
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: +
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: <
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: -
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: >
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: .
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Output: 2
MicheleRivaCode

Ok but I just wanted an "hello world" program
MicheleRivaCode

ASCII
A = 64
B = 65
C = 66
D = 67
a = 97
b = 98
c = 99
d = 100
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
++++++++++
+++++++
.MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
1
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
2
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
3
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
4
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
5
Command: +
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
5
Command: [
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
5
Command: >
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
5
Command: + (19 times)
0
19
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
5
Command: <
0
19
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
4
Command: -
0
19
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
4
Command: ]
0
19
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
[
>
+++ +++ +++
+++ +++ +++ +
< -
]MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
0
95
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: >
0
95
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: +
0
96
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: +
0
97
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
0
Command: .
0
97
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
Output: 97
MicheleRivaCode

Brainfuck
Brainfuck
+[-[<<[+[--->]-[<<<]]]>>>-]>-.---.>..>.<<<<-.<+.>>>>>.>.<<.<-.
MicheleRivaCode

MicheleRivaCode

Choon
AGb-A#A#+A+%A#DF-AC#MicheleRivaCode

Elang
"" .H .e .l .l .o ., ._ .w .o .r .l .d .! ()MicheleRivaCode

Integ
](104)](101)](108)](108)](111)](44)](32)](119)](111)](114)](108)](100)](10)MicheleRivaCode

Befunge
>>v
v1?2v
3
> > >: v
|-&<
$
>"!tcerroC">:v
|,<
@MicheleRivaCode

when would I typically use these languages?
MicheleRivaCode

Sort numbers in a ragged list
https://codegolf.stackexchange.com/questions/244101/sort-numbers-in-a-ragged-list
input: [[4, 7], [5, 3, [], [6, [2]]]
output: [[÷2, 3], [4, 5, [], [6, [7]]]]
FṢṁJelly
N`\d+Retina
1N→_a`\d+`?λ←_a1+→_a`\d+`?Ẏ⌊s←_a iS;øṙ
Vyxal
n=>n.replace(r=/\d+/g,_=>n.match(r).sort((a,b)=>a-b)[i++],i=0)
JavaScript
MicheleRivaCode

Non-textual programming languages
MicheleRivaCode

Piet

MicheleRivaCode

Piet

MicheleRivaCode

Piet Mondrian
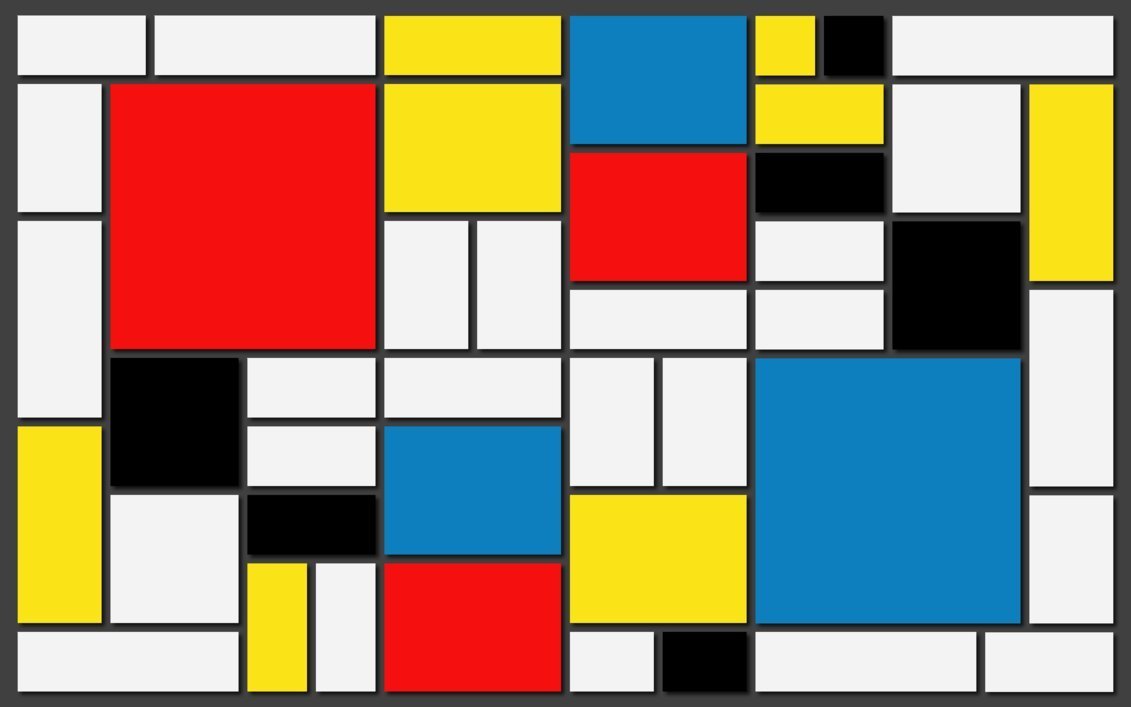
MicheleRivaCode

Whitespace
MicheleRivaCode

Whitespace
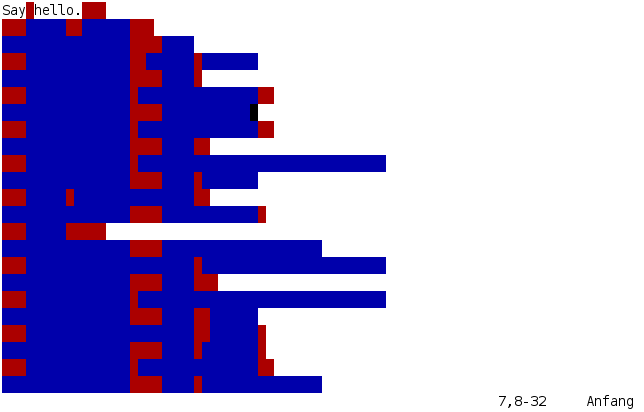
Tab
Space
MicheleRivaCode

Velato

MicheleRivaCode

Non-English-based programming languages
MicheleRivaCode

Teuton
# for ~ fuer
# in ~ im
# range ~ intervall
# print ~ drucke
fuer i im intervall(9)[::-1]:
drucke i
# while ~ solange
# True ~ Wahr
# try ~ versuche
# except ~ ausser;
# ZeroDivisionError ~ NullDivisionsFehler
# return ~ zurueck
solange Wahr:
versuche:
1/0
ausser NullDivisionsFehler:
zurueckMicheleRivaCode

Linotte
BonjourLeMonde:
début
affiche "Bonjour le monde!"MicheleRivaCode

SAKO
K) PROGRAM DRUKUJE NAPIS HELLO WORLD
LINIA
TEKST:
HELLO WORLD
KONIECSystem Automatycznego Kodowania Operacji
MicheleRivaCode

Rapira
ПРОЦ СТАРТ()
ВЫВОД: 'Привет, мир!'
КОН ПРОЦMicheleRivaCode

ひまわり
「Hello, World!」と、表示。 ’母艦(メインフォーム)に表示。
「Hello, World!」と、言う。 ’ダイアログボックスで表示。Himawari
MicheleRivaCode

قلب
(قول "مرحبا يا عالم")Qalb
MicheleRivaCode

易语言
公开 类 启动类
{
公开 静态 启动()
{
控制台.输出("你好,世界!");
}
}EPL (Easy Programming Language)
MicheleRivaCode

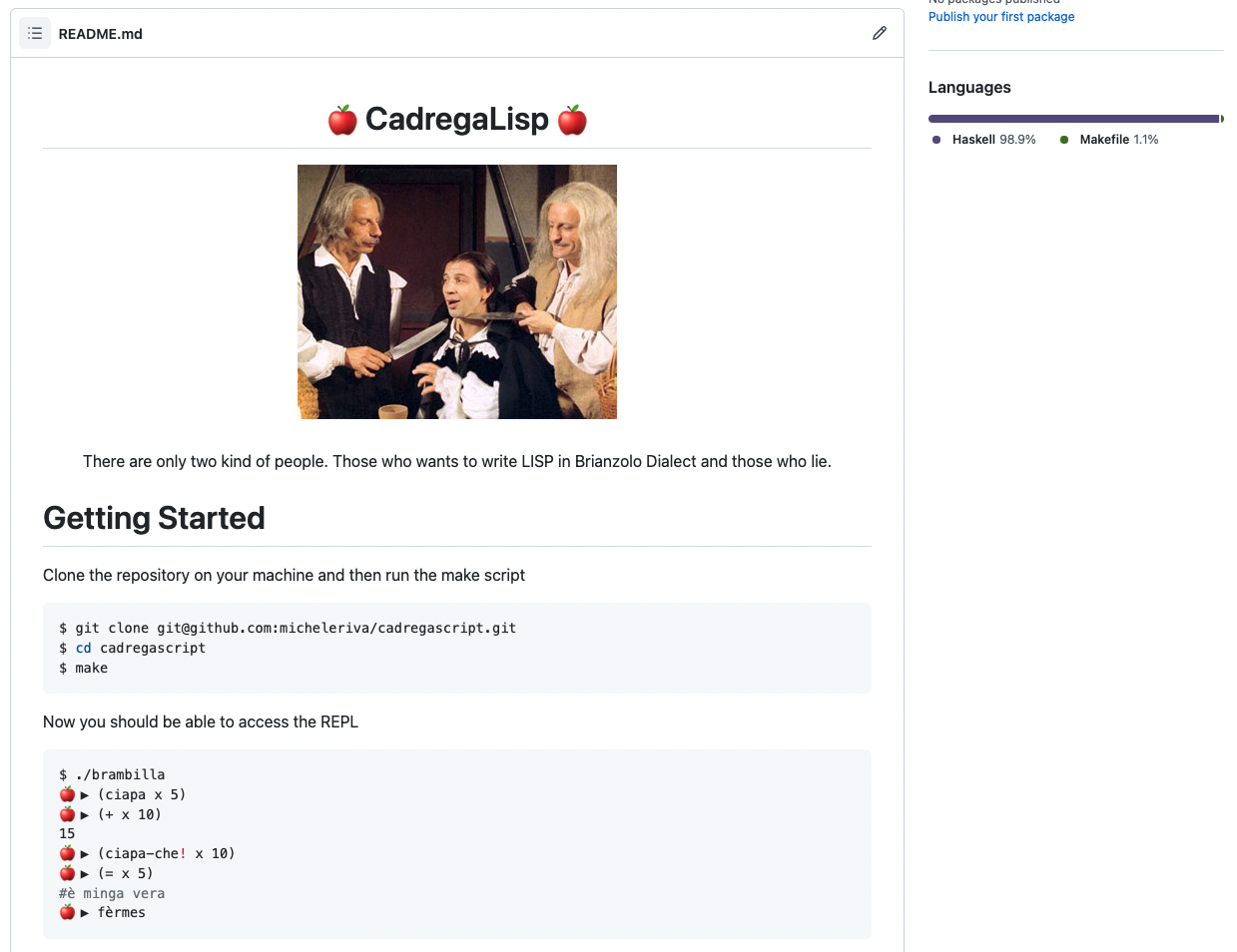
Bonus: CadregaLISP
$ ./brambilla
🍎 ▶ (ciapa x 5)
🍎 ▶ (+ x 10)
15
🍎 ▶ (ciapa-che! x 10)
🍎 ▶ (= x 5)
#è minga vera
🍎 ▶ fèrmeshttps://github.com/micheleriva/CadregaLisp
MicheleRivaCode

MicheleRivaCode

So, are all programming languages in English?
MicheleRivaCode

nope!
MicheleRivaCode


MicheleRivaCode

@MicheleRiva

@MicheleRivaCode

/in/MicheleRiva95

www.micheleriva.dev

