Functional Programming
What is it? Why should I care?
Disclaimer:

Not
If you have questions or need something repeated, please interrupt. I have been talking about these things for years and may gloss over something unintentionally.

You will see more from Professor Dijkstra
Motivation:
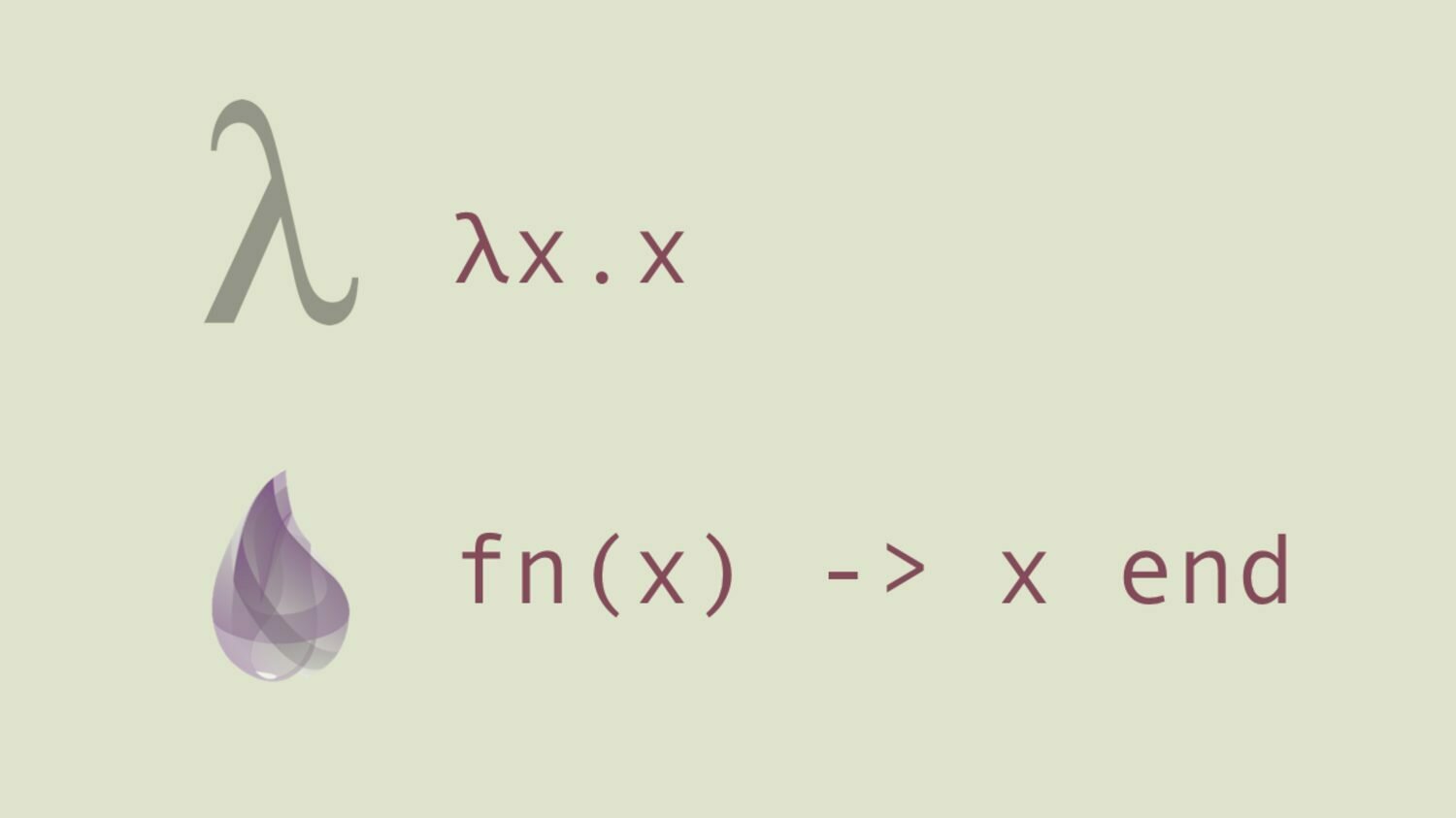
Alonzo Church:
What is it?
In computer science, functional programming is a programming paradigm where programs are constructed by applying and composing functions. It is a declarative programming paradigm in which function definitions are trees of expressions that map values to other values, rather than a sequence of imperative statements which update the running state of the program.
What is a value?
In computer science and computer programming, a data type (or simply type) is a collection or grouping of data values, usually specified by a set of possible values, a set of allowed operations on these values, and/or a representation of these values as machine types.
Integer
1
6471
193
-92
String
Integer
Bool
"Hello, World!"
True
False
What is a function?
Domain
Co-Domain
Every member of the Domain must map to a single member of the Co-domain. The inverse is not necessarily true.
Integer
Bool
f
Functional Purity

Yeah, but

What do we mean by "pure"?
- Output depends only on input
- Never mutate input
- Deterministic - same input returns same output
- Function signature defines the entire function
- No additional effects
- Referential Transparency
A Programmer's View of a Function
f(a) -> b
Type a
Type b
What about f(b) -> a?
Well, except...
f(a) -> b?
Type a
Type b
So what?
f(a) -> b
Type a
Type b
Type c
g(b) -> c
h(a) -> c
A composition "h" will exist for every valid function "f" and "g"
Imperative
1) Place a slice of bread on the plate
2) Spread a thin layer of peanut butter on top
3) Spread a thin layer of jelly on top
4) Cover with a slice of bread
Declarative
A peanut butter sandwich is a thin layer of peanut butter and jelly between two slices of bread.
Imperative
1) Find ML Price
2) Apply Override, if present
3) Apply ramp adjustment
4) Apply Upper Guardrail
5) Apply Lower Guardrail
6) Result is final price
Declarative
PF = M(GL,m(GU, (PML | ((PO V PML) * Ramp))))
A declarative definition implies one to many sets of imperative steps, but a series of imperative steps does not necessarily imply a definition
Imperative
= means "assign"
int i = 5
1) Create an integer shaped allocation on the stack
2) Put the value 5 in there (for now)
Declarative
= means "is"
int i = 5
"i" is the member of the set of integers identified by 5
Can everything be a pure function?
No:
1) IO has to be ordered
2) Current date must be obtained
3) Random numbers are sometimes necessary
4) Exceptional situations occur when 1,2 or 3 fails
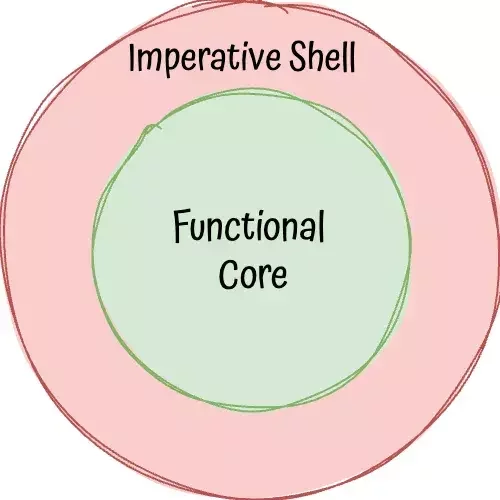
The key is to separate the two - everything that can be pure, should be (all logical branching). Other stuff needs to be imperative (no logical branching)
We call this...