Building and Deploying Apps with Docker!

12:30 pm - 2:30 pm 6th July, 2024


Hi, I am Milind
- 8+ years in building large scale ecommerce.
- Checkout, Payments, Promotions & Integrations
- Java/Spring, PHP and JavaScript/Node.js
- commercetools, Magento/Adobe Commerce, Shopify and Hybris/SAP Commerce.
Operating System
- an interface between user and hardware
- manages resources like memory, cpu, files and devices
- networking, security and process management




Linux
- Linux® is an open source operating system (OS).
- Kernel: The base component of the OS.
- System user space: The administrative layer for system-level tasks like configuration and software install. shell, daemons, processes and the desktop environment.
- Applications: Apps include everything from desktop tools and programming languages to multiuser business suites.
Linux Kernel

Linux Container
Namespace
Control Group
A Linux® container is a set of 1 or more processes that are isolated from the rest of the system.
Linux kernel feature that partition kernel resources such that one set of processes sees one set of resources, while another set of processes sees a different set of resources.
It allows you to allocate resources such as CPU time, system memory, network bandwidth, etc, so that an activity per service instance can be ran and constrained by cgroups on the system.
Exercise 1
# CLI to List system namespaces.
lsns --help
# list all ns
lsnsVirtualization vs Containers
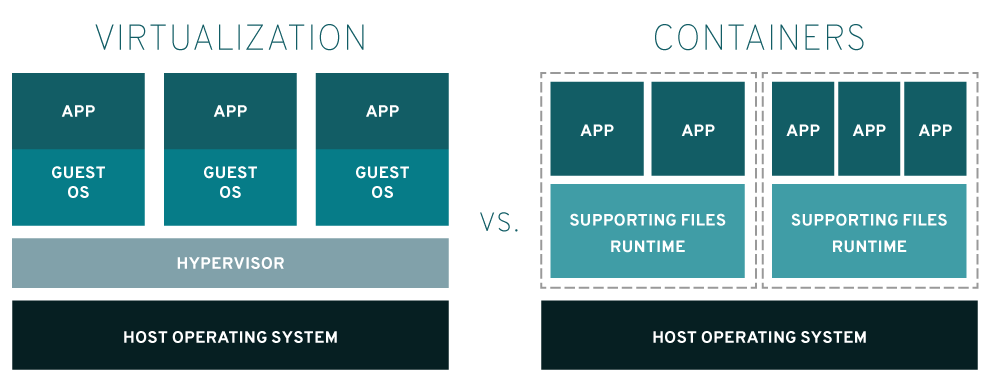
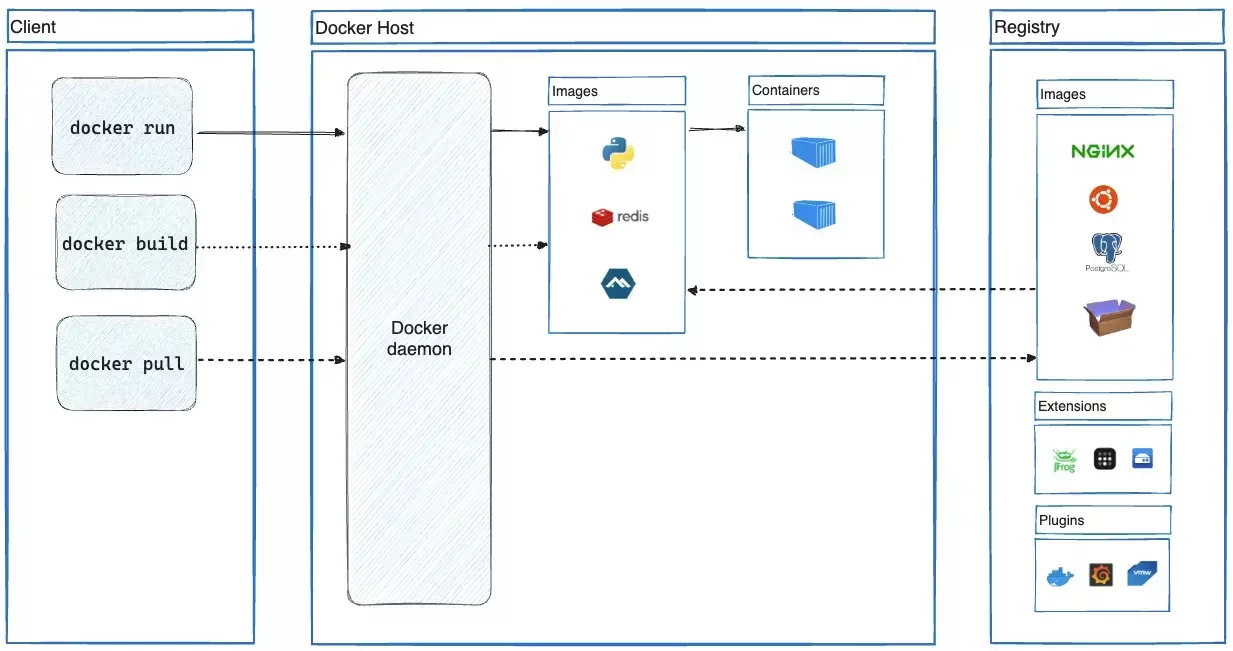
Docker
Docker is an open platform for developing, shipping, and running containerized applications.
Why Docker ?
- Solves the “works on my machine” problem.
- Rapid CI/CD
- Easy Auto Scaling. GCP Cloud Run, Azure Functions, AWS ECS
Installing Docker
# 1. Set up Docker's apt repository.
# Add Docker's official GPG key:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# Add the repository to Apt sources:
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
# 2. Install the Docker packages.
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
# Docker Service Start
sudo service docker start
# Verify that the Docker Engine installation is successful by running the hello-world image.
sudo docker run hello-world
WSL 2
Exercise 2: Running a Docker Container
# download an docker image, eg nginx
docker pull nginx
# run image, use -d to run in background
docker run --name exercise2 -p 8080:80 nginx
# check in browser
http://localhost:8080/
# check docker running process
docker ps
# stop
docker stop exercise2
# restart
docker start exercise2
# check logs
docker logs exercise2
# Get PID for docker container
docker inspect --format '{{.State.Pid}}' exercise2
# List docker container ns
sudo ls -la /proc/7059/nsBuilding a Docker Container: Dockerfile
A Dockerfile is a text document that contains all the commands a user could call on the command line to assemble an image.
ADD Add local or remote files and directories.
ARG Use build-time variables.
CMD Specify default commands.
COPY Copy files and directories.
ENTRYPOINT Specify default executable.
ENV Set environment variables.
EXPOSE Describe which ports your application is listening on.
FROM Create a new build stage from a base image.
HEALTHCHECK Check a container's health on startup.
LABEL Add metadata to an image.
MAINTAINER Specify the author of an image.
ONBUILD Specify instructions for when the image is used in a build.
RUN Execute build commands.
SHELL Set the default shell of an image.
STOPSIGNAL Specify the system call signal for exiting a container.
USER Set user and group ID.
VOLUME Create volume mounts.
WORKDIR Change working directory.Exercise 3: Dockerize a Node.js API
# Build a docker container
docker build -t node-api --no-cache .
# Run a docker container
docker run -p 3000:3000 node-api
# Remove image
docker rmi node-api --force
# Clear cache!
docker system prune -a
# Dockerfile
FROM node:22-alpine
RUN mkdir -p /home/node/app/node_modules && chown -R node:node /home/node/app
WORKDIR /home/node/app
COPY package*.json ./
USER node
RUN npm install
COPY --chown=node:node . .
EXPOSE 3000
ENTRYPOINT [ "node", "index.js" ]Exercise 4: Storing a Container Image
- Register at Google Cloud and Setup Billing.
- Create 'Artifact Registry' repository.
- Setup Google Cloud CLI on Local.
- Run below commands to push an image
gcloud config set project milindsingh
gcloud auth login
gcloud auth configure-docker asia-south2-docker.pkg.dev
docker build -t asia-south2-docker.pkg.dev/milindsingh/docker-meetup/node-api:2024.07.06.1 .
docker push asia-south2-docker.pkg.dev/milindsingh/docker-meetup/node-api:2024.07.06.1Exercise 5: Deploying Containerized App on Google Cloud
- Register on Google Cloud and Setup Billing.
- Create new service in 'Cloud Run'
- Choose container created in previous exercise.
- Select region and set port as 3000.
- Create and test url.
Docker Compose
Docker Compose is a tool for defining and running multi-container applications.
# compose.yaml
services:
nginx:
image: "nginx"
ports:
- "80:80"
node:
image: "node"
redis:
image: "redis:alpine"Exercise 5: Running multiple containers
References
- https://www.javatpoint.com/operating-system
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/linux/what-is-linux
- https://github.com/torvalds/linux
- https://www.redhat.com/en/topics/containers/whats-a-linux-container
- https://hub.docker.com/_/nginx
- https://docs.docker.com/get-started/overview/
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/
- https://www.tutorialspoint.com/docker-container-network-namespace-is-invisible
- https://github.com/nginxinc/docker-nginx/blob/master/stable/debian/Dockerfile
- https://docs.docker.com/reference/dockerfile/
- https://docs.docker.com/compose/gettingstarted/
- https://github.com/vercel/next.js/blob/canary/examples/with-docker/Dockerfile