DYNAMIC COMPRESSOR (CENTRIFUGAL COMPRESSOR)
Mya, Fazlein, Ben, Adib, Ainul, Farouk
OPERATING PRINCIPLE

Gas enters the suction port and travel to discharge port.
Gas velocity is accelerated through the diffuser assembly and into the circular volute.
Kinetic energy is converted into pressure as gas speed slows in discharge port.
1.
2.
3.
What is Dynamic Compressor?
A type of compressor that delivers larger volumes of air at lower pressures. Common types of dynamic compressors include centrifugal and axial compressors.
Centrifugal Compressor
A type of dynamic compressor that compresses air and expels it with a centrifugal force from a rotating wheel with radial vanes. Centrifugal compressors are often used for fans and cooling units.
Axial Compressor
A type of dynamic compressor in which gas flows parallel to the rotation of the axis.
Single Stage
- compressed the gas once
- designed for high gas f/rates and low discharge pressure
- the impeller is located at the nondrive end of the shaft (outboard of the nondrive end radial bearing)
Multistage
- compressed the gas several times
- designed for high gas f/rates and high discharge pressure
- The impellers may be mounted on the same shaft or on different shafts.


Basic Component
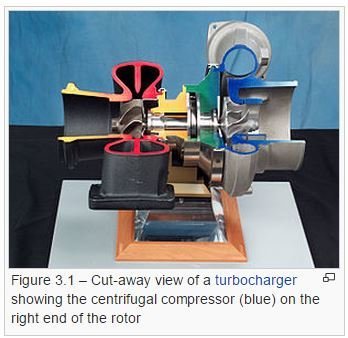
Basic component
1) Inlet
- It may include features such as a valve, stationary vanes/airfoils (used to help swirl the flow) and both pressure and temperature instrumentation
2) Centrifugal impeller
- Impeller's rotating set of vanes (or blades) that gradually raises the energy of the working gas
3) Diffuser
- Downstream of the impeller in the flow path, it is the diffuser's responsibility to convert the kinetic energy (high velocity) of the gas into pressure by gradually slowing (diffusing) the gas velocity.
4) Collector
- A collector’s purpose is to gather the flow from the diffuser discharge annulus and deliver this flow to a downstream pipe.
COMMON PROBLEMS
(and troubleshooting)

PROS
-
High reliability, eliminating the need for multiple compressors and installed standby capacity.
-
Machine prices lower.
-
Less plot area of installation.
-
Small and light weight.
-
Low maintenance cost.
-
No lube oil contamination of process gas.
-
Absence of any pressure pulsation above surge point.
CONS
-
Lower efficiency than most positive displacement types.
-
Due to recycle not efficient below the surge point.
-
Very sensitive to changes in gas properties, especially molecular weight.
-
Not effective for low molecular weight gases. The pressure ratio capability per stage is low, tending to require a large number of machine stages, hence mechanical complexity.