Arrays and
ArrayList

Like, what's an Array?
An array is an object
which holds 0 or more
objects or primitives
- An array of primitives holds the primitives themselves
- An array of objects holds references
- The objects themselves are still on the heap
Array storage
- The contents of an array are stored in a contiguous block of memory
- All the items in the array are the same size
- Just like string characters, array items are numbered (indexed) starting from 0
- Arrays offer fast random access - Java always knows exactly where each item is in memory
- (item index * sizeof(item)) bytes from the start
From FlatLand to Tesseracts
and beyond
-
Arrays can have more than one dimension
- An array is an object, so this is just an array of arrays
- Each array after the first level can be a different length
- Each individual array is in contiguous memory, but the total multi-dimensional array isn't
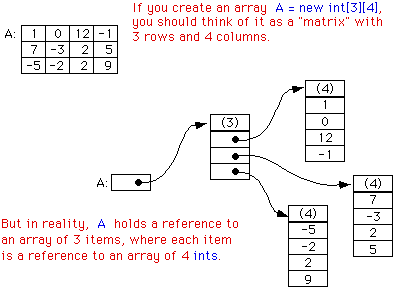
An array in memory
The magic of life
Creating an array involves three steps:
- Declaring it
- Allocating it
- Initializing the elements
Declaring an array
Brackets can be either in the middle or at the end:
int[] intArray; //single-dimensional array of intsint intArray[]; //also a 1D array of ints
To declare a multi-dim array, use multiple sets of brackets:
int[][] intArray; //two-dimensional array of intsDouble doubleArray[][][]; //3D array of Double objects
Arrays can hold any type
Really anything:
- Primitives
- Interfaces
- Abstract classes
- Concrete classes
Array allocation
Declaration doesn't allocate memory - we have to do this separately.
int ints[]; // declarationints = new int[5]; // allocation
A multi-dimensional array can be allocated all at once.
double[][] coords; // declarationcoords = new double[3][4]; // allocation
Size doesn't have to be a constant.
Random r = new Random();int[] whoKnowsHowManyInts = new int[r.nextInt()];
More allocation
You can have 0-sized arrays:
int[] noInts = new int[0];Multi-dimension arrays can be allocated in multiple steps:
// leave one or more sizes off at the endint[][][] threeDInt = new int[3][][];// allocate from the left to the rightfor(int i = 0; i < threeDInt.length; i++) {threeDInt[i] = new int[i + 1][];for(int j = 0; j < threeDInt[i].length; j++) {threeDInt[i][j] = new int[2 + j];}}
Things you definitely can't do
Put the size in the declaration:
int[5] fiveInts; // compilation errordouble[4] fourDoubles = new double[4]; // compilation error
Allocate an array with a fractional size:
int[] twoAndAHalfInts = new int[2.5]; // compilation errorAllocate a negative-sized array:
int[] negArray = new int[-1]; // runtime errorLeave sizes off the middle of a multi-dim allocation:
int[][] twoDArray = new int[][3]; // compile errorint[][][] threeDArray = new int[2][][3]; // compile error
Are you really a nihilist?
After allocation, array elements hold the default value of the appropriate type (e.g., 0 for int, false for boolean, null for objects)
If you want something else, you'll need to put it there yourself.
You can init with a loop:
int[] ints = new int[3];for(int i = 0; i < ints.length; i++) {ints[i] = i * 10;}
You can init with a snoop:
String[] snoops = new String[2];snoops[0] = "dog";snoops[1] = "lion"
You can new things from thin air:
Set<String>[] sets = new Set[2];
sets[0] = new TreeSet<String>();
sets[1] = new HashSet<String>();
You can store things anywhere:
int[] bunchOfInts = new int[100];bunchOfInts[36] = 92;bunchOfInts[84] = 6;bunchOfInts[2] = 83765;
All together now
We can declare, allocation, and initialize all at once.
int intArray[] = {0, 1};
String[] strArray = {"Summer", "Winter"};
int multiArray[][] = { {0, 1}, {3, 4, 5} };The new is optional. These are the same:
int intArray2[] = new int[]{0, 1};
String[] strArray2 = new String[]{"Summer", "Winter"};
int multiArray2[][] = new int[][]{ {0, 1}, {3, 4, 5}};The compiler infers the size in this case. You can't specify it yourself.
// these don't compile
int intArray2[] = new int[2]{0, 1};
String[] strArray2 = new String[2]{"Summer", "Winter"};
int multiArray2[][] = new int[2][]{ {0, 1}, {3, 4, 5}};
However...
You can use in-place initialization, but specify null to skip initializing some parts.
int[][][] arr = {{null}, null, {{3, 4, 5}}};
Getting things back out
Simple: just put the index in brackets.
int i = someInts[1];Object o = strings[3];
Accessing an invalid index is a run-time error:
int arNeg = ar[-1]; // throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
int arPartEnd = ar[10]; // throws if the size is less than 11
But using a non-int index is a compile error:
int fracIndex = intArray[2.4]; // doesn't compile
Looping
All arrays have a length property (not method):
int[] arr = somethingWhichAllocatesArray();for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {System.out.println(arr[i]);if(i == arr.length / 2) {System.out.println("Half-way");}}
You can also use the new enhanced for loop:
int[] arr = somethingWhichAllocatesArray();for(int arrItem : arr) {System.out.println(arrItem);// no way of getting the position in here, only the value}
Quick Check (p204)
Line1> String multiStrArr[][] = new String[][] {
Line2> {"A", "B"},
Line3> null,
Line4> {"Jan", "Feb", null},
Line5> };
Which of the following individual options are true for the previous code?
- a. Code on line 4 is the same as {"Jan", "Feb", null, null},
- b. No value is stored at multiStrArr[2][2]
- c. No value is stored at multiStrArr[1][1]
- d. Array multiStrArr is asymmetric.
Answers
- a. False. Line 4 creates an array of length 3. This code creates an array of length 4.
- b. False. multiStrArr[2][2] holds the value null.
- c. True. There is no value at multiStrArr[1][1].
- d. True.
- multiStrArr[0].length == 2
- multiStrArr[1].length == 1
- multiStrArr[2].length == 3
Array Types - Interface
If the array type is an interface, you can store null or anything that implements that interface:
interface MyInterface {}
class MyClass1 implements MyInterface {}
class MyClass2 implements MyInterface {}
class Test {
MyInterface[] interfaceArray = new MyInterface[]
{
new MyClass1(),
null,
new MyClass2()
};
}
Array Types - Abstract Class
If the array type is an abstract class, you can store null or instances of concrete classes which extend that abstract class.
abstract class Vehicle{}
class Car extends Vehicle {}
class Bus extends Vehicle {}
class Test {
Vehicle[] vehicleArray = {
new Car(),
new Bus(),
null
};
}You can't instantiate an abstract class, which is why you can't store instances of it!
Array Types - Object[]
If the array type is Object, you can store null or any non-primitive type.
interface MyInterface {} class MyClass1 implements MyInterface {} abstract class Vehicle{} class Car extends Vehicle {}class Test { Object[] objArray = new Object[] { new MyClass1(), null, new Car(), new java.util.Date(), new String("name"), 3, // this gets autoboxed into an Integer new Integer [7] // arrays are objects, too! }; }
Members of Arrays
There's not much:
- length
- public member variable, number of items in the array
- clone()
- public method, overrides Object.clone()
- makes a shallow copy of the array
- All the normal methods inherited from Object
ArrayList Stands Alone
-
On the Java I test, that is - all the other Collection classes are reserved for the Java II test
- A reasonable choice - it's almost certainly the most widely used of the Collection classes
Why use ArrayList?
- Resizeable
- No need to specify initial size
- Can expand or shrink as needed
- Implements the List interface and, by extension, Collection
- You can iterate over it with an Iterator/ListIterator
- Supports generics
Other trivial things
- Allows null values to be added to it
- Allows duplicate values
- Maintains insertion order
Getting your hands on one
Pretty simple:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CreateArrayList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<String>();
}
}Or, in Java 7, you can let Java figure out the type on the right side:
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CreateArrayList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<>();
}
}Behind the scenes
ArrayList actually stores your items in an Object[] array!
private transient Object[] elementData;
So why add the overhead of an ArrayList class?
- ArrayList provides the illusion of a resizeable array.
Adding Elements
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class AddToArrayList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// add at the end
list.add("one"); // {"one"}
list.add("two"); // {"one", "two"}
list.add("four"); // {"one", "two", "four"}
// add at the specified position, shifting anything there over
list.add(2, "three"); // {"one", "two", "three", "four"}
}
}
Behind the scenes
- Initial capacity is 10
- There's an optimization for empty ArrayLists, which may have been added after the book was written
- Capacity is set to 10 when the first item is added
- If you add an item which fits in the current capacity, it is placed into the internal array
- If you add an item which doesn't fit, Java creates a new, larger, array, and copies the data over
Accessing ArrayList Items
Most basic method:
- get(int index)
Throws IndexOutOfBoundsException if you pass a bad index.
Iterating over ArrayList
The enhanced for loop makes it easy.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class AccessArrayList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<>();
myArrList.add("One");
myArrList.add("Two");
myArrList.add("Four");
myArrList.add(2, "Three");
for (String element : myArrList) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}
Manually Iterating
You can use Iterator or ListIterator (which provides bidirectional traversal).
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.ListIterator;
public class AccessArrayListUsingListIterator {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<String>();
myArrList.add("One");
myArrList.add("Two");
myArrList.add("Four");
myArrList.add(2, "Three");
ListIterator<String> iterator = myArrList.listIterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
}
}
Using an iterator also allows you to remove items from the ArrayList.
Replacing ArrayList Items
Just like an array, you can set a value at a given index.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class ReplaceElementInArrayList {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<String>();
myArrList.add("One");
myArrList.add("Two");
myArrList.add("Three");
myArrList.set(1, "One and Half");
for (String element : myArrList) {
System.out.println(element);
}
}
}set() will throw IndexOutOfBoundsException if you pass an invalid index
Modifying items stored in ArrayList
One way of modifying items is to call methods on them from inside a for loop.
import java.util.ArrayList; public class ModifyArrayListWithStringBuilder { public static void main(String args[]) { ArrayList<StringBuilder> myArrList = new ArrayList<StringBuilder>(); myArrList.add(new StringBuilder("One")); myArrList.add(new StringBuilder("Two")); myArrList.add(new StringBuilder("Three")); for (StringBuilder element : myArrList) { element.append(element.length()); }for (StringBuilder element : myArrList) { System.out.println(element); } } }
Deleting ArrayList Items
ArrayList methods:
- remove(int index)
- Removes the item at the given index, shifting any items after it to the left
- remove(Object o)
- Finds the given object, if it is in the array, and removes it, shifting as above. Uses .equals() to do the checking.
- Returns true if the item was found and removed, or false if it wasn't found.
The million-dollar question
What if you have an ArrayList<Integer> ???
Adding multiple items
Add the contents of another Collection, either at the end or at a given index:
- addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)
- addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)
Remember, this is just copying references! Your ArrayList will point to the same objects as the Collection you're copying from.
Quick Check (p 206)
What is the output of the following code?
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<String>(); String one = "One"; String two = new String("Two"); myArrList.add(one); myArrList.add(two);ArrayList<String> yourArrList = myArrList; one.replace("O", "B");for (String val : myArrList) { System.out.print(val + ":"); } for (String val : yourArrList) { System.out.print(val + ":"); }
- a. One:Two:One:Two:
- b. Bne:Two:Bne:Two:
- c. One:Two:Bne:Two:
- d. Bne:Two:One:Two:
Answer
a. One:Two:One:Two:
The two ArrayLists, myArrList and yourArrList, are references to the same ArrayList in memory and hence, the same Strings.
Since Strings are immutable, and the return value of one.replace("O", "B"); isn't assigned to anything, the ArrayList values will be {"One", "Two"}
Clearing ArrayLists
You can delete all the items in the ArrayList with .clear().
This will null out all the references in the ArrayList and set its size to 0.
I'm not sure if it's guaranteed to maintain the same capacity as it did before calling clear(), but the Oracle JVM does.
Accessing Individual items
Some ArrayList methods related to accessing items:
- get(int index)
- returns the element at the given index
- size()
- Returns the number of items in the ArrayList (like array.length)
- indexOf(Object o)
- Returns the index of the first occurance of o, or -1 if none
- lastIndexOf(Object o)
- Returns the index of the last occurance of o, or -1 if none
indexOf/lastIndexOf search by looping through the ArrayList and checking with equals()
Cloning an ArrayList
.clone() makes a shallow copy of the ArrayList. It returns Object, so you have to cast.
ArrayList<StringBuilder> myArrList = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("Jan");
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder("Feb");
myArrList.add(sb1);
myArrList.add(sb2);
ArrayList<StringBuilder> clonedArrList = (ArrayList<StringBuilder>)myArrList.clone();
System.out.println(clonedArrList == myArrList); // false
System.out.println(clonedArrList.equals(myArrList)); // true
System.out.println(sb1 == clonedArrList.get(0)); // true, same ref
System.out.println(sb2 == clonedArrList.get(1)); // true, same ref
Copying ArrayLists
We can also use the constructor which takes a Collection.
ArrayList<StringBuilder> myArrList = new ArrayList<>();
StringBuilder sb1 = new StringBuilder("Jan");
StringBuilder sb2 = new StringBuilder("Feb");
myArrList.add(sb1);
myArrList.add(sb2);
ArrayList<StringBuilder> clonedArrList = new ArrayList<>(myArrList);
System.out.println(clonedArrList == myArrList); // false
System.out.println(clonedArrList.equals(myArrList)); // true
System.out.println(sb1 == clonedArrList.get(0)); // true, same ref
System.out.println(sb1 == clonedArrList.get(0)); // true, same refOr even create an empty ArrayList and use addAll.
ArrayList<StringBuilder> clonedArrList = new ArrayList<>();
clonedArrList.addAll(myArrList);
ArrayList --> Array
You can convert an ArrayList to an array with the .toArray() method.
ArrayList<String> myArrList = new ArrayList<>();
myArrList.add("Hi");
myArrList.add("Dudes");
String[] myArr = (String[]) myArrList.toArray();
toArray() returns an Object[], so you have to cast.
Note that this is a shallow copy of the data - so new array, but same Object references inside it.