Average, Median and Proportion
Tall
- Machine readable
- Repeats one or more categorical/discrete keys
- 1 record = multiple rows
- Often easier to do calculations
Wide
- Human readable
- Minimal repetition
- 1 record = 1 row
- Often corresponds to historical format
Nominal, Textual, Qualitative or Dimensional
- Textual
- Usually categorical
- Usually mutually exclusive
- Can't be quantified
- Can have a controlled vocabulary
- Can't usually be ordered
- Fruit boxes, marriage status, item type, hair color
Ordinal, Numeric, Quantitative or Measurable
- Numeric
- Usually can be counted or measured
- Can't have a controlled vocabulary
- Orderable
Discrete Measure
- Limited number of possible values
- Whole, non-divisible items
- Countable but not measurable
- Usually orderable
- Dates (1808 vs 1809)
- Counts of items (5 children, 4 beavers, 3 skittles, 1 keg)
- Can find a median, average, and sum
Continuous Measure
- Numeric
- Infinite number of possible values
- Can't have a controlled vocabulary
- Always orderable
- Weight, financial cost, distance, time
- Can find a median or average but can't find a sum (average weight of people in class vs total weight of people in class)
US States with lowest number of motor vehicle crash deaths, 2018
Absolute numbers
US States with lowest number of motor vehicle crash deaths per population, 2018
Proportionate to Population
US States with lowest number of motor vehicle crash deaths per miles traveled, 2018
Proportionate to Population and Miles Traveled

Non-Proportionate numbers are misleading!
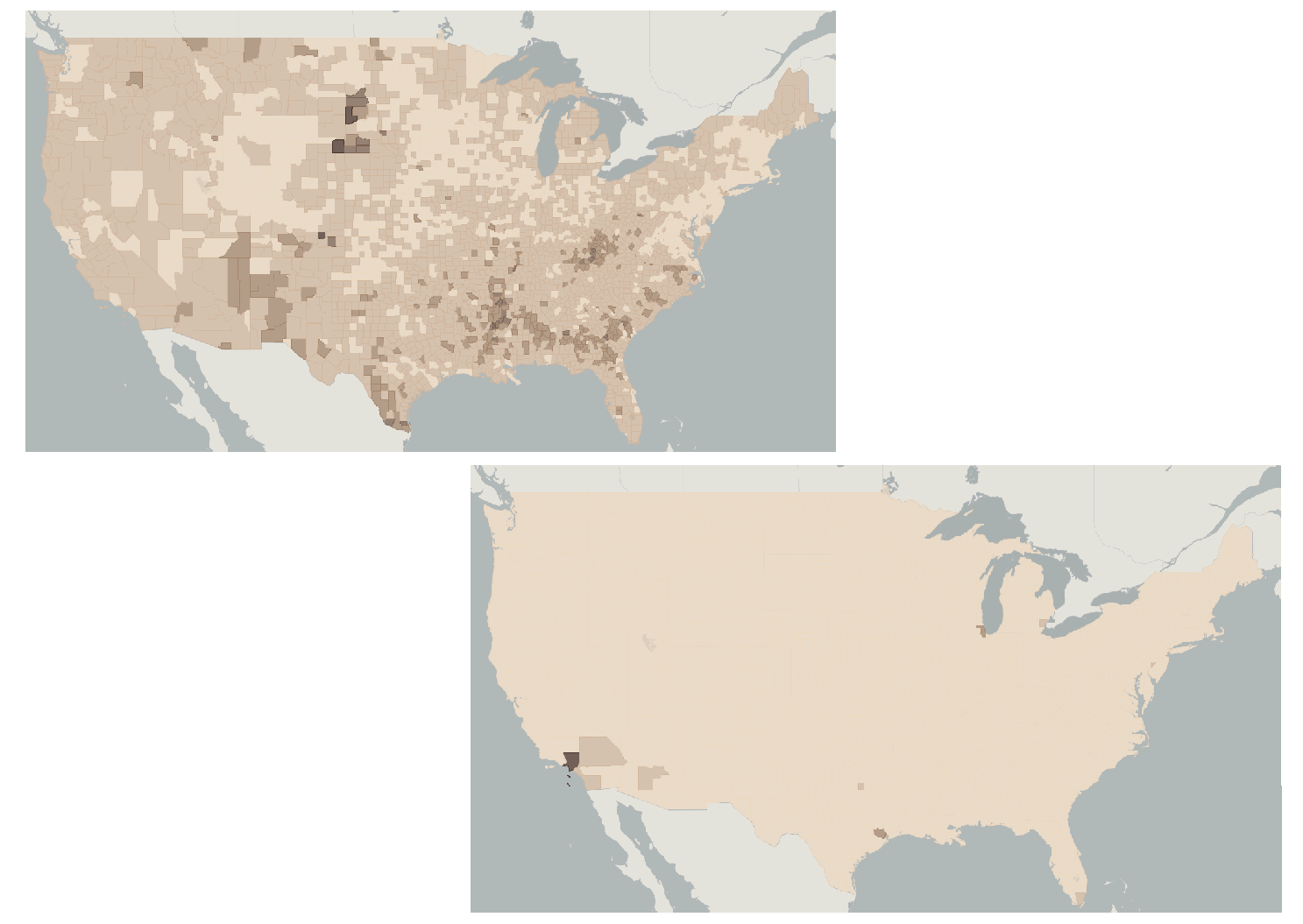
Individuals below poverty line by percent of county population vs absolute numbers
