CSS (FUN)damentals

CSS Fundamentals
What is CSS?
CSS controls the style of the HTML content. It allows you to change the colors, layouts, fonts and much more.
Separate CSS file is referred to as a style sheet.

CSS Fundamentals
Basic CSS Example
body{
background: blue;
color: white;
font-size: 35px;
}
CSS Fundamentals
Basic CSS Example
/* "body" is a selector */
body{
/* "background" is a property name */
/* "blue" is a value */
background: blue;
}
CSS Fundamentals
body => Selector
background => Property
blue => Value
Selector, Property, Value

CSS Fundamentals
Option 1: Including <style> tags in the <head> of the HTML file
How do I include CSS in my page?
<head>
<style>
body{
background: black;
color: white;
}
</style>
</head>
CSS Fundamentals
How do I include CSS in my page?
OPTION 2: Use inline-styling to directly style an element in your HTML
<body style="background:blue; color:white;">
Everything inside your body.
</body>
CSS Fundamentals
How do I include CSS in my page?
OPTION 3: Use an external stylesheet and include it in the HEAD of your document
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
</head>*IMPORTANT*
href is url where the stylesheet lives relative to your index.html

CSS Fundamentals
The Box Model
In a document, each element is represented as a rectangular box. Determining the size, properties — like its color, background, borders aspect — and the position of these boxes is the goal of the rendering engine.

CSS Fundamentals
The Box Model
In CSS, each of these rectangular boxes is described using the standard box model. This model describes the content of the space taken by an element. Each box has four edges: the margin edge, border edge, padding edge, and content edge.

CSS Fundamentals
The Box Model

CSS Fundamentals
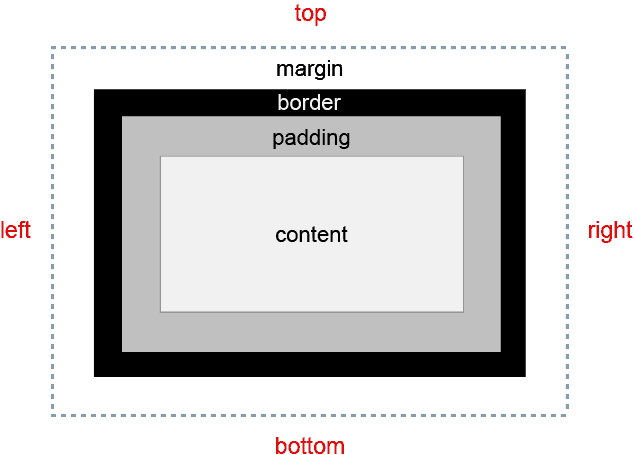
Content Area
The content area is the area containing the real content of the element
CSS properties width, min-width, max-width, height, min-height and max-height control the content size.

CSS Fundamentals
Padding Area
The padding area extends the content area with the empty area between the content and the eventual borders surrounding it
The space between the padding and the content edge can be controlled using the padding-top, padding-right, padding-bottom,padding-left and the shorthand padding CSS properties.

CSS Fundamentals
CSS Shorthand
padding-top: 10px;
padding-right: 15px;
padding-bottom: 12px;
padding-left: 17px;
padding: 10px 15px 12px 17px;
padding: 10px 15px;
padding: 10px; Border
The border area extends the padding area with the area containing the borders
p {
border-style: solid;
border-width: 5px;
border-color: #98bf21;
border-radius: 10%;
border-color: yellow;
}
CSS Fundamentals
Margin Area
The margin area extends the border area with an empty area used to separate the element from its neighbors
div {
margin: 20px 0px;
}
CSS Fundamentals
ID VS Class
ID's: Should be unique
Classes: Can be applied to many things
#idNAME {
/* apply your styling */
}
.classNAME{
/* apply your styling; */
}
CSS Fundamentals
How do I include classes and id's in my HTML?
<div id="one" class="cube">1 - ONE</div>
<div id="two" class="cube">2 - TWO</div>
CSS Fundamentals
Pseudo - Classes
A CSS pseudo-class is a keyword added to selectors that specifies a special state of the element to be selected.
Example :hover will apply a style when the user hovers over the element specified by the selector.

CSS Fundamentals
Pseudo - Classes
#one:hover{
background: purple;
color: yellow;
font-size: 24px;
}
CSS Fundamentals
Pseudo - Classes
- :focus
- :hover
- :first-child
- :visited
Common Pseudo Classes

CSS Fundamentals
Hex Values
#000000 is black, the starting point.
#ff0000 stands for the brightest red.
#00ff00 stands for the brightest green.
#0000ff stands for the brightest blue.
#ffffff ???

CSS Fundamentals
CSS Properties
div {
color: #006600;
border: 5px dashed blue;
margin: 10px;
padding: 1px;
height: 250px;
width: 250px;
}
CSS Fundamentals
Fonts
div {
font-family: "font name", back-up font;
}

CSS Fundamentals
Background Images
CSS
body {
background-image: url("paper.gif");
background-size: cover;
}
CSS Fundamentals
CSS Properties
Box - Shadow
box-shadow: 10px 5px 5px black;
CSS Fundamentals
CSS Properties
Position
position: relative | fixed | absolute | static;
CSS Fundamentals
static: default, cannot set top/bottom/left/right properties
fixed: element is relative to the browser window, will not move if window is scrolled
relative: relative to normal position in HTML flow. Often used to contain absolute elements
absolute: relative to the first parent element that's not static
CSS Properties
z-index
z-index: -1;
CSS Fundamentals
For overlapping elements, specifies stack order.
An element with greater stack order is always in front of an element with a lower stack order.
CSS Properties
Float
float: left | right | none ;
The float CSS property specifies that an element should be taken from the normal flow and placed along the left or right side of its container, where text and inline elements will wrap around it.

CSS Fundamentals
CSS Properties
Clear
The clear property specifies whether an element can be next to floating elements that precede it or must be moved down (cleared) below them.
clear: none | left | right | both;

CSS Fundamentals
Specificity
p = 1 (1 HTML selector)
div p = 2 (2 HTML selectors: 1+1)
.tree = 10 (1 class selector)
div p.tree = 12 (2 HTML selectors + a class selector: 1+1+10)
#baobab = 100 (1 id selector)
body #content .alternative p = 112 (HTML + id + class + HTML: 1+100+10+1)
inline > id > class > HTML selector
How to calculate?
HTML Selector = 1, Class = 10, ID = 100, Inline = 1000

CSS Fundamentals