Manajemen State
(State Management)
Pemrograman Mobile

Septian Cahyadi, M.Kom. & Muhamad Saad Nurul Ishlah, M.Comp.
Dept. Sistem Informasi & Dept. Ilmu Komputer, Universitas Pakuan
Agenda Kuliah
- Paradigma Deklaratif (Declarative) vs Imperatif (Imperative)
- Ephemeral State vs App State
- Manajemen State (StatefulWidget & InheritedWidget)
- Opsi lain Manajemen State

State Management
What is it?

Flutter membangun antarmuka pengguna dengan merefleksikan state saat ini
Flutter membangun antarmuka pengguna dengan merefleksikan state saat ini

Paradigma pemrograman Declarative

Declarative vs Imperative
Widget
Container
ButtonA
ButtonB
Text
// onClicked Callback
onClicked () {
// Imperative: Mengubah
Text text = getObjectText();
text.setColor("blue");
// Declarative: Mengganti
return TextWidget(
color: blue,
);
}Text
Declarative vs Imperative
Widget
Container
ButtonA
ButtonB
Text
// onClicked Callback
onClicked () {
// Imperative: Mengubah
Text text = getObjectText();
text.setColor("blue");
// Declarative: Mengganti
return TextWidget(
color: blue,
);
}Text
Declarative vs Imperative
Widget
Container
ButtonA
ButtonB
Text
// onClicked Callback
onClicked () {
// Imperative: Mengubah
Text text = getObjectText();
text.setColor("blue");
// Declarative: Mengganti
return TextWidget(
color: blue,
);
}Text
Declarative vs Imperative
Widget
Container
ButtonA
ButtonB
// onClicked Callback
onClicked () {
// Imperative: Mengubah
Text text = getObjectText();
text.setColor("blue");
// Declarative: Mengganti
return TextWidget(
color: blue,
);
}Text
State?
State == Data
Data yang berhubungan dengan Domain aplikasi, seperti TODO List, Cart Items, etc..
int age;
String title;
int counter;
List<Todo> todoList;
bool isActivated;
State
- Arti luas: state adalah segala sesuatu yang ada di memori saat aplikasi berjalan.
- aset aplikasi,
- semua variabel yang disimpan framework Flutter tentang UI,
- status animasi, tekstur, font
- dll
- Tidak semua kita kelola
- Data apa pun yang dibutuhkan untuk membangun kembali UI kapanpun.
State Management
==
Data Management
Ephemeral vs App State
Ephemeral State
- UI state atau locale state
- Widget lain jarang membutuhkan state ini
- Tidak berubah secara kompleks
- Dapat dikelola dengan kelas State & metode setState dalam StatefulWidget
App State
- Shared state
- State level aplikasi
- Biasanya digunakan oleh banyak widget
- Banyak opsi untuk mengelola, contoh: InheritedWidget, provider, riverpod, mobx, redux, dll
Ephemeral State
Contoh
- Halaman saat ini pada PageView
- Progress Animasi
- Tab yang terpilih
App State
Contoh
- User preferences
- Login info
- Notification
- Shopping cart
- Read/unread state dari artikel di aplikasi News
Contoh Ephemeral State
class MyHomepage extends StatefulWidget {
const MyHomepage({super.key});
@override
State<MyHomepage> createState() => _MyHomepageState();
}
class _MyHomepageState extends State<MyHomepage> {
int _index = 0;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return BottomNavigationBar(
currentIndex: _index,
onTap: (newIndex) {
setState(() {
_index = newIndex;
});
},
// ... items ...
);
}
}_index tidak diakses Widget lain, hanya digunakan dalam MyHomepage saja
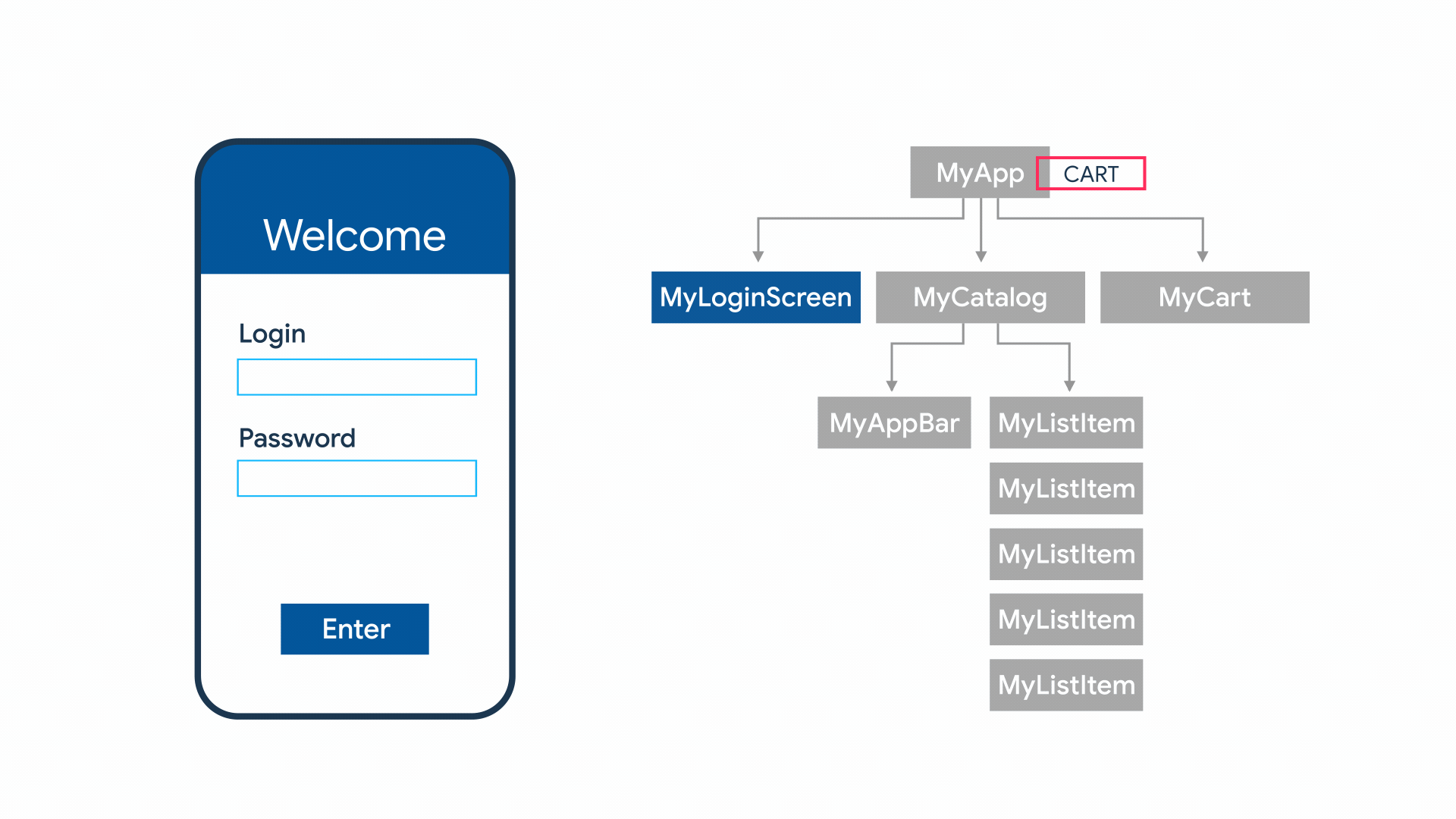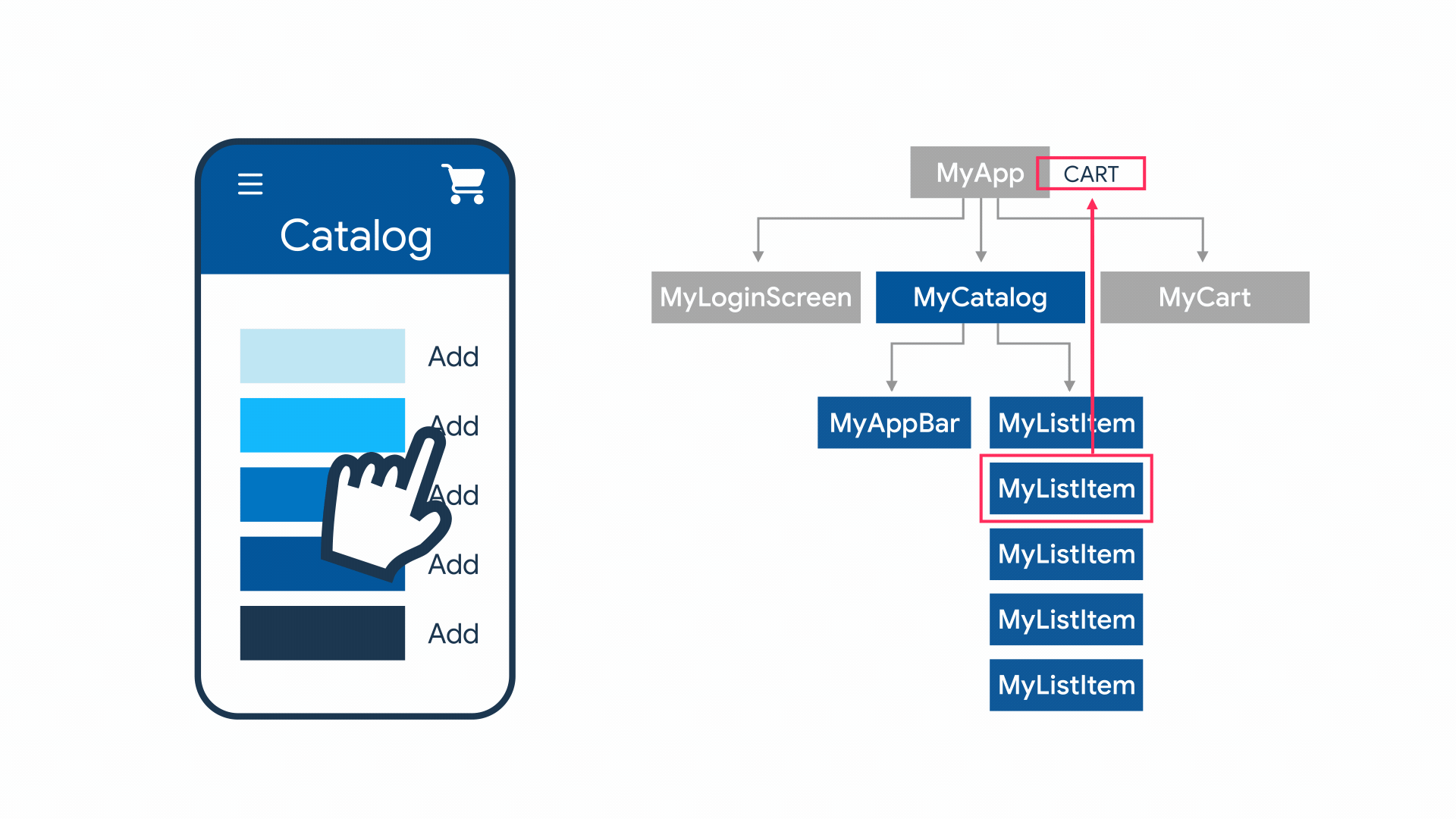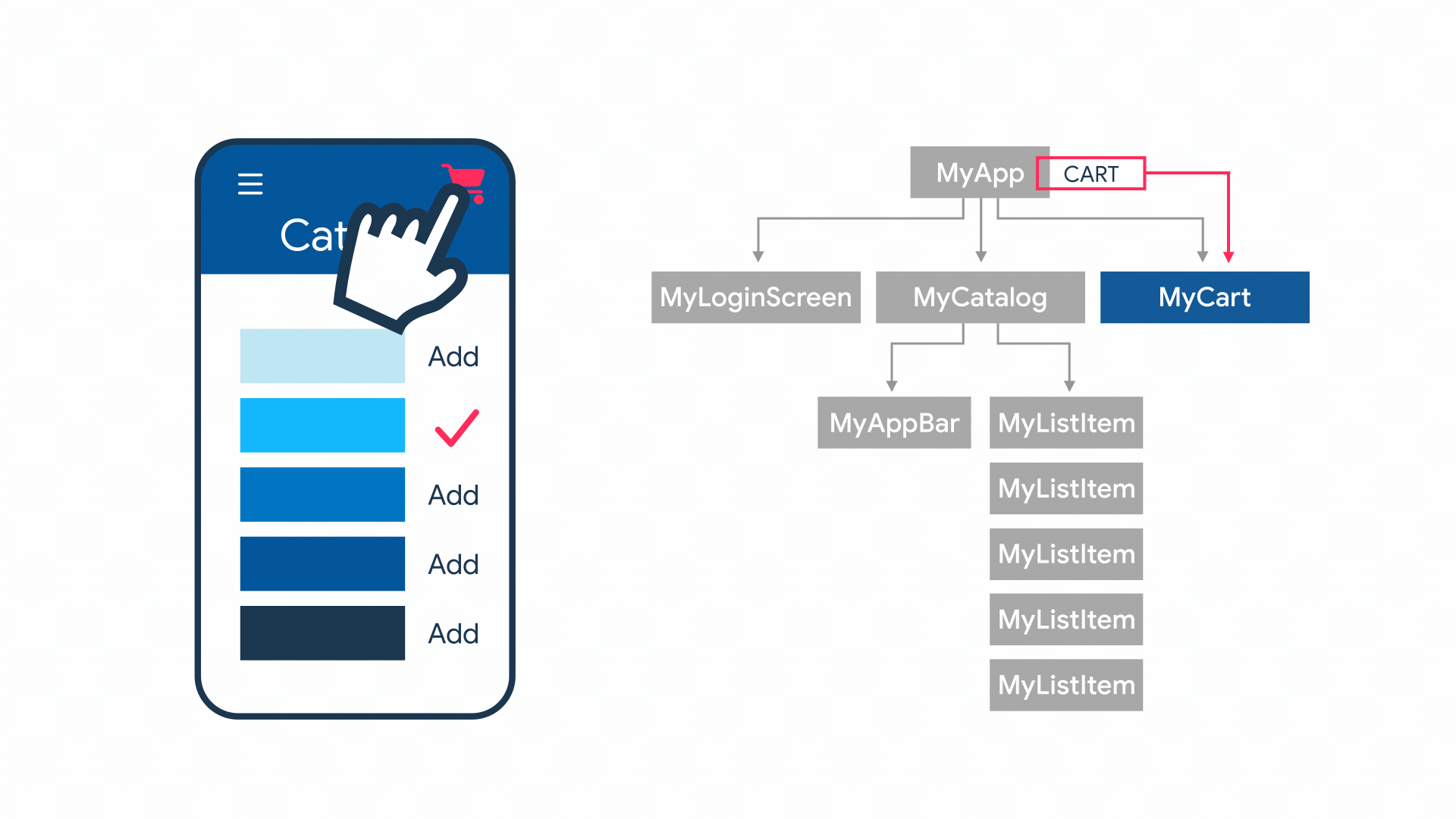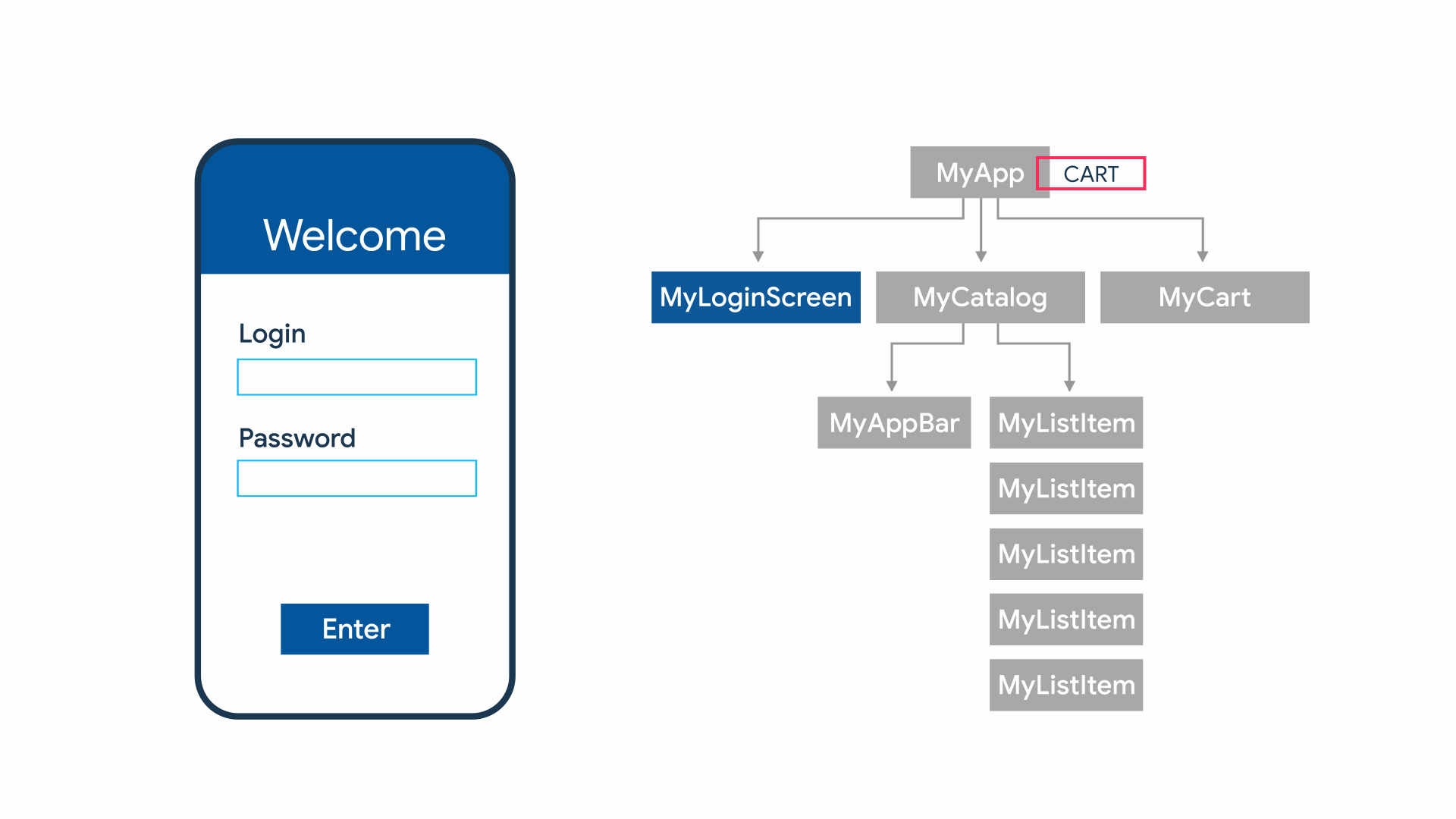
Contoh App State
Membedakan State?
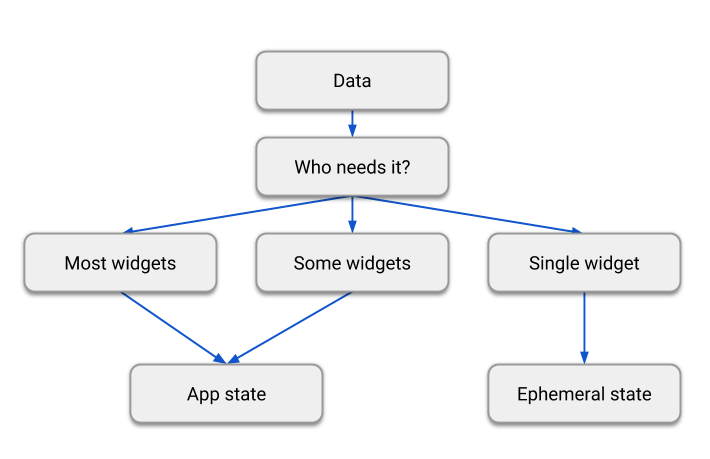
Bagaimana Memulai?
Memulai mengelola State
- Mulai dari Ephemeral State
- Ketika aplikasi mulai membesar, mungkin butuh App State
“The rule of thumb is: Do whatever is less awkward.”
- Dan Abramov (React setState vs Redux's store)
Manajemen State
(Application State)
Mengelola Data melalui Widget Tree
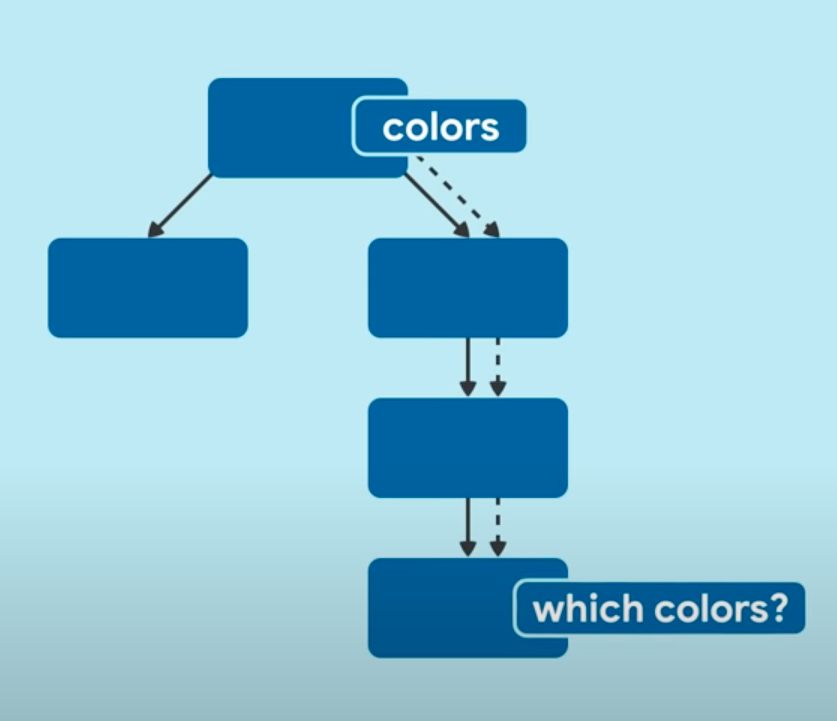
-
Memberikan Data dari Widget atas ke widget bawah (Lifting State Up)
-
Cons: Widget yang tidak menggunakan Data, mendapat data
-
Bisa sangat berantakan, update data. callback hell
Mengelola Data melalui InheritedWidget
-
Membuat subclass InheritedWidget
-
Akses data dari widget yang hanya membutuhkan
-
Begitupun untuk mengupdate
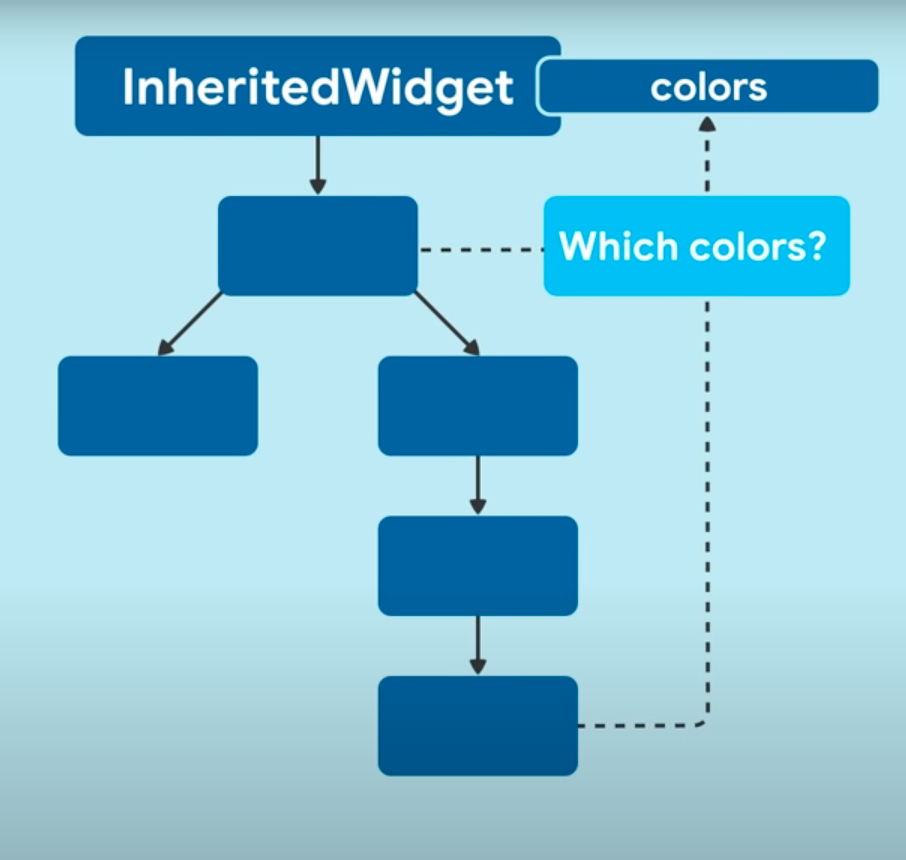
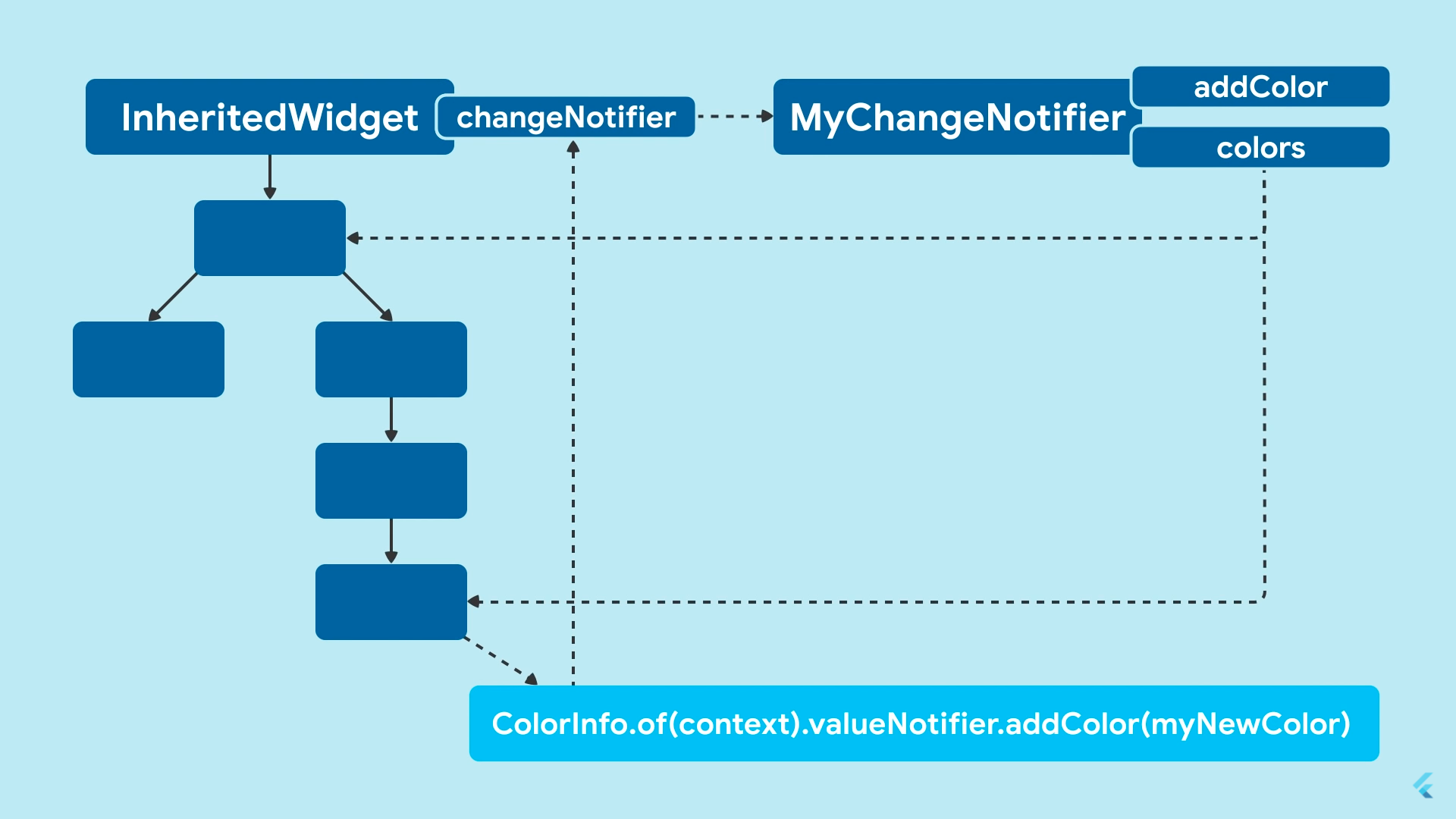
Contoh Inherited Widget
// Definisikan subclass InheritedWidget
class FrogColor extends InheritedWidget {
const FrogColor({
Key? key,
required this.color,
required Widget child,
}) : super(key: key, child: child);
final Color color;
static FrogColor of(BuildContext context) {
final FrogColor? result = context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<FrogColor>();
assert(result == null, 'No FrogColor found in context');
return result!;
}
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(FrogColor old) => color != old.color;
}
// Gunakan di dalam widget yang membutuhkan
class MyPage extends StatelessWidget {
const MyPage({Key? key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
body: FrogColor(
color: Colors.green,
child: Builder(
builder: (BuildContext innerContext) {
return Text(
'Hello Frog',
style: TextStyle(color: FrogColor.of(innerContext).color),
);
},
),
),
);
}
}
Opsi Pengelolaan State Lain
- Provider
- Riverpod
- Redux
- Fish-REdux
- BLoC / Rx
- GetIt
- MobX
- dll
https://docs.flutter.dev/development/data-and-backend/state-mgmt/options
Manajemen State
dengan Provider
Manajemen State dengan Provider
// Copyright 2019 The Chromium Authors. All rights reserved.
// Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license that can be
// found in the LICENSE file.
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/foundation.dart';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:provider/provider.dart';
import 'package:window_size/window_size.dart';
void main() {
setupWindow();
runApp(
// Provide the model to all widgets within the app. We're using
// ChangeNotifierProvider because that's a simple way to rebuild
// widgets when a model changes. We could also just use
// Provider, but then we would have to listen to Counter ourselves.
//
// Read Provider's docs to learn about all the available providers.
ChangeNotifierProvider(
// Initialize the model in the builder. That way, Provider
// can own Counter's lifecycle, making sure to call `dispose`
// when not needed anymore.
create: (context) => Counter(),
child: const MyApp(),
),
);
}
const double windowWidth = 360;
const double windowHeight = 640;
void setupWindow() {
if (!kIsWeb && (Platform.isWindows || Platform.isLinux || Platform.isMacOS)) {
WidgetsFlutterBinding.ensureInitialized();
setWindowTitle('Provider Counter');
setWindowMinSize(const Size(windowWidth, windowHeight));
setWindowMaxSize(const Size(windowWidth, windowHeight));
getCurrentScreen().then((screen) {
setWindowFrame(Rect.fromCenter(
center: screen!.frame.center,
width: windowWidth,
height: windowHeight,
));
});
}
}
/// Simplest possible model, with just one field.
///
/// [ChangeNotifier] is a class in `flutter:foundation`. [Counter] does
/// _not_ depend on Provider.
class Counter with ChangeNotifier {
int value = 0;
void increment() {
value += 1;
notifyListeners();
}
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
const MyApp({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
useMaterial3: true,
),
home: const MyHomePage(),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
const MyHomePage({super.key});
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: const Text('Flutter Demo Home Page'),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: [
const Text('You have pushed the button this many times:'),
// Consumer looks for an ancestor Provider widget
// and retrieves its model (Counter, in this case).
// Then it uses that model to build widgets, and will trigger
// rebuilds if the model is updated.
Consumer<Counter>(
builder: (context, counter, child) => Text(
'${counter.value}',
style: Theme.of(context).textTheme.headlineMedium,
),
),
],
),
),
floatingActionButton: FloatingActionButton(
onPressed: () {
// You can access your providers anywhere you have access
// to the context. One way is to use Provider.of<Counter>(context).
//
// The provider package also defines extension methods on context
// itself. You can call context.watch<Counter>() in a build method
// of any widget to access the current state of Counter, and to ask
// Flutter to rebuild your widget anytime Counter changes.
//
// You can't use context.watch() outside build methods, because that
// often leads to subtle bugs. Instead, you should use
// context.read<Counter>(), which gets the current state
// but doesn't ask Flutter for future rebuilds.
//
// Since we're in a callback that will be called whenever the user
// taps the FloatingActionButton, we are not in the build method here.
// We should use context.read().
var counter = context.read<Counter>();
counter.increment();
},
tooltip: 'Increment',
child: const Icon(Icons.add),
),
);
}
}
Contoh dalam Aplikasi Counter
- Install package
Providerdan import - Buat Model dengan menggunakan
ChangeNotifier - Sediakan model untuk semua widget dalam aplikasi. Dapat menggunakan
ChangeNotifierProviderdalam metoderunApp - Konsumsi model dalam widget yang membutuhkan. Gunakan
Consumer
Diskusi
Ada pertanyaan?
Referensi
- State Management. https://docs.flutter.dev/development/data-and-backend/state-mgmt/intro. diakses: 25 Mei 2022
- Inherited Widgets Explained - Flutter Widgets 101 Ep. 3. Nov 2018. Google Developers. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zbm3hjPjQMk
- Tutorial Flutter – State Management Menggunakan Provider (Bagian 1). Des 2021. Muhamad Ishlah. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dFJK3NN-L0k
- Tutorial Flutter – State Management Menggunakan Provider (Bagian 2). Des 2021. Muhamad Ishlah. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_XCSeHozJjM