암호화된 JSON 포멧의 데이터셋을 읽어
퀴즈를 내는 C언어 프로그램
제주대학교 - 김무훈, 김태영, 서현우
GPG로 암호화된 퀴즈 데이터셋 복호화, 파일 불러오기
typedef struct { // 퀴즈 JSON 데이터 형식에 맞춘 구조체
char question[100];
char options[4][50];
int answer;
} Quiz;
void decryptGPG(const char* encryptedFile, char** decryptedString) {
char command[256]; // GPG 복호화 시작
snprintf(command, sizeof(command), "gpg --batch --yes --decrypt %s", encryptedFile);
FILE* pipe = popen(command, "r");
if (!pipe) {
printf("GPG 복호화 명령을 실행하는 데 실패했습니다\n");
exit(1);
}
char buffer[1024]; // 파일 불러오기 시작
size_t totalSize = 0;
*decryptedString = NULL;
while (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), pipe) != NULL) {
size_t len = strlen(buffer);
*decryptedString = (char*)realloc(*decryptedString, totalSize + len + 1);
strcpy(*decryptedString + totalSize, buffer);
totalSize += len;
}
pclose(pipe);
if (*decryptedString == NULL) {
printf("복호화가 실패했거나 빈 결과가 나왔습니다\n");
exit(1);
}
}여기서 잠깐, GPG
(GNU Privacy Guard) 이란?
GNU Privacy Guard는 오픈소스 암호화 소프트웨어로, 시만텍 회사의 암호화 프로그램 PGP를 대체하기 위해 GNU 프로젝트의 일환으로 개발되었습니다.
*GNU 프로젝트: 오픈소스를 가장 처음, 자유 소프트웨어라는 개념으로 시작한 리처드 스톨먼의 주도하에 시작된 자유 소프트웨어 운동입니다.
이 운동에 참여한 유명한 다른 도구로는 bash, linux, emacs,
gcc(unix-like 시스템에 쓰이는 C 컴파일러) 등이 있습니다.

GnuPG 로고 - 출처 Wikimedia Commons
문자열 ➡️ JSON 객체 ➡️ 구조체 변환 과정

퀴즈 출제 및 풀이
int numQuestions = (rand() % numQuizzes) + 1;
printf("총 %d의 문제 세트 중 %d개의 문제를 출제합니다.\n",numQuizzes, numQuestions);
if (numQuestions < 1 || numQuestions > numQuizzes) {
printf("잘못된 문제 수입니다. 종료합니다.\n");
json_object_put(parsedJson);
return 1;
}
int indices[MAX_QUIZZES];
for (size_t i = 0; i < numQuizzes; i++) {
indices[i] = i;
}
shuffle(indices, numQuizzes);
int userAnswer;
int score = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < numQuestions; i++) {
int quizIndex = indices[i];
printf("%s\n", quizzes[quizIndex].question);
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
printf("%d. %s\n", j + 1, quizzes[quizIndex].options[j]);
}
printf("정답을 입력하세요: ");
scanf("%d", &userAnswer);
}if (userAnswer - 1 == quizzes[quizIndex].answer) {
printf("정답입니다!\n");
score++;
} else {
printf("오답입니다! 정답은 %s 입니다.\n", quizzes[quizIndex].options[quizzes[quizIndex].answer]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("총 %d문제 중 %d문제를 맞추셨습니다.\n", numQuestions, score);
json_object_put(parsedJson);
return 0;
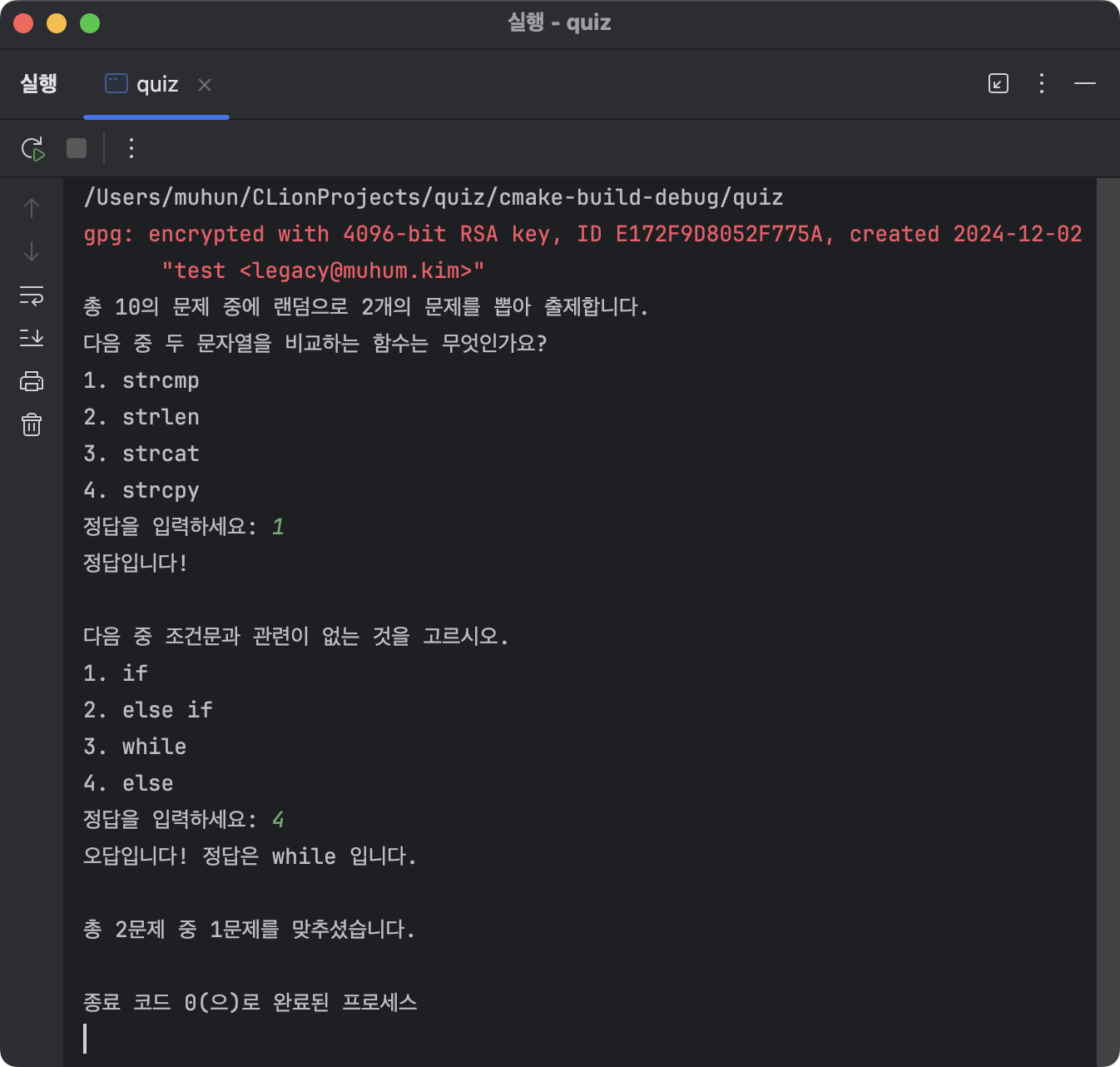
최종 실행 결과
void shuffle(int *array, size_t n) {
if (n > 1) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
size_t j = i + rand() / (RAND_MAX / (n - i) + 1);
int t = array[j];
array[j] = array[i];
array[i] = t;
}
}
}