Immutable Data Structures

What's the difference?
Normal object in JavaScript
var person = {
name: 'Byomkesh Bakshi',
occupation: 'being awesome'
};
person.occupation = 'being not so awesome';
console.log(person);
// Object {name: "Byomkesh Bakshi", occupation: "being not so awesome"}With immutable-js (a library from facebook)
var map1 = Immutable.Map({a:1, b:2, c:3});
var map2 = map1.set('b', 50);
map1.get('b'); // 2
map2.get('b'); // 50Why use immutable ds?
- Easy undo/redo/time-travel (actually trivial). Very hard to do using mutable data structures
- Easier concurrency primitives (no explicit locks/synchronized)
- Thread safe
- Because they never change, no worrying about if they change mid operation in a thread - Easy value comparision between data (== returns instantly). No deep comparisons required.
- Immutable data can be used as map keys or set values
- Easy caching (they never change, so just cache the reference and not the whole thing)
Why use immutable ds?
- No defensive copying
- Easy to find bugs
Most of the bugs are due to state change and when using mostly immutable data structures you know exactly where to look for while finding bugs (hint: where you do state changes)
Code for undo/redo
History.prototype.undo = function() {
if(currentIndex === 0) {
return this.history[currentIndex];
}
currentIndex -= 1;
return this.getCurrentItem();
}
History.prototype.redo = function() {
if(currentIndex === (this.history.length - 1)) {
return this.history[currentIndex];
}
currentIndex += 1;
return this.getCurrentItem();
}
But aren't they slow?
- Nope
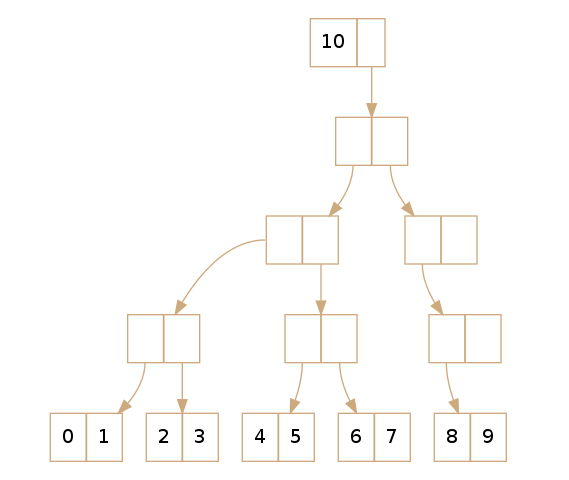
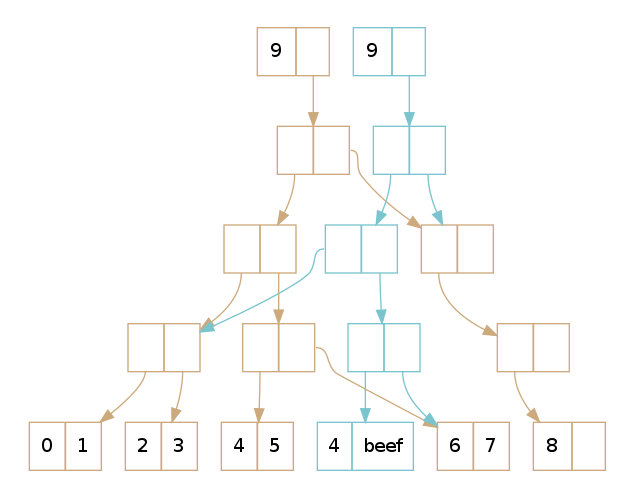
- Implemented using persistent data structures
- Uses hash mapped array tries and path copying
JavaScript has it?
- Nope
- But there are libraries