前陣子接觸OCR的一些分享
By Frankie Xu
預防針時間
大約一年前玩的,有些資訊是以前整理的
如有錯誤還請多多指教、包涵
不是很深入的技術研討,較偏向經驗分享,
希望能幫助接觸ocr的朋友節省時間
淺談 OCR
OCR(Optical Character Recognition)
中文為光學文字辨識的縮寫,透過光學輸入的技術掃描印刷上的文字轉化為圖像,並利用識別技術把圖像中的文字轉換成文本格式。
最常見的AI應用除了語音辨識、影像辨識及自然語言處理外,OCR文字識別也正被廣泛地使用。
圖片 -> 文字 ; 非結構化 -> 結構化
-
影像輸入
透過各種具光學設備的攝影器材將文本中的文字轉化為影像。
掃描的解析度越高,便對文字識別工作越有利。
- 影像前處理
由於紙張的印刷質量和掃描儀本身都可能影響文件影像的清晰度,所以在進行文字識別之前,要先清除圖片上的污點。而處理圖像的方法包括版面分析、行字切分、圖像降噪、文字特徵提取等等,來提高OCR的準確性及有效性
基本流程
OCR應用場景
- 結構化資料、節省人力
- 自動化流程 RPA
- 智慧監控 (車牌辨識等等)
最佳方案 : 自行開發 vs 使用服務
- 該 case 可行性 (技術門檻) ?
- 成本考量 (開發時間、金錢成本,服務費用)
- 商品化、輸出可能性?
-
自動化爬蟲 -> 驗證碼 (流程自動化 RPA)
-
結構化 -> 客戶文本照片 -> 讓某段業務流程自動化
(RPA + 結構化資料)
個人遇到的場景
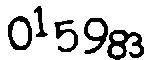
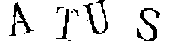
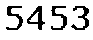

驗證碼
- 只做前處理,直接用免費開源的ocr引擎
- 針對特例(型態特別、前處理難度高) 自行 train model
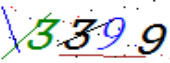

結構化客戶文本照片
- 一般表格 -> 現成表格ocr
- 格式稍複雜表格
- 極度複雜表格
- 各類表格版面不同
- 中文字形 ocr 門檻高
-> 使用線上ocr服務
自行開發成本高
- 各種拍攝場景
- 拍攝角度
- 各牌手機
掃出結果 ≠ 結構化
淺談影像前處理
- 最早由英特爾公司啟動的開源電腦視覺庫
- 介面主要支援語言: c++, c, python, java, matlab, c#, ruby
- 不只影像處理,影像辨識、物體辨識等功能也很強大
ocr 常用處理
- 灰階
- 二值化
- 形態學
- 透視校正
灰階

灰階
- openCV 顏色預設排列方式為 BGR
import cv2
image = cv2.imread('lena.jpg')
image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.imshow('Result', image)
cv2.waitKey(0)- 要進行二值化必須先轉成灰階
- 灰度值 : 0到255,白色255,黑色0
二值化

二值化
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('gradient.png',0)
ret,thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
ret,thresh2 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV)
ret,thresh3 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TRUNC)
ret,thresh4 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO)
ret,thresh5 = cv2.threshold(img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV)
titles = ['Original Image','BINARY','BINARY_INV','TRUNC','TOZERO','TOZERO_INV']
images = [img, thresh1, thresh2, thresh3, thresh4, thresh5]
for i in xrange(6):
plt.subplot(2,3,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
給定 global threshold (閾值)
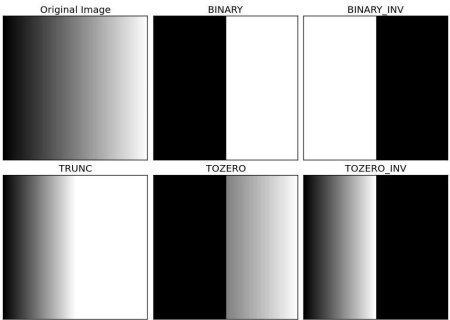
常用算法
-
Threshold Binary:即二值化,將大於閾值的灰度值設為最大灰度值,小於閾值的值設為0。 -
Threshold Binary, Inverted:將大於閾值的灰度值設為0,其他值設為最大灰度值。 -
Truncate:將大於閾值的灰度值設為閾值,小於閾值的值保持不變。 -
Threshold to Zero:將小於閾值的灰度值設為0,大於閾值的值保持不變。 -
Threshold to Zero, Inverted:將大於閾值的灰度值設為0,小於閾值的值保持不變。
但應用場景流程需要自動化,給定 global 閾值不太可行
自動化 Adaptive threshold (自適應閾值)
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('sudoku.png',0)
img = cv.medianBlur(img,5)
ret,th1 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY)
th2 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(img,255,cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C,\
cv.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
th3 = cv.adaptiveThreshold(img,255,cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C,\
cv.THRESH_BINARY,11,2)
titles = ['Original Image', 'Global Thresholding (v = 127)',
'Adaptive Mean Thresholding', 'Adaptive Gaussian Thresholding']
images = [img, th1, th2, th3]
for i in xrange(4):
plt.subplot(2,2,i+1),plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()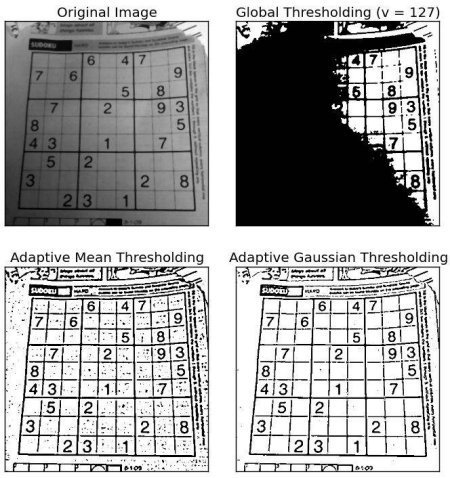
自動化 Adaptive threshold (自適應閾值)
常見 Adaptive threshold 演算法
- cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_MEAN_C:這種演算法的閾值是鄰域面積的平均值。
- cv.ADAPTIVE_THRESH_GAUSSIAN_C:這種演算法的閾值是鄰域值的加權和,權重值為高斯通道 (高斯函数)
蠻適合處理光影不均的影像
Otsu 大津二值化演算法
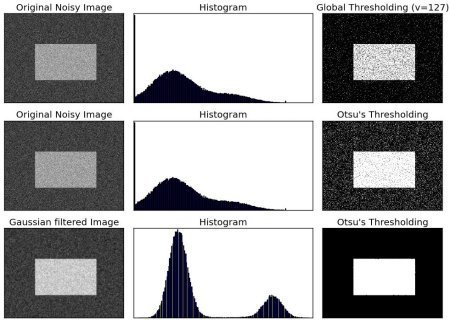
灰度直方圖 -> 找出加權平方差最小的閾值,適合灰度直方圖呈現明顯雙峰的影像
Otsu 大津二值化演算法
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv.imread('noisy2.png',0)
# global thresholding
ret1,th1 = cv.threshold(img,127,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY)
# Otsu's thresholding
ret2,th2 = cv.threshold(img,0,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY+cv.THRESH_OTSU)
# Otsu's thresholding after Gaussian filtering
blur = cv.GaussianBlur(img,(5,5),0)
ret3,th3 = cv.threshold(blur,0,255,cv.THRESH_BINARY+cv.THRESH_OTSU)
# plot all the images and their histograms
images = [img, 0, th1,
img, 0, th2,
blur, 0, th3]
titles = ['Original Noisy Image','Histogram','Global Thresholding (v=127)',
'Original Noisy Image','Histogram',"Otsu's Thresholding",
'Gaussian filtered Image','Histogram',"Otsu's Thresholding"]
for i in xrange(3):
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+1),plt.imshow(images[i*3],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+2),plt.hist(images[i*3].ravel(),256)
plt.title(titles[i*3+1]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.subplot(3,3,i*3+3),plt.imshow(images[i*3+2],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i*3+2]), plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([])
plt.show()沒有哪種演算法最好,
因應各種場景遇到的影像,判定適合用哪種演算法

skimage (scikit-image)
(Python)
形態學
- 腐蝕
- 膨脹
- 開運算
- 閉運算
腐蝕


卷積核內全部都是白才會留白,否則黑
腐蝕前景(白色)物體的邊界
去除白色躁點、切割兩個相連物體等等...
腐蝕
import cv2
import numpy as np
img = cv2.imread('j.png',0)
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations = 1)
cv2.imshow('j',erosion)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()膨脹
與腐蝕相反,
卷積核內只要有一點白就會填白
膨脹前景(白色)物體的邊界
開與閉運算
- 開運算: 侵蝕再膨脹
- 閉運算: 膨脹再侵蝕




透視變形校正
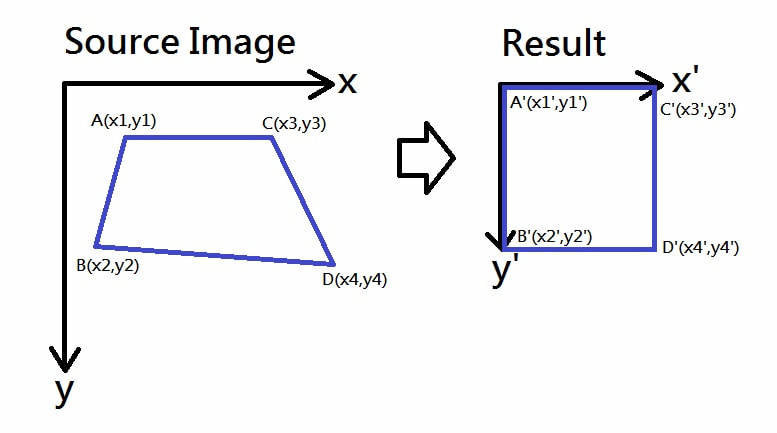
難題: 文本邊角的座標未知
透視變形校正
- 邊緣偵測
- 物體偵測
- 直線偵測
透視變形校正
場景需求 -> 文本複雜度 -> 使用線上ocr服務 -> 影像標準化 -> 解析