Market research - customer discovery
Petar Atanasovski
GoDaddy

Today We Will...
2. Learn from our experience
1. Get theoretical base
3. Practice
Today We Will...
2. Learn from our experience
1. Get theoretical base
3. Practice
Today We Will...
2. Learn from our experience
1. Get theoretical base
3. Practice
My First Experience...
2. Learn from our experience
3. Get theoretical base
1. Practice


What is it?


A mindset, or way of thinking, with a commitment to achieve a totally waste-free operation that’s focused on your customer’s success
Source: David Hogg, High Performance Solutions, 2008


The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
Target Customers
Customer Segmentation
1. Demographic (Years, Gender, Marital status, Incomes, Education)
2. Psychographic (Believes, Opinions, Interests, Values)
3. Behavioral (Performing particular action & how often)
4. Needs (Same product, different needs)
Customer Segmentation
1. Demographic (Years, Gender, Marital status, Incomes, Education)
2. Psychographic (Believes, Opinions, Interests, Values)
3. Behavioral (Performing particular action & how often)
4. Needs (Same product, different needs)
Customer Segmentation
1. Demographic (Years, Gender, Marital status, Incomes, Education)
2. Psychographic (Believes, Opinions, Interests, Values)
3. Behavioral (Performing particular action & how often)
4. Needs (Same product, different needs)
Customer Segmentation
1. Demographic (Years, Gender, Marital status, Incomes, Education)
2. Psychographic (Believes, Opinions, Interests, Values)
3. Behavioral (Performing particular action & how often)
4. Needs (Same product, different needs)
Customer Segmentation
1. Demographic (Years, Gender, Marital status, Incomes, Education)
2. Psychographic (Believes, Opinions, Interests, Values)
3. Behavioral (Performing particular action & how often)
4. Needs (Same product, different needs)
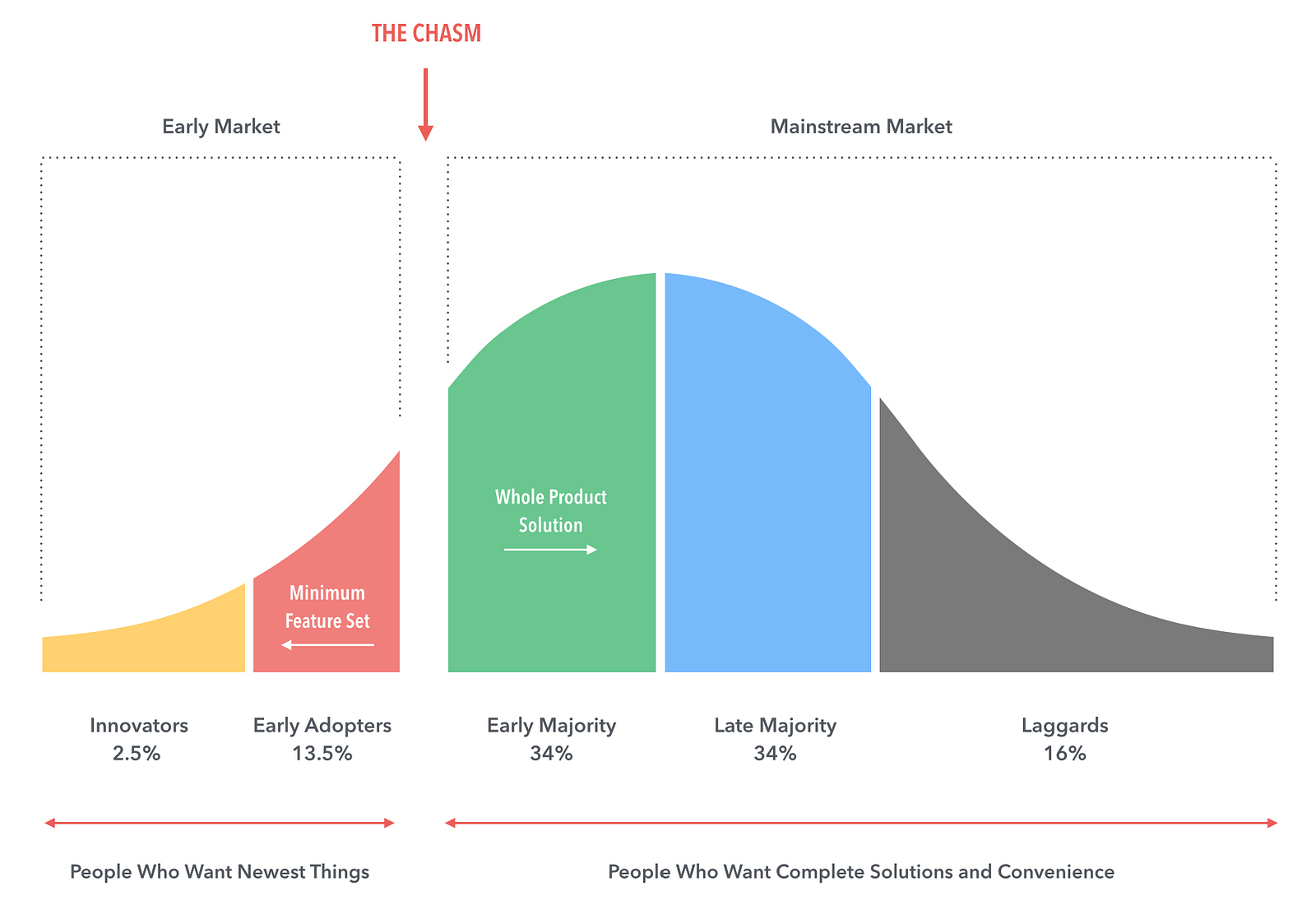
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
1. Innovators
2. Early Adopters
3. Early Majority
4. Late Majority
5. Laggards
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
1. Innovators
2. Early Adopters
3. Early Majority
4. Late Majority
5. Laggards
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
1. Innovators
2. Early Adopters
3. Early Majority
4. Late Majority
5. Laggards
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
1. Innovators
2. Early Adopters
3. Early Majority
4. Late Majority
5. Laggards
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
1. Innovators
2. Early Adopters
3. Early Majority
4. Late Majority
5. Laggards
Technology Adoption Lifecycle
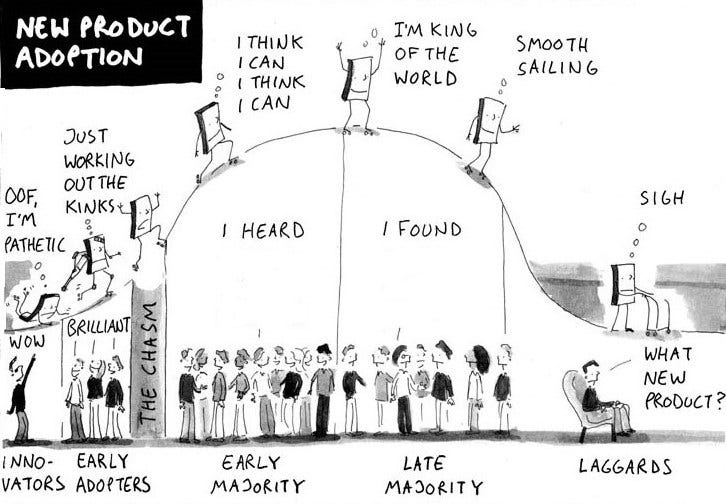
Technology Adoption Lifecycle

Source: https://fakecrow.com
INVEST:
- Independent
- Negotiable
- Valuable
- Estimable
- Small
- Testable
Customer Underserved Needs
Problem Space Validation before offering solution
User Story
As a [type of user], I want to [do something], so that I can [desired benefit].
Value Proposition is a statement that explains what benefit you provide for who and how you do it uniquely well.
People think focus means saying yes to the thing you've got to focus on. But that's not what it means at all. It means saying no to the hundred other good ideas that there are. You have to pick carefully. I'm actually as proud of the things we haven't done as the things I have done. Innovation is saying no to 1,000 things.
Steve Jobs
Value Proposition

The main reason products fail is because they don't meet customer needs in a way that is better than other alternatives.
Source: Dan Olsen, The Lean Product Playbook





Problem Space VS Solution Space
"A pen that works in zero gravity"
"A way to record notes in zero gravity"
What VS How
The "what" describes the benefits that the product should give the customer - what the product will accomplish for the user or allow the user to accomplish.
The "how" is the way in which the product delivers the "what" to the customer.
The "how" is the design of the product and the specific technology used to implement the product.
"What" is problem space.
"How" is solution space.
The "what" describes the benefits that the product should give the customer - what the product will accomplish for the user or allow the user to accomplish.
The "how" is the way in which the product delivers the "what" to the customer.
The "how" is the design of the product and the specific technology used to implement the product.
"What" is problem space.
"How" is solution space.
The "what" describes the benefits that the product should give the customer - what the product will accomplish for the user or allow the user to accomplish.
The "how" is the way in which the product delivers the "what" to the customer.
The "how" is the design of the product and the specific technology used to implement the product.
"What" is problem space.
"How" is solution space.



How It Started
Identify underserved customer needs


1. How do you find an information when you don't know something about our company (or some procedure)?
2. How often do you need to ask others for some information? Can you name some previous examples?
3. What is your favorite website for finding an answer related to your profession? Why that website, what makes it special?

4. What is your favorite website for learning? Why that website, what makes it special?
5. Which questions you were looking for recently?
6. My favorite communication channel in company is...? Why?

7. Which knowledge am I missing the most in my work?
8. What is your favorite method for getting new knowledge in the company?
9. When was the last time that you found all answers to your questions on one place for completing some task? Which task that was?













Practice Time
Let's practice - The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
Let's practice - The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
Let's practice - The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
Let's practice - The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers
Let's practice - The six steps
of the Lean Product Process
1. Determine your target customers
2. Identify underserved customer needs
3. Define your value proposition
4. Specify your minimum viable product (MVP) feature set
5. Create your MVP prototype
6. Test your MVP with customers

Present Your Ideas
Questions
THANK YOU!
@AtanasovskiP
www.atanasovski.rs
petar.atanasovski@gmail.com
GoDaddy
