Developing a HTTP API

SHODO

Hello! I'm Nathan.

- Co-founder of Shodo Lille
- Backend developer
- Pushing Go to production since 2014
- Worked 10 years at OVHcloud
- Inclusion & Diversity activist
- https://bento.me/nathan-castelein

What about you?

The next four hours

Welcome to the "Developing a HTTP API" training
This presentation is in English. Many terms do not have a proper translation in French.

Schedule
Morning session
- 9h: Session start
- 10h: 5 minutes break
- 11h: 10 minutes break
- 12h: 5 minutes break
- 13h: Session ends
Afternoon session
- 14h: Session start
- 15h: 5 minutes break
- 16h: 10 minutes break
- 17h: 5 minutes break
- 18h: Session ends
What do you expect
from this training?

Content
- Developing an API, the why
- Our projet: Charlie's Shelter, a place for animals
- Using a SQL database in Go
- Writing a HTTP API
A four-hours training means ...
- Something like 40% of theory, 60% of practice
- A lot of resources will be provided to go further outside of the training session
- Some topics are excluded from this training session
- Sometimes, it's my point of view
- I'm available for any question following the session: nathan.castelein@shodo-lille.io
Prerequisites
- Go v1.22
- Visual Studio Code
- Git
- (optional) Docker for PostgreSQL
Developing an API, the why

Developing an API, the why
Expose your services to your customers through a well-known protocol: HTTP.
Go is a solid candidate for writing micro-services. Developing performant APIs becomes a key point to propose this kind of architecture.
Charlie's Shelter, a place for animals

Charlie's Shelter

You're helping a friend in their dream: a shelter for old animals!
They need a bit of help to create their website.
You start by creating a database to store all information, and a HTTP API to give access to the stored information.
Charlie's Shelter
This project is based on the Swagger Petstore Sample.
In this project, we will learn:
- How to work with a database
- How to create a HTTP API
Questions?

Thanks Lexica Aperture for generating wonderful images.
Using a SQL database in Go

Simple SQL schema
CREATE TABLE category (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT UNIQUE NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE pet (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL,
category INT REFERENCES category(id)
);
INSERT INTO category(name) VALUES ('Dog'), ('Cat'), ('Hamster'), ('Rabbit');
INSERT INTO pet(name, category) VALUES
('Rafale', 1),
('Rio', 1),
('Mia', 2),
('Laverne', 3);Start the database with Docker
$ cd database
$ docker run -d --name gocourse-postgres \
-v ./init.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/init.sql \
-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=test \
-e POSTGRES_USER=gocourse \
-e POSTGRES_DB=gocourse \
-p 5432:5432 \
postgres:latest
a6fb78c839629d9cf71a2cf7fca9d6bfbbdd3233da2201d7170447d99a75a527
$ docker exec -it gocourse-postgres psql -U gocourse
psql (16.1 (Debian 16.1-1.pgdg120+1))
Type "help" for help.
gocourse=# select * from pet;
id | name | category
----+---------+----------
1 | Rafale | 1
2 | Rio | 1
3 | Mia | 2
4 | Laverne | 3
(4 rows)Run a PostgreSQL database with the schema using Docker
Don't have Docker?

I provide you a PostgreSQL DSN (data source name).
You can use it in the project by exporting it as an ENV variable:
$ export PG_DSN='...'The database/sql package

Connect to the database: the standard database/sql package
Go provides a standard SQL package to work with a database.
First of all, let's see how we can connect to the database.
Useful link:
Connect to a database
package connect
import (
"database/sql"
"os"
)
func getPostgreSQLDSN() string {
if pgdsn := os.Getenv("PG_DSN"); pgdsn != "" {
return pgdsn
}
return "postgres://gocourse:test@localhost:5432/gocourse?sslmode=disable"
}
func SQL() (*sql.DB, error) {
return sql.Open("postgres", getPostgreSQLDSN())
}Connect to a database
$ go test .
--- FAIL: TestConnect (0.00s)
connect_test.go:12: err = 'sql: unknown driver "postgres" (forgotten import?)'; want nil
FAIL
FAIL github.com/nathancastelein/go-course-api/database/connect 0.289s
FAILConnect to a database: using a driver
The sql package must be used in conjunction with a database driver.
The database driver implements the database interface to properly discuss with a given type of database.
As we are using PostgreSQL, we will use lib/pq, the famous driver for PostgreSQL: https://github.com/lib/pq
List of drivers: https://go.dev/wiki/SQLDrivers
Connect to a database
package connect
import (
"database/sql"
"os"
_ "github.com/lib/pq"
)
func getPostgreSQLDSN() string {
if pgdsn := os.Getenv("PG_DSN"); pgdsn != "" {
return pgdsn
}
return "postgres://gocourse:test@localhost:5432/gocourse?sslmode=disable"
}
func SQL() (*sql.DB, error) {
return sql.Open("postgres", getPostgreSQLDSN())
}
Blank identifier
Blank identifier _ can be used to import a package.
If you import a package and not using it in your code, it does not compile.
Blank identifier allows the import, and it will only call the init() function of the package.
In our case, lib/pq has an init function which registers the driver for database/sql.
The init function
// from lib/pq
func init() {
sql.Register("postgres", &Driver{})
}Init function is a simple function that will be executed before anything else.
You can't manage errors properly with the init function.
Using database/sql package
Now that we have a connection to the database, we will be able to perform queries on the database.
database/sql is a low-level package, so we don't have a lot of helpers to make things easier.
Let's have our first SELECT!
Exec vs. Query
Exec
https://pkg.go.dev/database/sql#DB.Exec
Exec executes a query without returning any rows.
DELETE, UPDATE, INSERT
Returns the number of affected rows.
Query
https://pkg.go.dev/database/sql#DB.Query
Query executes a query that returns rows.
SELECT
Returns the data.
A simple query
func SimpleQuery() (bool, error) {
query := `SELECT 1 = 1;`
db, err := database.ConnectSolution()
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
rows, err := db.Query(query)
if err != nil {
return false, err
}
for rows.Next() {
var result bool
if err := rows.Scan(&result); err != nil {
return false, err
}
return result, nil
}
return false, errors.New("no data")
}Writing your first SELECT
Write the SelectAllPetNames function.
Query: SELECT pet.name FROM pet;

file/to/open.go$ go test -run ^TestSelectAllPetNames$File to open:
Test your code:
database/sql/select.goThe first SELECT
func SelectAllPetNames() ([]string, error) {
query := `SELECT pet.name FROM pet;`
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
rows, err := db.Query(query)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
petNames := make([]string, 0)
for rows.Next() {
var petName string
if err := rows.Scan(&petName); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
petNames = append(petNames, petName)
}
return petNames, nil
}Select pets and their category
package shelter
type Pet struct {
Id int
Name string
Category string
}Package shelter describes one struct to manage pets.
Let's select from database using those struct.
Complex SELECT
Write the SelectAllPets function.

file/to/open.go$ go test -run ^TestSelectAllPets$File to open:
Test your code:
database/sql/select.go...
query := `SELECT
pet.id,
pet.name,
category.name
FROM pet
INNER JOIN category
ON pet.category = category.id;`
...Complex SELECT
func SelectAllPetsSolution() ([]shelter.Pet, error) {
query := `SELECT pet.id, pet.name, category.name FROM pet INNER JOIN category ON pet.category = category.id;`
db, err := database.ConnectSolution()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
rows, err := db.Query(query)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pets := make([]shelter.Pet, 0)
for rows.Next() {
pet := shelter.Pet{}
if err := rows.Scan(&pet.Id, &pet.Name, &pet.Category); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pets = append(pets, pet)
}
return pets, nil
}Passing parameters to a query
Both Exec and Query methods have a variadic parameter, to provide values to the query, while avoiding SQL injection.
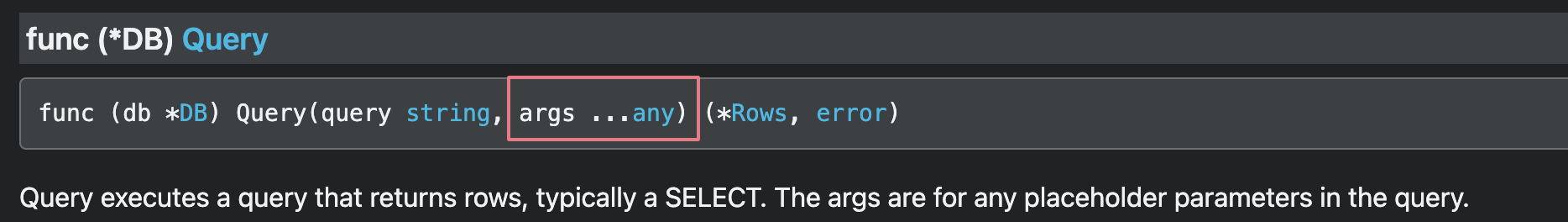
Passing parameters to a query
func QueryWithArgs() {
...
query := `SELECT * FROM pet WHERE name = $1 OR name = $2;`
rows, err := db.Query(query, "Rio", "Rafale")
...
}Passing parameters to a query or an exec: the UPDATE
Write the UpdatePetName function to update the pet name for a given id.

file/to/open.go$ go test -run ^TestUpdatePetName$File to open:
Test your code:
database/sql/update.go...
query := `UPDATE pet
SET name = $1
WHERE id = $2;`
...Exec: the UPDATE example
func UpdatePetName(id int, newName string) error {
query := `UPDATE pet SET name = $1 WHERE id = $2`
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return err
}
result, err := db.Exec(query, newName, id)
if err != nil {
return err
}
rowsAffected, err := result.RowsAffected()
if err != nil {
return err
}
if rowsAffected != 1 {
return errors.New("update failed, no rows affected")
}
return nil
}A bit unfriendly, isn't it?

Using database/sql is a good way to start for simple usage, but it quickly becomes unfriendly.
If you want to go further:
https://go.dev/wiki/SQLInterface
Hopefully, the community provides packages to manage database discussions... with ORMs!
SQL ORMs

Go well-know ORMs
| ORM | Github | # of stars |
|---|---|---|
| SQLx | https://github.com/jmoiron/sqlx | 15k |
| Gorm | https://github.com/go-gorm/gorm | 35k |
| ENT | https://github.com/ent/ent | 15k |
| SQLBoiler | https://github.com/volatiletech/sqlboiler | 6.5k |
| SQLc | https://github.com/sqlc-dev/sqlc | 10k |
Go has many ORMs available on Github, but some of them have more success than others:
SQLx

sqlx: an extension to Go database/sql
SQLx is an extension to the database/sql package.
It provides helpers to easily unwrap data from SQL to your structures.
It provides quite the same API (Query, Exec), and some new functions:
- Select, to select multiple rows
- Get, to select a single row
SQLx
/*
CREATE TABLE person (
first_name text,
last_name text,
email text
);
*/
type Person struct {
FirstName string `db:"first_name"`
LastName string `db:"last_name"`
Email string `db:"email"`
}The best way to use SQLx is to create a struct to welcome your data from the database. The struct has fields that correspond to the output of your SELECT.
Go struct tags
Struct tags are small pieces of metadata attached to fields of a struct that provide instructions to other Go code that works with the struct.
Struct tags are key-value pairs.
The most common one is the json tag.
type Person struct {
Name string `db:"name" json:"name" example:"whatyouwant"`
}SELECT with SQLx
func SelectWithSQLx() error {
// Select multiple rows
people := []Person{}
if err := db.Select(&people, "SELECT * FROM person ORDER BY first_name ASC"); err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println("I found people: ", people)
// Select a single row
jason := Person{}
if err := db.Get(&jason, "SELECT * FROM person WHERE first_name=$1", "Jason"); err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Println("Hello you", jason)
}SELECT with SQLx
Write the SelectAllPets function.

file/to/open.go$ go test -run ^TestSelectAllPets$File to open:
Test your code:
database/sqlx/select.goSELECT with SQLx
type Pet struct {
Id int `db:"id"`
Name string `db:"name"`
Category string `db:"category"`
}Select all pets with SQLx
func SelectAllPets() ([]shelter.Pet, error) {
query := `SELECT pet.id as id, pet.name as name, category.name as category FROM pet INNER JOIN category ON pet.category = category.id;`
db, err := connect.ConnectSQLx()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pets := make([]shelter.Pet, 0)
err = db.Select(&pets, query)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return pets, nil
}Select one pet with SQLx
func SelectOnePet(id int) (*shelter.Pet, error) {
query := `SELECT pet.id as id, pet.name as name, category.name as category FROM pet INNER JOIN category ON pet.category = category.id WHERE pet.id = $1;`
db, err := connect.ConnectSQLx()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pet := Pet{}
err = db.Get(&pet, query, id)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &shelter.Pet{
Id: pet.Id,
Name: pet.Name,
Category: pet.Category,
}, nil
}ORMs

ORMs: Code-first vs. Schema-first
Code-first
You write your structs/objects, you add some meta-data, then the database schema is created from your code.
Schema-first
You write your database schema, then your code (structs/objects) is generated from your schema.
Code-first ORMs

Gorm
Full-featured ORM. You write your structs, all links and constraints between them. Then you apply this on your database, and your schema is created according to your codebase.
Some of the features:
- Associations
- Hooks
- Automigration
- Transactions
- ...

Gorm structure declaration
type User struct {
ID uint `gorm:"primaryKey"`
CreatedAt time.Time
UpdatedAt time.Time
DeletedAt gorm.DeletedAt `gorm:"index"`
Name string
}Declare a struct, and add tags to declare your schema.
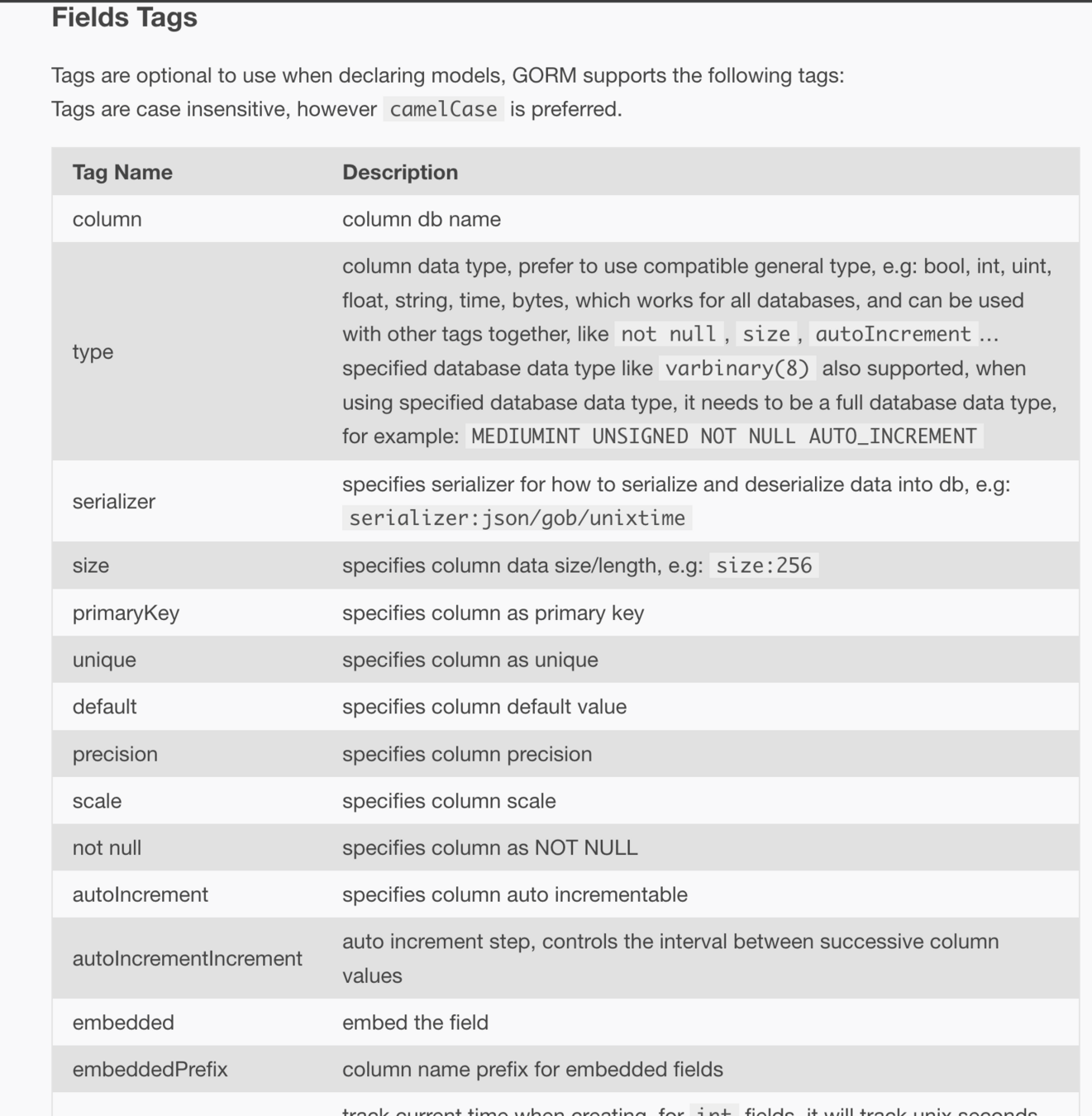
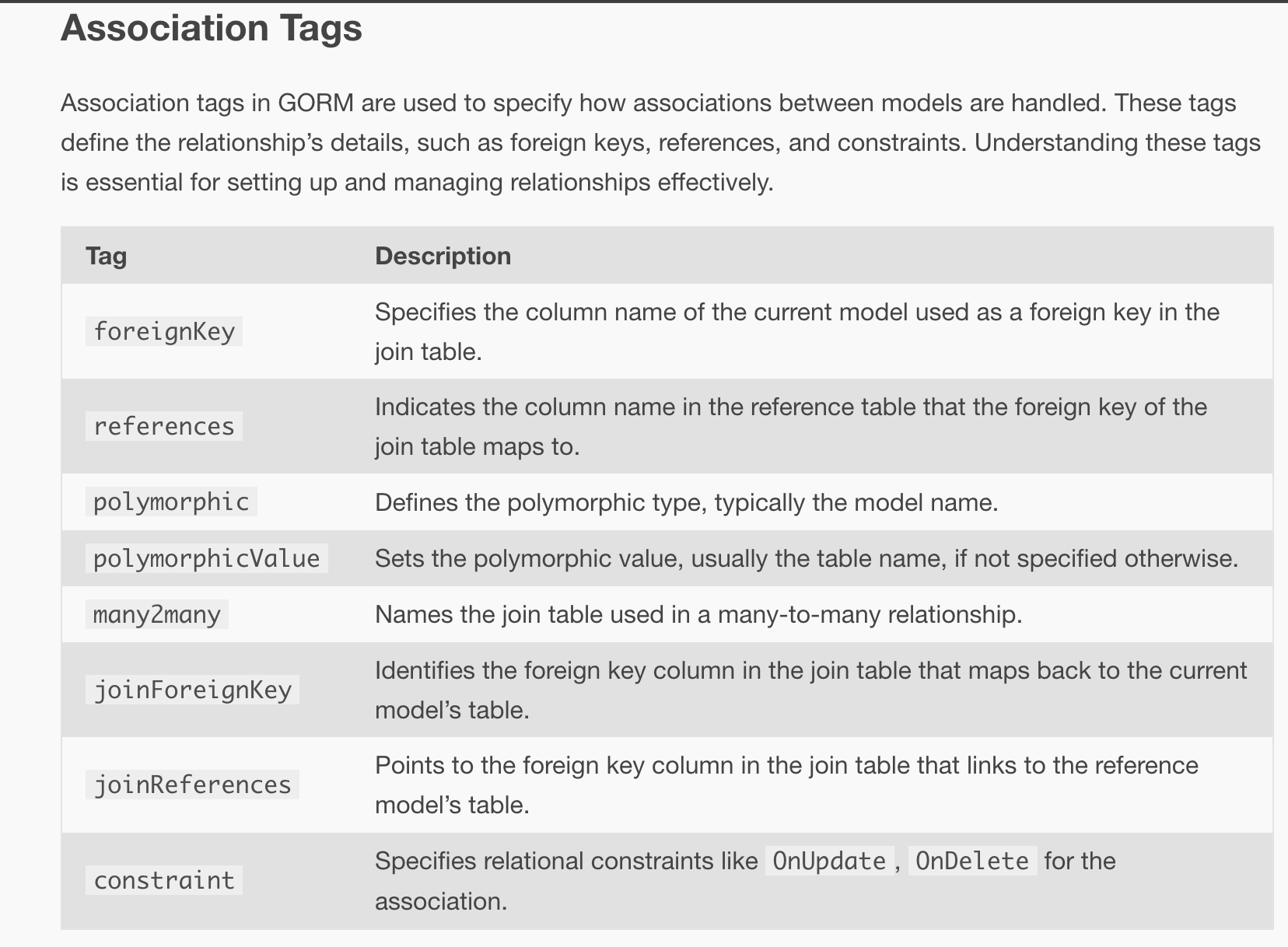
Gorm tags
Gorm usage
// Get first matched record
db.Where("name = ?", "Nathan").First(&user)
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = 'Nathan' ORDER BY id LIMIT 1;
// Get all matched records
db.Where("name <> ?", "Nathan").Find(&users)
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE name <> 'Nathan';
// Struct
db.Where(&User{Name: "Nathan", Age: 33}).First(&user)
// SELECT * FROM users WHERE name = "Nathan" AND age = 33 ORDER BY id LIMIT 1;
db.First(&user)
user.Name = "Roger"
user.Age = 33
db.Save(&user)
// UPDATE users SET name='Roger', age=33, updated_at = '2013-11-17 21:34:10' WHERE id=111;
Gorm limits
type User struct {
gorm.Model
Firstname string `gorm:"default:Nathan"`
Lastname string
CompanyID int
Company Company `gorm:"constraint:OnUpdate:CASCADE,OnDelete:SET NULL;"`
FullName string `gorm:"->;type:GENERATED ALWAYS AS (concat(firstname,' ',lastname));default:(-);"`
}
Is the purpose of your Go code to dictate your SQL schema?
Gorm limits
Gorm is a magic box. It can be really powerful, but its code-first approach creates a huge dependency to the tool, and can easily result with poor database performances.
Moreover Gorm is kind of a black box, performing some requests you're not thinking of, sometimes not useful.
ENT
ENT example
// User schema.
type User struct {
ent.Schema
}
// Fields of the user.
func (User) Fields() []ent.Field {
return []ent.Field{
field.Int("age"),
field.String("name"),
field.String("username").
Unique(),
field.Time("created_at").
Default(time.Now),
}
}ENT features
func QueryUser(ctx context.Context, client *ent.Client) (*ent.User, error) {
u, err := client.User.
Query().
Where(user.Name("Nathan")).
// `Only` fails if no user found,
// or more than 1 user returned.
Only(ctx)
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed querying user: %w", err)
}
log.Println("user returned: ", u)
return u, nil
}Based on your description, ENT will generate your SQL schema, then your Go structures. You will then be able to use the generated code.
Schema-first ORM

SQLc: generate code from SQL requests
sqlc generates type-safe code from SQL. Here's how it works:
- You write queries in SQL.
- You run sqlc to generate code with type-safe interfaces to those queries.
- You write application code that calls the generated code.
Works for Go, Kotlin, Python and Typescript. Mainly use database/sql package.
SQLc: https://play.sqlc.dev/
SQLBoiler: generate code from SQL schema
SQLBoiler comes with an approach to read the database schema, then generate code from it:
- Write your schema (use tools like SQL migrate to manage migrations)
- Launch SQLboiler tool
- Use generated code to query the database
Why I recommend SQLBoiler?

It allows you to focus on your database schema first.
It follows OVHcloud database team way of working.
It's powerful and will provide good help to discuss with the database.
WILFRIED
APPROVES
Install and use SQLBoiler
$ go install github.com/volatiletech/sqlboiler/v4@latest
$ go install github.com/volatiletech/sqlboiler/v4/drivers/sqlboiler-psql@latest
$ sqlboiler -c sqlboiler.toml psql# sqlboiler.toml configuration file
[psql]
dbname = "gocourse"
host = "localhost"
port = 5432
user = "gocourse"
pass = "test"
sslmode = "disable"SQLBoiler generation
SQLBoiler generates a lot of files, for different tables and types.
It provides helper to query the database: https://github.com/volatiletech/sqlboiler?tab=readme-ov-file#query-building
SQLBoiler, some examples
// SELECT COUNT(*) FROM pilots;
count, err := models.Pilots().Count(ctx, db)
// SELECT * FROM "pilots" LIMIT 5;
pilots, err := models.Pilots(qm.Limit(5)).All(ctx, db)
// SELECT * FROM "pilots" WHERE "name"=$1;
pilots, err := models.Pilots(qm.Where("name=?", "Porco")).All(ctx, db)
// type safe version of above
pilots, err := models.Pilots(models.PilotWhere.Name.EQ("Porco")).All(ctx, db)
// SELECT * FROM "pilots" WHERE "name"=$1 LIMIT 1;
pilot, err := models.Pilots(models.PilotWhere.Name.EQ("Porco")).One(ctx, db)
// SELECT * FROM "pilots" WHERE id = $1;
pilot, err := models.FindPilot(ctx, db, 42)models is the name of the generated package by SQLBoiler with structs and methods.
SELECT with SQLBoiler
Write the SelectAllPets and SelectOnePet functions.

file/to/open.go$ go test -run ^TestSelectAllPets$
$ go test -run ^TestSelectOnePet$File to open:
Test your code:
database/sqlboiler/select.goSelect with SQLBoiler
func SelectAllPets() ([]shelter.Pet, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pets, err := models.Pets().All(ctx, db)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
shelterPets := make([]shelter.Pet, len(pets))
for i, pet := range pets {
category, err := pet.PetCategory().One(ctx, db)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
shelterPets[i] = shelter.Pet{
Id: pet.ID,
Name: pet.Name,
Category: category.Name,
}
}
return shelterPets, nil
}Select one pet
func SelectOnePet(id int) (shelter.Pet, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
pet, err := models.FindPet(ctx, db, id)
if err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
category, err := pet.PetCategory().One(ctx, db)
if err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
return shelter.Pet{
Id: pet.ID,
Name: pet.Name,
Category: category.Name,
}, nil
}SQLBoiler update
func UpdatePetName(id int, newName string) error {
ctx := context.Background()
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return err
}
databasePet, err := models.FindPet(ctx, db, id)
if err != nil {
return err
}
databasePet.Name = newName
_, err = databasePet.Update(ctx, db, boil.Infer())
return err
}SQLBoiler insert
func InsertNewPet(pet shelter.Pet) (shelter.Pet, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
db, err := connect.SQL()
if err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
category, err := models.Categories(models.CategoryWhere.Name.EQ(pet.Category)).One(ctx, db)
if err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
databasePet := models.Pet{
Name: pet.Name,
Category: null.NewInt(category.ID, true),
}
if err := databasePet.Insert(ctx, db, boil.Infer()); err != nil {
return shelter.Pet{}, err
}
return shelter.Pet{
Id: databasePet.ID,
Name: databasePet.Name,
Category: category.Name,
}, nil
}SQL and null values
Go database/sql package provides NullX types to handle nullable values.
If your field is nullable in your database, then consider using the proper Null type to pass or get the field.
Choose the right ORM
Code-first
Make things easier for a PoC. Focus on your code, not on your database.
Hard to maintain on large codebase, pollute your code.
Bad experience with Gorm.
Schema-first
Focus on your database first, then on your code. You can keep your code clean from database-related information.
Take more time to get results.
Choose the right ORM
Take time to test a bit the different solutions. You can start with SQLx, then migrate to a more complex ORM if needed.
If you do so, I'd suggest to use SQLBoiler.
Writing a HTTP API

Writing a HTTP API
What are we looking for when writing a HTTP API?
- Routing
- Write outputs
- Reading inputs
- Middlewares
Let's have an example of those concepts in Go standard library: net/http
Router
Also known as multiplexer/mux.
Role:
- Associate an incoming request to a function
- Request is defined by its path (/pet), and its method (GET)
- Associated function is known as Handler
Handlers
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello World!\n")
}In Go, a Handler is a specific function with a given signature.
In our example, HelloWorld is a HTTP handler, and can be used as it.
Routing
package main
import (
"fmt"
"net/http"
)
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello World!\n")
}
func main() {
http.HandleFunc("/hello", HelloWorld)
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil)
}Write ouputs
To write a response, we have a dedicated object in the handler signature: the http.ResponseWriter object!
This object is an interface!
Interfaces
An interface type is defined as a set of method signatures.
A value of interface type can hold any value that implements those methods.
Interface
package main
import (
"fmt"
)
type Hello interface {
Say() string
}
func Print(helloInterface Hello) {
fmt.Println(helloInterface.Say())
}
type MyStruct struct{}
func (m MyStruct) Say() string {
return "Hello from MyStruct"
}
func main() {
m := MyStruct{}
Print(m)
}
Back to http.ResponseWriter
Let's have a look on the methods of this interface:
- Header() to write HTTP headers
- Write([]byte) (int, error) to write content
-
WriteHeader(statusCode int) to write the HTTP response code
-
Only the first call will have an effect
-
Write ouputs
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Header().Add("Content-Type", "text/plain")
w.Write([]byte("Hello World!\n"))
}Write outputs in a JSON format
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
output := map[string]string{
"firstname": "Ada",
"lastname": "Lovelace",
}
body, err := json.Marshal(output)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(string(body))
}To transform Go objects into proper JSON, we can use the encoding/json package! It provides a json.Marshal(object) function.
Write outputs
Let's write a simple function to write our result!

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/result_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/result.goWrite outputs
func WriteJSONResult(w http.ResponseWriter, statusCode int, result interface{}) {
b, err := json.Marshal(result)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
w.Write([]byte(http.StatusText(http.StatusInternalServerError)))
return
}
w.Header().Add("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.WriteHeader(statusCode)
w.Write(b)
}Read inputs
You probably noticed that a HTTP handler in Go has a signature with two parameters:
- a http.ResponseWriter
- a http.Request
Let's now have a look on the second one!
Reading inputs:
the http.Request object
On a request, inputs can be read from multiple sources:
- Query parameter: GET localhost:8080?input=value
- HTTP header
- Path parameter: GET localhost:8080/pet/1
- Request body: string, JSON, XML, ...
All of this can be read from the http.Request object given in the Handler signature!
Query parameter
request.URL.Query().Get("input")Header
request.Header.Get("Content-Type")Path parameter
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
name := r.PathValue("name")
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello %s!\n", name)
}
func main() {
mux := http.NewServeMux()
mux.Handle("/hello/{name}", http.HandlerFunc(HelloWorld))
http.ListenAndServe(":8080", mux)
}Path parameter can be fetched using request.PathValue().
Note that this is only working while using the new Mux server (Go 1.22)
Body
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
body, err := io.ReadAll(request.Body)
...
}A HTTP request can contain a body. The body is represented as a buffer, that we need to consume to access to all the data.
Read inputs
Complete all functions to read from the http.Request object!

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/request_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/request.goRead inputs
func QueryParamString(request *http.Request, paramName string) string {
return request.URL.Query().Get(paramName)
}
func QueryParamInt(request *http.Request, paramName string) (int, error) {
paramAsString := request.URL.Query().Get(paramName)
return strconv.Atoi(paramAsString)
}
func Header(request *http.Request, headerName string) string {
return request.Header.Get(headerName)
}
func Path(request *http.Request, parameterName string) string {
return request.PathValue(parameterName)
}
func PathInt(request *http.Request, parameterName string) (int, error) {
paramAsString := request.PathValue(parameterName)
return strconv.Atoi(paramAsString)
}
func Body(request *http.Request) ([]byte, error) {
body, err := io.ReadAll(request.Body)
return body, err
}Read JSON
We usually dialog with JSON format through HTTP APIs.
How to read and parse JSON from the body?
Read JSON
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
input := []byte(`{
"firstname": "Grace",
"lastname": "Hopper"
}`)
result := make(map[string]string)
err := json.Unmarshal(input, &result)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(result)
}Limits
{
"name": "Nathan",
"age": 34
}What if our json looks like this?
Let's use structs and JSON tags!
package main
import (
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
)
type Person struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Age int `json:"age"`
}
func main() {
input := []byte(`{
"name": "Grace",
"age": 34
}`)
var result Person
err := json.Unmarshal(input, &result)
if err != nil {
panic(err)
}
fmt.Println(result.Name, result.Age)
}JSON tags
JSON tags are mainly used to dictate how an object should be marshalled and unmarshalled in JSON.
It works in both directions!
Pet shelter API
Looks like we now have many functions that will help us to write the Pet Shelter API!
Pet shelter router
func NewServer(shelter shelter.PetRepository) *Server {
server := &Server{
shelter: shelter,
mux: http.NewServeMux(),
}
server.mux.HandleFunc("GET /pet", server.ListPetsHandler)
server.mux.HandleFunc("GET /pet/{id}", server.GetOnePetHandler)
server.mux.HandleFunc("PUT /pet/{id}", server.UpdatePetHandler)
return server
}
func (s *Server) Run() error {
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":8080",
Handler: s.mux,
}
slog.Info("Listening...", slog.String("address", "localhost:8080"))
return server.ListenAndServe()
}List pets
Write the ListPetsHandler.

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/list_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/list.goList pets
func (s *Server) ListPetsHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
pets, err := s.shelter.SelectAllPets()
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprint(w, err.Error())
return
}
WriteJSONResult(w, http.StatusOK, pets)
}
Get pet by ID
Write the GetOnePetHandler!

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/getById_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/getById.goGet pet by ID
func (s *Server) GetOnePetHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
id, err := PathInt(r, "id")
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusBadRequest)
fmt.Fprintf(w, "invalid pet id %d", id)
return
}
pet, err := s.shelter.SelectOnePet(id)
if err != nil {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusInternalServerError)
fmt.Fprint(w, err.Error())
return
}
WriteJSONResult(w, http.StatusOK, pet)
return
}Get pet by id - step 2
Let's now imagine we want to accept a query parameter:
- GET /pet/42?format=lowercase
When this parameter is given, we want to return the object with json keys lowercased. Write the required code!

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/getById_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/getById.go{
"id": 1,
"name": "Daffy",
"category": "duck"
}Get pet by ID - step 2
func (s *Server) GetOnePetHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
...
pet, err := s.shelter.SelectOnePet(id)
...
if QueryParamString(r, "format") == "lowercase" {
type tmp struct {
Id int `json:"id"`
Name string `json:"name"`
Category string `json:"category"`
}
p := tmp{
Id: pet.Id,
Name: pet.Name,
Category: pet.Category,
}
WriteJSONResult(w, http.StatusOK, p)
return
} else {
WriteJSONResult(w, http.StatusOK, pet)
return
}
}Update a pet
Last but not least, it's time to read some JSON input to update a pet with a new name!
Update a pet
This is the provided input of your API:
You will need to read body and unmarshal the JSON (into a struct or a map).

file/to/open.goapi/nethttp/update_test.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/nethttp/update.goPUT /pet/{id}
{
"newName": "Robert"
}Update a pet
type updatePet struct {
NewName string `json:"newName"`
}
func (s *Server) UpdatePetHandler(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
id, err := PathInt(r, "id")
if err != nil {
...
}
body, err := Body(r)
if err != nil {
...
}
updateInfos := updatePet{}
if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &updateInfos); err != nil {
...
}
if updateInfos.NewName == "" {
...
}
err = s.shelter.UpdatePetName(id, updateInfos.NewName)
if err != nil {
...
}
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
}net/http, a powerful standard package
net/http is a powerful package, providing you features to build your HTTP API.
But if you start to work on a huge project, you will notice that you will often write the same methods again and again for:
- Encode and write results
- Manage authentication and middlewares
- ...
This is why you can also have a look on non-standard web frameworks for your projects!
Web frameworks: work easier thanks to the community
Web frameworks will provide helpers for:
- HTTP routing
- Binding input and output JSON, XML, form payload, ...
- Error handling
- Middlewares
- ...
Most famous web frameworks
Over the years, multiple web frameworks became famous for Go.
| Web Framework | Github | # of stars |
|---|---|---|
| Gin | https://github.com/gin-gonic/gin | 75k |
| Echo | https://github.com/labstack/echo | 28k |
| Chi | https://github.com/go-chi/chi | 17k |
| Iris | https://github.com/kataras/iris | 25k |
The best one?

All of them, or none of them. No huge differences between them, there is no wrong choice.
Starting with net/http is also a good choice to do not have dependencies and understand the concepts!
Let's have a focus on Echo!
Echo, a simple example
https://echo.labstack.com/
// Handler
func hello(c echo.Context) error {
return c.JSON(http.StatusOK, map[string]string{"Hello": "World!"})
}
func main() {
// Echo instance
e := echo.New()
// Routes
e.GET("/", hello)
// Start server
e.Logger.Fatal(e.Start(":8080"))
}Each web framework defines a way to declare handlers, and to register routes.
Working with
OpenAPI 3

An API is a contract.
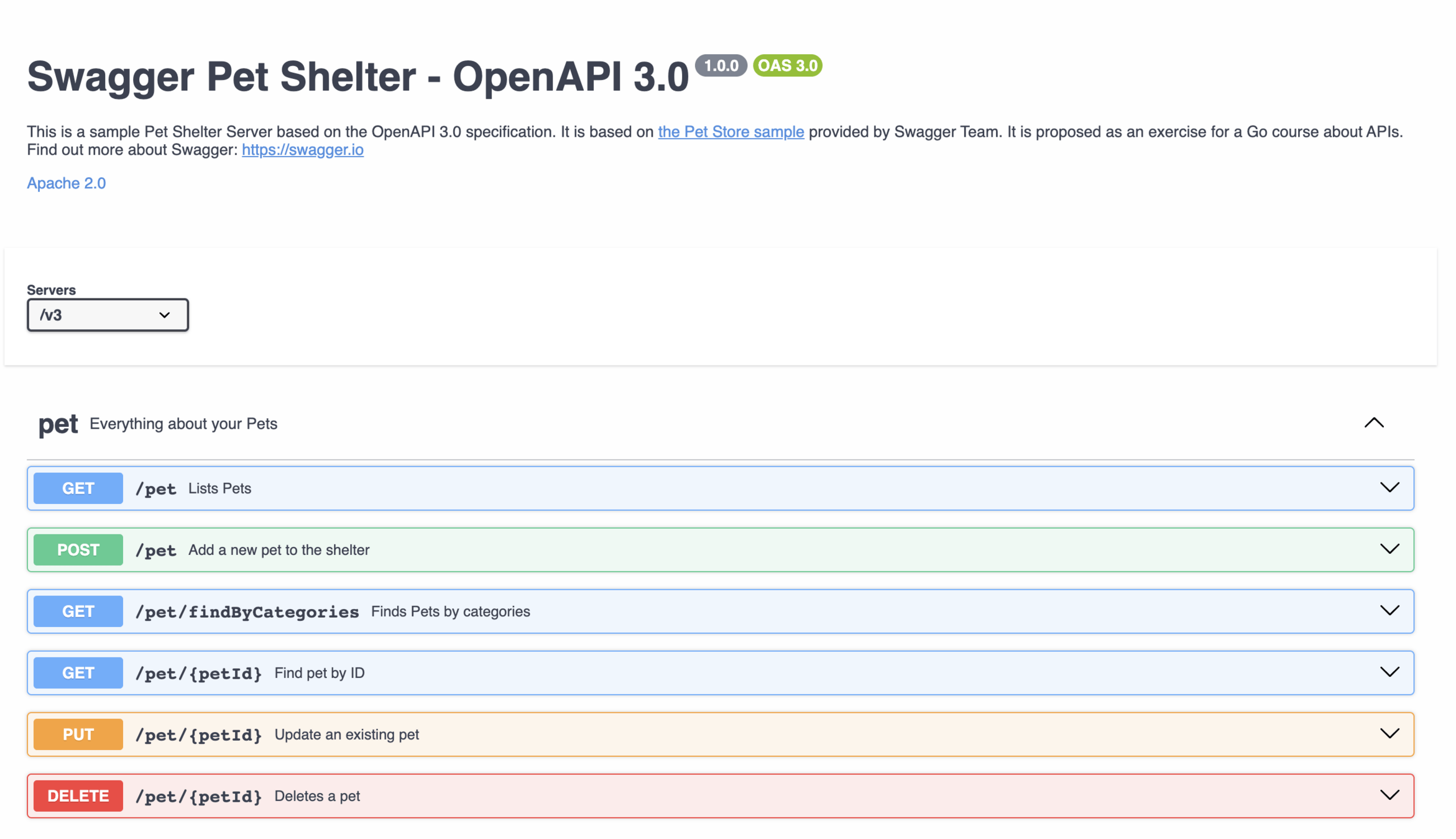
When you design an API, you write a contract with your customers.
You propose a set of endpoints and associated methods to use your services in a certain way.
This contract is a building block of your API.
A contract? Meet OpenAPI 3
The OpenAPI Specification (OAS) defines a standard, language-agnostic interface to HTTP APIs which allows both humans and computers to discover and understand the capabilities of the service without access to source code, documentation, or through network traffic inspection.
An OpenAPI definition can then be used by documentation generation tools to display the API, code generation tools to generate servers and clients in various programming languages, testing tools, and many other use cases.
Working with OpenAPI 3
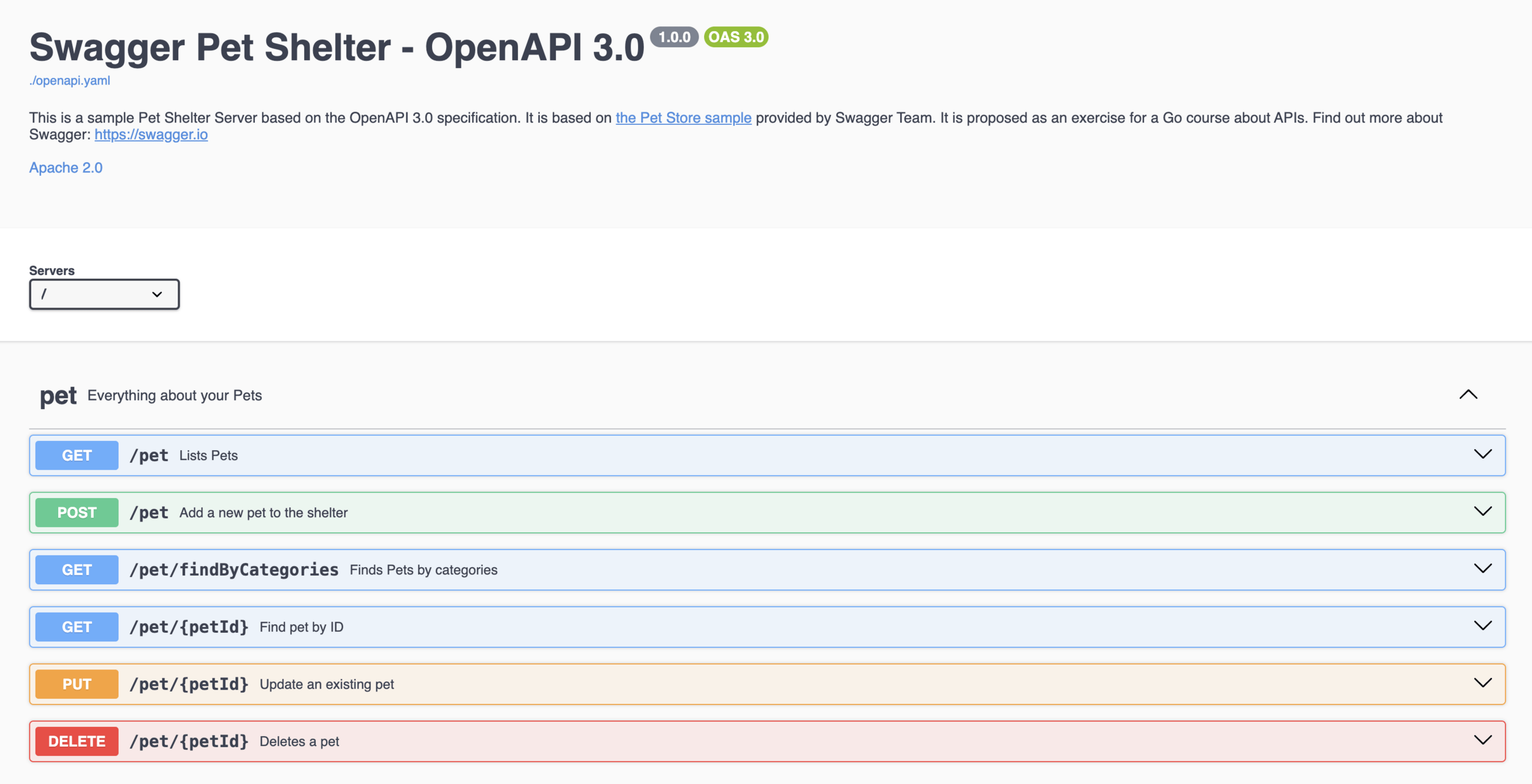
Working with OpenAPI 3
In Go, you have two choices to work with OpenAPI 3...
- Schema-first: Write your OpenAPI 3 file, then generate code and HTTP handlers from the schema
- Code-first: Annotate your code with information related to your schema, then generate the OpenAPI 3 schema from your code
Schema-first approach
$ go install github.com/deepmap/oapi-codegen/v2/cmd/oapi-codegen@latest
$ oapi-codegen -package petshelter openapi.yaml > petshelter.gen.goThanks to this tool: https://github.com/deepmap/oapi-codegen
It generates structures for inputs and outputs, http handlers, and client boilerplate. It provides a lot of options for configuration.
Other tools:
Code-first approach
There are no viable approach for OpenAPI 3. But there are alternative working with OpenAPI 2: https://github.com/swaggo/swag
// ListAccounts godoc
// @Summary List accounts
// @Description get accounts
// @Tags accounts
// @Accept json
// @Produce json
// @Param q query string false "name search by q" Format(email)
// @Success 200 {array} model.Account
// @Failure 400 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 404 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Failure 500 {object} httputil.HTTPError
// @Router /accounts [get]
func (c *Controller) ListAccounts(ctx *gin.Context) {
q := ctx.Request.URL.Query().Get("q")
accounts, err := model.AccountsAll(q)
if err != nil {
httputil.NewError(ctx, http.StatusNotFound, err)
return
}
ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, accounts)
}Schema-first or code-first?
As I did for SQL ORMs, I'd definitely suggest to use schema-first approach.
You focus on your API contract, then you generate boilerplates and write your handlers.
OpenAPI 3 is a powerful specification, and a lot of tools can be helpful to work with your API. So I'd suggest to work on a proper OpenAPI 3 definition and generate what you need (boilerplates, tests, SDK, etc.)
Echo & OpenAPI 3

First of all, let's generate boilerplates using oapi-codegen
$ cd openapi
$ oapi-codegen -package openapi ./openapi.yaml > petshelter.gen.goIt generates a petshelter.gen.go file
oapi-codegen result
...
// ServerInterface represents all server handlers.
type ServerInterface interface {
// Lists Pets
// (GET /pet)
ListPets(ctx echo.Context) error
// Add a new pet to the shelter
// (POST /pet)
AddPet(ctx echo.Context) error
// Finds Pets by categories
// (GET /pet/findByCategories)
FindPetsByCategories(ctx echo.Context, params FindPetsByCategoriesParams) error
// Deletes a pet
// (DELETE /pet/{petId})
DeletePet(ctx echo.Context, petId int) error
// Find pet by ID
// (GET /pet/{petId})
GetPetById(ctx echo.Context, petId int) error
// Rename a pet
// (POST /pet/{petId}/rename)
RenamePetById(ctx echo.Context, petId int) error
}
...ListPets
List all pets using sqlboiler.SelectAllPets function.
The newOpenAPIPet function is provided to create an openapi.Pet from a shelter.Pet.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
ListPets
func (s *Server) ListPets(ctx echo.Context) error {
pets, err := sqlboiler.SelectAllPets()
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "internal server error")
}
jsonPets := make([]openapi.Pet, len(pets))
for i, pet := range pets {
jsonPets[i] = newOpenAPIPet(pet)
}
return ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, jsonPets)
}FindPetsByCategories
List pets filtered by categories using sqlboiler.SelectByCategories.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
FindPetsByCategories
func (s *Server) FindPetsByCategories(ctx echo.Context, params openapi.FindPetsByCategoriesParams) error {
pets, err := sqlboiler.SelectByCategories(params.Categories...)
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "internal server error")
}
jsonPets := make([]openapi.Pet, len(pets))
for i, pet := range pets {
jsonPets[i] = newOpenAPIPet(pet)
}
return ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, jsonPets)
}GetPetById
Get one pet using sqlboiler.SelectOnePet function.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
GetPetById
func (s *Server) GetPetById(ctx echo.Context, petId int) error {
pet, err := sqlboiler.SelectOnePet(petId)
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusNotFound, "pet not found")
}
return ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, newOpenAPIPet(*pet))
}AddPet
Add a new pet using sqlboiler.InsertNewPet function.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
AddPet
func (s *Server) AddPet(ctx echo.Context) error {
addPet := openapi.AddPetJSONRequestBody{}
if err := ctx.Bind(&addPet); err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "fail to read body")
}
pet, err := sqlboiler.InsertNewPet(&shelter.Pet{
Name: addPet.Name,
Category: addPet.Category,
})
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "fail to insert pet")
}
return ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, newOpenAPIPet(*pet))
}DeletePet
Delete one pet using sqlboiler.DeleteOnePet function.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
DeletePet
func (s *Server) DeletePet(ctx echo.Context, petId int64) error {
err := sqlboiler.DeleteOnePet(int(petId))
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "deletion failed")
}
return ctx.NoContent(http.StatusOK)
}RenamePetById
Rename a pet using sqlboiler.UpdatePet function.

File to open:
api/echo/codegen/server.gofile/to/open.go$ go run *.goTest your code:
RenamePetById
func (s *Server) RenamePetById(ctx echo.Context, petId int) error {
updatePet := openapi.RenamePetByIdJSONRequestBody{}
if err := ctx.Bind(&updatePet); err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusBadRequest, "fail to read body")
}
if err := sqlboiler.UpdatePetName(petId, updatePet.Name); err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "fail to update pet")
}
pet, err := sqlboiler.SelectOnePet(petId)
if err != nil {
return ctx.String(http.StatusInternalServerError, "fail to select pet")
}
return ctx.JSON(http.StatusOK, newOpenAPIPet(pet))
}Middleware

Middleware
A middleware in a web framework is a piece of code that will be called on each request.
In a middleware, you will be able to perform actions before and/or after each request, stop the request, etc.
Common usages:
- Logs
- Authentication
- Timeout
- Prometheus
- ...
Middleware with net/http
func Logger(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
slog.Info("starting request")
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
slog.Info("request end")
})
}
func HelloWorld(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {
w.WriteHeader(http.StatusOK)
w.Write([]byte("Hello World!\n"))
}
func main() {
http.Handle("GET /hello", Logger(http.HandlerFunc(HelloWorld)))
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}Middleware chain
func main() {
http.Handle("GET /hello", TimeElapsed(Logger(http.HandlerFunc(HelloWorld))))
if err := http.ListenAndServe(":8080", nil); err != nil {
log.Fatal(err)
}
}Middleware can be chained.
Middleware
Let's write a middleware which print the time elapsed for a request to be performed. Check the package time!
Expected output:

file/to/open.go$ go run *.goFile to open:
Test your code:
api/middleware/time.goThen curl
http://localhost:8080/hello
elapsed time=247.417µsMiddleware
func TimeElapsed(next http.Handler) http.Handler {
return http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
startedAt := time.Now()
next.ServeHTTP(w, r)
slog.Info("elapsed", slog.Any("time", time.Since(startedAt)))
})
}
Middleware in echo
func LogTime(next echo.HandlerFunc) echo.HandlerFunc {
return func(c echo.Context) error {
start := time.Now()
if err := next(c); err != nil {
c.Error(err)
}
elapsed := time.Since(start)
c.Logger().Printf("time elapsed: %s", elapsed)
return nil
}
}
What's next?
Complete usage of the standard library:
https://www.jetbrains.com/guide/go/tutorials/rest_api_series/stdlib/
A simple tutorial with Go and Gin: https://go.dev/doc/tutorial/web-service-gin
Learn Echo's features: https://echo.labstack.com/docs
Dive into OpenAPI 3: https://swagger.io/specification/
Ask me if you have any questions!
Thanks! Questions?


