Appcelerator's Titanium
Intro
"An open, extensible development environment for creating beautiful native apps across different mobile devices and OSs including iOS, Android, and BlackBerry, as well as hybrid and HTML5. It includes an open source SDK with over 5,000 device and mobile operating system APIs, Studio, a powerful Eclipse-based IDE, Alloy, an MVC framework and Cloud Services for a ready-to-use mobile backend." – appcelerator.com
Titanium SDK
"The Titanium SDK helps you to build native cross-platform mobile application using JavaScript and the Titanium API, which abstracts the native APIs of the mobile platforms. Titanium empowers you to create immersive, full-featured applications, featuring over 80% code reuse across mobile apps. Appcelerator licenses Titanium under the Apache 2 license and is free for both personal and commercial use." – appcelerator.com
What problem solves?
Each platform has their own native controls, also, their own UX flows, Titanium try to solve this problems.
Foursquare
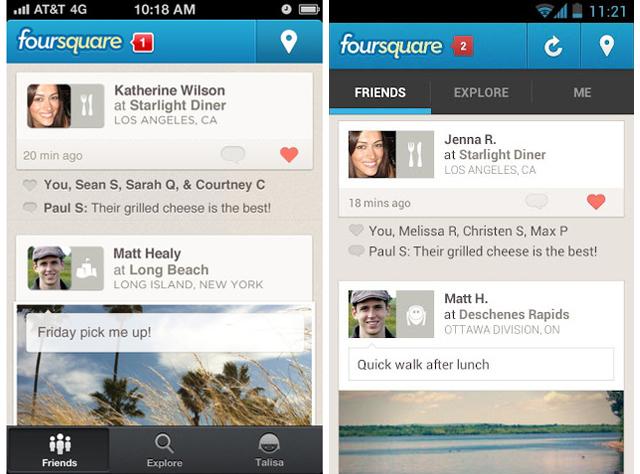
Demo
Classic
tiapp.xml is the file where all the application saves it's configuration.
app.js works as the main entry point of our application.
The Resources folder saves all our JavaScript code, also our assets.
i18n folder has our strings to be translated.
CommonJS Module Specification is implemented, so require() function works like in node.js, YAY!.
UI implementation isn't so easy, some logic needs to be written in order to handle different platforms.
Alloy
"It is a development framework to facilitate the rapid development of high quality mobile applications. It follows a model-view-controller (MVC) architecture and using XML and CSS it provides a simple model for separating the application user interface, business logic and data models." – appcelerator.com
Features
Standard MVC framework built on Node.js with Backbone.js and Underscore.js support.
Fully code your app using XML, CSS (likely) and JavaScript.
Use Alloy CSS themes to manage your app’s look and feel.
Easily bind data sources to your apps’ user interface.
Reusable widgets support.
Offline storage support.
Fully integrated with Studio.
Models
Models inherit from the Backbone.Model class.
Model anatomy
exports.definition = {
config : {
// table schema and adapter information
},
extendModel: function(Model) {
_.extend(Model.prototype, {
// Extend, override or implement Backbone.Model
});
return Model;
},
extendCollection: function(Collection) {
_.extend(Collection.prototype, {
// Extend, override or implement Backbone.Collection
});
return Collection;
}
} Model local instance
var book = Alloy.createModel('book', {title:'Green Eggs and Ham', author:'Dr. Seuss'});
var title = book.get('title');
var author = book.get('author');
// Label object in the view with id = 'label'
$.label.text = title + ' by ' + author; Model global instance
// This will create a singleton if it has not been previously created,
// or retrieves the singleton if it already exists.
var book = Alloy.Models.instance('book'); Models
Models inherit from the Backbone.Model class.
To access a model locally in a controller, use the Alloy.createModel method.
You can also create a global singleton instance of a model, either in markup or in the controller, which may be accessed in all controllers.
Model local collection
var library = Alloy.createCollection('book');
library.fetch(); // Grab data from persistent storageModel global collection
// This will create a singleton if it has not been previously created,
// or retrieves the singleton if it already exists.
var library = Alloy.Collections.instance('book');Models
Models inherit from the Backbone.Model class.
To access a model locally in a controller, use the Alloy.createModel method.
You can also create a global singleton instance of a model, either in markup or in the controller, which may be accessed in all controllers.
Collections are ordered sets of models and inherit from the Backbone.Collection class.
You can create a collection via Alloy.createCollection method or Alloy.Collections.instance to access it globally.
Controllers
Controllers contain the application logic used to control the UI and communicate with the model.
Controller anatomy
// controllers/index.jsfunction doClick(e) {
alert($.label.text);
}
$.index.open(); // views/index.xml<Alloy>
<Window class="container">
<Label id="label" onClick="doClick">Hello, World</Label>
</Window>
</Alloy>
Controllers
Controllers contain the application logic used to control the UI and communicate with the model.
All UI elements which have an id attribute in a view are automatically defined and available as a property prefixed by the special variable $ in the controller.
To access external controllers and views, use the Alloy.createController and Controller.getView methods, respectively.
Controllers
Controllers contain the application logic used to control the UI and communicate with the model.
All UI elements which have an id attribute in a view are automatically defined and available as a property prefixed by the special variable $ in the controller.
To access external controllers and views, use the Alloy.createController and Controller.getView methods, respectively.
Controllers can inherit from other controllers by assigning it a base (parent) controller: exports.baseController = "baseControllerName" .
Conditional code
OS_ANDROID, true if the current compiler target is Android.
OS_BLACKBERRY, true if the current compiler target is BlackBerry.
OS_IOS, true if the current compiler target is iOS.
OS_MOBILEWEB, true if the current compiler target is Mobile Web.
ENV_DEV, true if the current compiler target is built for development (running in the simulator or emulator).
ENV_TEST, true if the current compiler target is built for testing on a device.
ENV_PRODUCTION, true if the current compiler target is built for production (running after a packaged installation).
Conditional code
if (OS_IOS)
{
var closeButton = Ti.UI.createButton({
title: 'Close',
style: Ti.UI.iPhone.SystemButtonStyle.PLAIN
});
closeButton.addEventListener('click', function(){
$.window.close();
});
$.window.leftNavButton = closeButton;
} Passing arguments
When initializing an external controller, you can pass arguments to customize it, for instance, var controller = Alloy.createController("controller", {args1: "foo"}) . In the external controller, the special variable arguments[0] is used to receive the arguments.
Passing arguments
// views/row.xml<Alloy>
<TableViewRow id="rowView"/>
</Alloy>
// controllers/row.jsvar args = arguments[0] || {};
$.rowView.title = args.title || "";
$.rowView.url = args.url || ""; Passing arguments
var data = [];
for (var i = 0; i < source.length; i++) {
var arg = {
title: source[i].postTitle,
url: source[i].postLink
};
var row = Alloy.createController("row", arg).getView();
data.push(row);
}
$.tableView.setData(data); alloy.js
It's the initializer file.
Can be used to execute some code near the beginning of the application's lifecycle.
Views
"In Alloy, the view component represents the UI of the application, comprised of XML markup and Titanium style sheets. The XML markup defines the structure of the view, while the TSS file contains the styling elements applied to the XML markup--similar to the relationship between HTML and CSS." – appcelerator.com
XML
It abstracts the Titanium SDK UI components.
You do not need to code the creation and setup of these components using JavaScript and the Titanium SDK API.
Within a controller, a UI component can be referenced if its id attribute is defined.
XML
// views/index.xml<Alloy>
<Window class="container">
<Label id="label" onClick="doClick">Hello, World</Label>
</Window>
</Alloy>
TSS
Titanium Style Sheets (TSS) file uses a JSON-like syntax to define the attributes of elements in the XML files.
Attributes are the properties of the Titanium object.
Styles are defined at three different levels: markup element, class attribute and the id attribute.
TSS
// This is applied to any element with the class attribute assigned to "container"
".container": {
backgroundColor:"white"
},
// This is applied to all Labels in the view
"Label": {
width: Ti.UI.SIZE,
height: Ti.UI.SIZE,
color: "#000", // black
transform: Alloy.Globals.rotateLeft // value is defined in the alloy.js file
},
// This is only applied to an element with the id attribute assigned to "label"
"#label": {
color: "#999" /* gray */
} TSS
Titanium Style Sheets (TSS) file uses a JSON-like syntax to define the attributes of elements in the XML files.
Attributes are the properties of the Titanium object.
Styles are defined at three different levels: markup element, class attribute and the id attribute.
There's a global style file, called app.tss , which applies all styles defined inside it to all views.
You can specify platform or device size conditionals, [platform=ios,android], [platform=ios formFactor=tablet].
Custom query styles, also themes are allowed.