Towards an All-IP-Based UMTS System Architecture
Authors: Lieve Bos and Suresh Leroy, Alcatel
Presented by: Neil Koul
Background
UMTS
- Universal Mobile Telecommunications System
- 3rd Generation cell communication
- Based on the GSM system, maintained by 3GPP
- Was in competition with the cdmaOne technology
Main Goal
Clarify Implications of IP-based core network on UMTS
Virtual Home Environment
Standardizing capabilities instead of services.
What is VHE?
- Intended to allow users to access services outside of home network
- Make the user feel "virtually at home"
- Automatic message adaptation depending on what the user is connected to
VHE Terminology
- Service Capability Servers (SCSs) - servers that allow for services to be constructed
- Service Capability Features (SCFs) - classes/services constructed by SCSs
- Their purpose is to raise abstraction of network interfaces in order to simplify app development
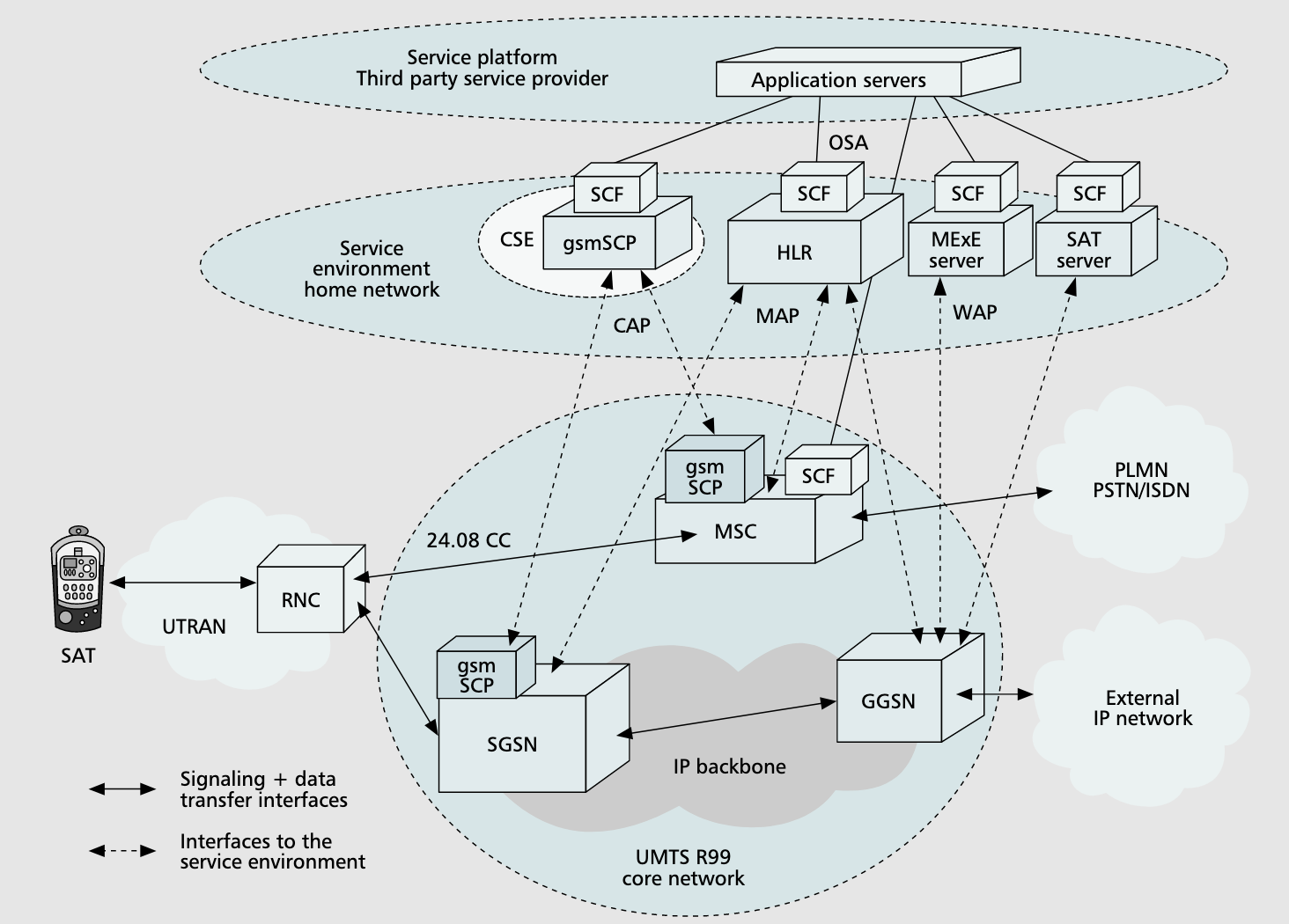
VHE SCSs
- UTMS call control servers- manage bearer/call control capabilities, R99 only allows circuit-switched telephony
- Home Location Register (HLR)- database that contains location and subscriber information
- Mobile Execution Environment (MExE)- a JVM or WAP browser, where value-added services are offered
- SIM application toolkit (SAT)- additional SIM features that allow for extra authentication information into terminals
- Customized Application for Mobile Networks Enhanced Logic (CAMEL)- extends traditional intelligent network scope.
R99 UMTS

Voice over IP
Is VoIP better than traditional telephony?
R00 Features
- IP-based multimedia services as extension of packet-switched services
- Circuit-switched transport is replaced by packet-based network transport
- IP transport on the Radio Access Network (RAN/UTRAN)
- Network architecture is independent of transport layer, can be ATM or IP
What it would take for all IP-based core
- Roaming and Handover to 2G support
- Support of 3G circuit-switched terminals (for backwards compatibility)
- Support of new speed, SMS and other services that are all legacy as well as new IP-based versions
R00 All-IP Architecture
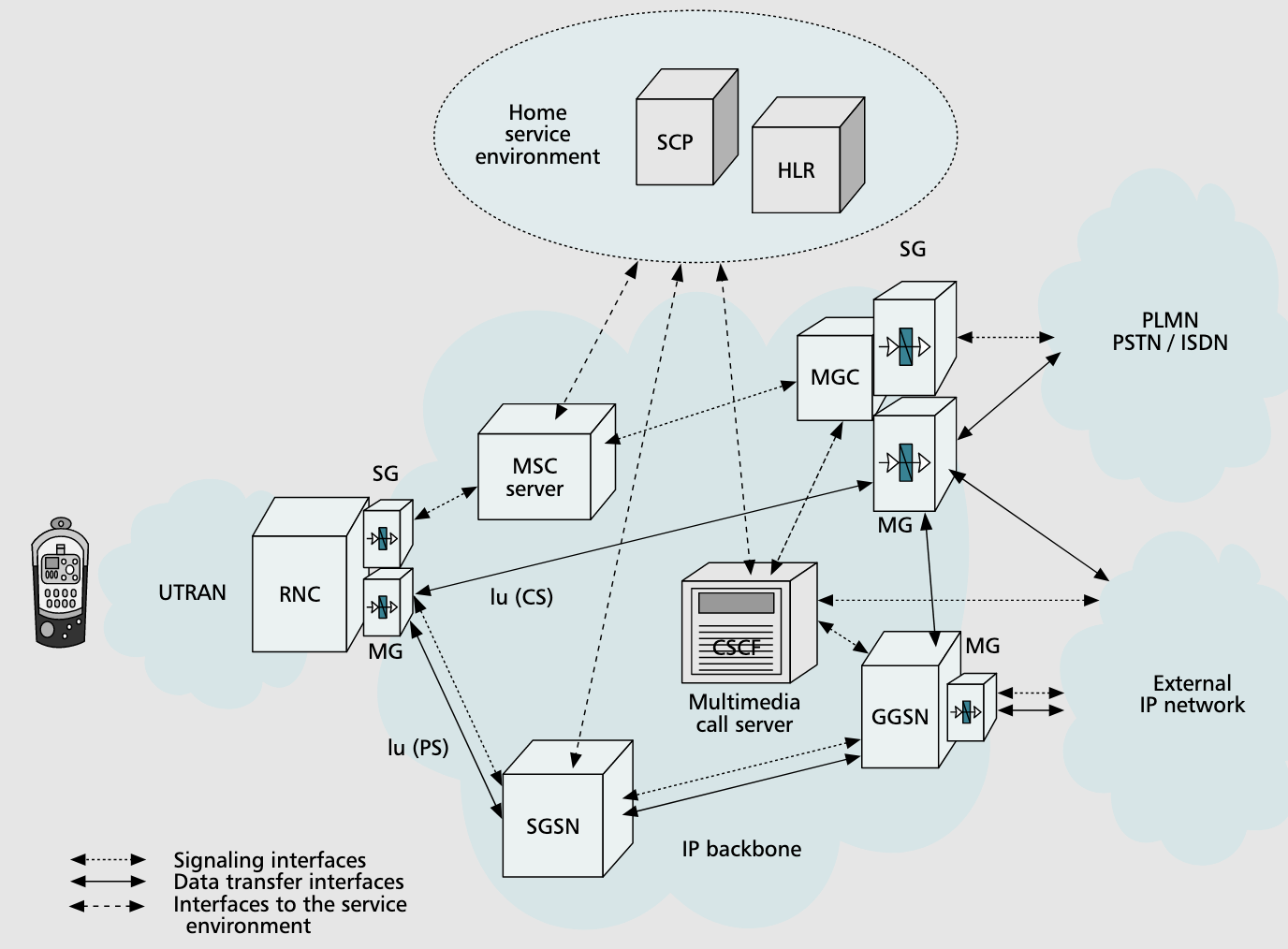
New Elements in IP Arch
- MSC- controls calls from circuit-switched terminals to mobile terminated calls, controls VoIP vs non VoIP
- Call state control function(CSCF)- provides/controls multimedia services for packet terminals
- MG at UTRAN side- transforms VoIP packets into UMTS frames
- MG at PTSN side- calls from PTSN converted into VoIP calls for transport in UMTS core network
- Signalling Gateway (SG)- relays all call-related signaling from PTSN/UTRAN on IP bearer and sends data to MGCF
- MGCF- control MGs, and provides translation
- Home Subscriber Server (HSS)- HLR extension with multimedia profile
VoIP in VHE
Two scenarios for providing VoIP in VHE
Scenario 1
SoftSSP Concept INAP/CAP
- The IN Application Part (INAP) triggers Service Control Point (SCP) reliant on Service Switching Point (SSP)
- CAMEL Application Part (CAP) is the same as INAP but in CAMEL
- The "SoftSSP" is to be build on top of the Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) server, to ensure that services can be provided via IN/CAMEL
- Mapping between the SIP call state model and the state model of IN/CAMEL
Scenario 1
VoIP on CSCF
- CSCF-SoftSSP must carry sufficient call data for the SoftSSP to deliver data to the SCP so service logic can function
- It also must allow SCP with the SoftSSP to control VoIP calls, like changing party address, add/remove media components, and to manipulate call information
Scenario 1
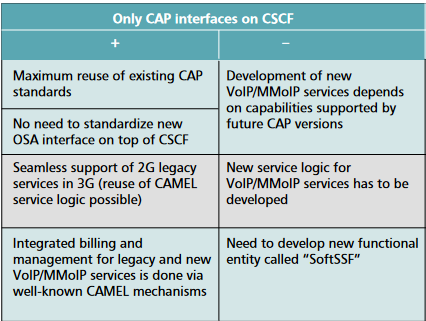
Advantages of SoftSSP
- Helps existing operators since UMTS R99 or GSM is already in use
- The newer CAMEL service environment creation methods work on legacy systems
- Mapping between CAP and SIP call control allow for VoIP to act like traditional services
Scenario 1
Disadvantage of SoftSSP
- Third Party Service providers can get access to the operators network via only the SCP
- They cannot get access to the CSCF, which implies no way of access to manage VoIP services
Scenario 2
3rd Party Support via CGI/CPL/SIP
- Two possible gateways for Third Party to allow access and control of network entities
- The Common Gateway Interface (CGI) : a mechanism already used on the internet for dynamic web pages, In the SIP, CGIs are triggered when requests arrive at server
- The the Call Processing Languages (CPL): Scripting language for network servers, allowing for immediate instantiation, and report back to controller CPL
Scenario 2
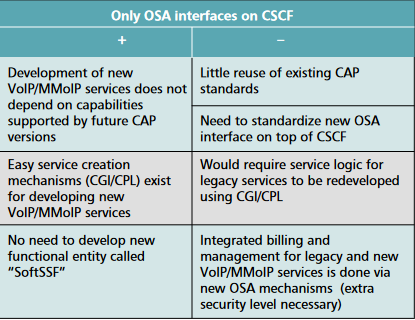
OSA arch for CGI and CPL
- Standardized representation for creating services in an order to enable multi vendor implementations
- Portability such that abstractions are defined and a high-level and are not SIP-specific, allowing portability between protocols
- Scripts are to be verified to ensure that it can run sucessfully
- Initiated services must be sure they can be terminated
- The integrity of other users must not be effected via the script run
OSA with SCP
vs
OSA with CSCF
Which is better?