Data Structures and Algorithms
muigai unaka
Week 1
Goals of this plan
- Learn Data Structures and Algorithms
- Identify patterns to determine the Data Structure(s) and Algorithm(s) to best solve a particular problem
- Practice and prepare technical interview skills
How do we reach our goal?
- Meet once a week for 12 weeks
- Commit 15 hours to reading and problem solving on our own time
- Mock Interview scenarios
- LEETCODE
First Half
- Stand Up
- Lecture
- Questions
- Break
- Lab
Second Half
- Lecture
- Questions
- Break
- Lab
- Wrap Up
In person structure
Data Structures
Grocery Store Analogy
Algorithms
JavaScript CTRL+R
function calculateBill(meal, taxRate = 0.05) {
const total = meal * (1 + taxRate) ;
return total;
}
const myTotal = calculateBill(100, 0.13);keyword
function name
parameters
default value
scope start
scope ends
return statement
variable to store returned value
name or reference
call, run or invoke
Arguments
Loops
const obj = { a:1, b:2, c:3 }
// loop over property names
for (let key in obj) {
console.log(key);
// logs a, b, c
}var n = 0;
var x = 0;
while (n < 3) {
n++;
x += n;
}const nums = [10, 20, 30];
let i;
let len = nums.length
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
console.log(nums[i])
}const arr = [3, 5, 7];
// loop over property values
for (let i of arr) {
console.log(i);
// logs 3, 5, 7
}for...in loop
while loop
for loop
for...of loop
Primitive Data Types
Number
String
Boolean
Undefined
Null
Object
/**
* Takes 2 numbers and returns their sum.
* @param {number} a the first number
* @param {number} b the second number
*
* @returns {number} the sum of a and b
* @example
* addNumbers(7, 22)
*/
function addNumbers(a, b) {
return a + b;
}const readline = require('readline');
const fs = require("fs");
// get file from path
const input_file_path = String(process.argv[2]);
// run node app.js ./path/to/file
const app = readline.createInterface({
input: fs.createReadStream(input_file_path),
output: process.stdout
});
app.on('line', (line) => {
// print each line
process.stdout.write(line)
});
app.on('close', () => {
process.stdout.write("All done")
})// debugger
var arr = [1,2,3,4,5];
debugger;
console.log(arr[2]);debugger
Preguntas?
Big O Notation
The language we use to describe the efficiency of algorithms
Time Complexity
Space Complexity
// Constant time array indexing
const card_deck = ['K', '2', '7', 'A']
// This is a constant time look-up
let first_card = card_deck[0]; // 'K'Constant
O (1)
Examples:
Array, Object & HashMap lookup by index or property
No matter how many cards are in a deck, to find the first card in the deck, it will take the same amount of time
Logarithmic
let myList = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9];
function binarySearch(myList, itemToFind) {
let low = 0, high = myList.length - 1,
mid, guessed;
while(low <= high) {
mid = Math.floor((low + high) / 2),
guessed = myList[mid];
if(guessed === itemToFind) {
console.log(
`Found ${itemToFind} at: ${mid}`
);
return;
}
if (itemToFind < guessed) {
high = mid - 1;
} else {
low = mid + 1;
}
}
// number not found, it doesnt exist !
return null;
}
binarySearch(myList, 3);Examples:
Divide + Conquer
With each iteration, cut the amount of sorted data being operated on in half. Think searching for a person in a Phone Book
O (log n)
Linear
const nums = [1,2,3,4,5];
let sum = 0;
for (let num of nums) {
sum += num;
}
console.log(sum);Examples:
Finding an item in an unsorted array
There is an execution for every value in our input
O (n)
Linearithmic
function linearithmic_example(n) {
// linear loop O(n) * ...
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// ...log (n) loop
for (let j = 1; j < n; j *= 2) {
// do something in constant time...
console.log(n);
}
}
}Examples:
heapsort, quicksort and merge sort
O (n log n)
Quadratic
/**
You want to avoid code which runs in O(n²)
as the number of operations increases
significantly when you introduce more elements.
**/
let singles = [1,2,3,4,5];
let doubles = [2,4,6,8,10];
// O(n) * O(n)
for (let single of singles) {
for (let double of doubles) {
console.log(single * double)
}
}Examples:
Nested for loops; bubble sort, selection sort and insertion sort
For each draw in a deck of cards, I draw another card from a separate deck of cards of equal size
O (n^2)
Polynomial
// cubic time is a type of polynomial time
// triple nested loop
function findXYZ(n) {
const solutions = [];
for (let x = 0; x < n; x++) {
for (let y = 0; y < n; y++) {
for (let z = 0; z < n; z++) {
if( 3*x + 9*y + 8*z === 79 ) {
solutions.push({x, y, z});
}
}
}
}
console.log(solutions);
return solutions;
}Examples:
triple nested loop
O (n^k)
Exponential
const fib = (num) => {
if (num <= 1) {
return num;
}
return fib(num - 2) + fib(num - 1);
}Examples:
Fibonacci, Getting all subsets of a string
The time it takes to process the output doubles with every additional input size
O (2^n)
// O (2^n) Exponential time (continued)
function getSubsets(n = '') {
const array = Array.from(n);
const base = [''];
const results = array.reduce((previous, element) => {
const previousPlusElement = previous.map(el => {
return `${el}${element}`;
});
return previous.concat(previousPlusElement);
}, base);
console.log(`getSubsets(${n}) // ${results.slice(0, 15).join(', ')}... `);
console.log(`n: ${array.length}, counter: ${results.length};`);
return results;
}
getSubsets('') // ...
// n = 0, f(n) = 1;
getSubsets('a') // , a...
// n = 1, f(n) = 2;
getSubsets('ab') // , a, b, ab...
// n = 2, f(n) = 4;
getSubsets('abc') // , a, b, ab, c, ac, bc, abc...
// n = 3, f(n) = 8;
getSubsets('abcd') // , a, b, ab, c, ac, bc, abc, d, ad, bd, abd, cd, acd, bcd...
// n = 4, f(n) = 16;
Factorial
// iterative factorial
function print_n_factorial(n) {
for (let i = 0; i <n ; i++) {
console.log(n)
print_n_factorial(n-1);
}
}
// recursive factorial
function recursive_factorial(n) {
if (n === 0) {
return 1;
}
// n! = n * (n-1)!
return n * factorial(n - 1);
} Examples:
List all permutations of array or string, Combination of all characters in String
O (n!)
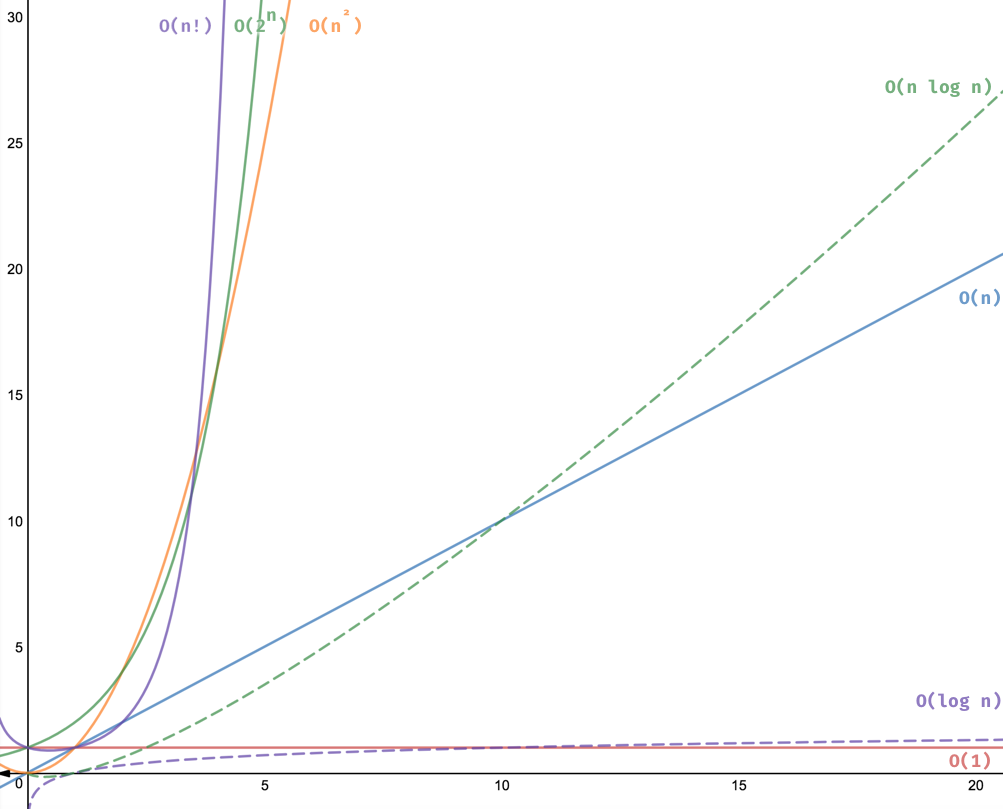
All running complexities graphs
Calculating Big O
- Worst case scenario
- Ignore and remove constants
- Use different terms for inputs (not only n)
- Drop non dominant ("faster") complexities