REDUX
a predictable state container
Creation
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=xsSnOQynTHs
Not React Specific, just a flux(ish) implementation to handle data flow
Copy of the Elm Architecture
Small
Less than 200 lines of code
2kB including dependencies
Small API
-
Single source of truth
-
State is read-only
-
Changes are made with pure functions
Three Principles
The Gist
The whole state of your app is stored in an object tree inside a single store.
The only way to change the state tree is to emit an action, an object describing what happened.
To specify how the actions transform the state tree, you write pure reducers.
That’s it!
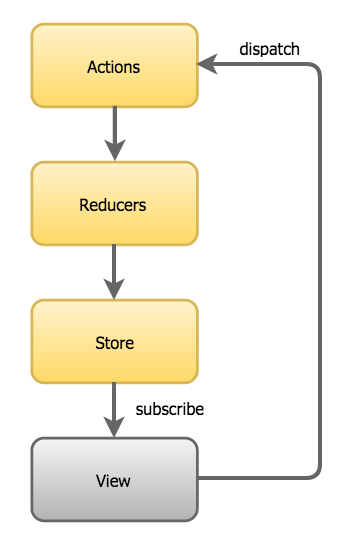
Basic Flow
import { createStore } from 'redux'
//Reducer
function counter(state = 0, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + 1
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - 1
default:
return state
}
}
//Store
let store = createStore(counter)
store.subscribe(() =>
console.log(store.getState())
)
//Actions
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' })
// 1
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' })
// 2
store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' })
// 1
Actions
Actions are payloads of information that send data from your application to your store. They are the onlysource of information for the store. You send them to the store using store.dispatch().
{
type: 'ADD_TOPIC',
title: 'Learn Redux'
}- must be JS object
- must contain a 'type' property
Since Actions are the only way to tell our app about changes we need to dispatch the action. This will be usually the result of a user event. This will connect our actions to our reducers
store.dispatch({type: 'ADD_TOPIC, title: 'Learn Redux' })Action Creators
functions that return Actions
function addTopic(title) {
return {
type: 'ADD_TOPIC',
title: title
}
}
store.dispatch(addTopic('Learn Redux'))Reducers
Actions describe the fact that something happened, but don’t specify how the application’s state changes in response. This is the job of a reducer.
In Redux, all application state is stored as a single object. It’s a good idea to think of its shape before writing any code. What’s the minimal representation of your app’s state as an object?
{
topics: [
{
id: 1,
title: 'Learn Redux',
speaker: 'Nick',
completed: true
},
{
id: 2,
title: 'GraphQL',
speaker: 'Randy',
completed: false
}
],
currentTopic: 2,
visibilityFilter: 'SHOW_COMPLETED'
}Now that we’ve decided what our state object looks like, we’re ready to write a reducer for it. The reducer is a pure function that takes the previous state and an action, and returns the next state.
(previousState, action) => newStateIt’s very important that the reducer stays pure. Things you should never do inside a reducer:
- Mutate its arguments;
- Perform side effects like API calls and routing transitions;
- Call non-pure functions, e.g. Date.now() or Math.random().
Store
The Store is the object that brings the actions and reducers together.
Create by giving it a reducer (or set of reducers) and an optional initial state