React
React
- library for managing view
- component based
- helps split the app into small pieces
- used to create SPA
Client
Server
Database
HTTP
browser
request
html page
Client
Server
Database
HTTP
React in browser, mobile app...
API
request
data
Single page application
Web server
html, js
HTML Page
- import React & ReactDOM
<html>
<head>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js" crossorigin></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js" crossorigin></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
</div>
</body>
<script>
... your code
</script>
</html>Building blocks
Elements
- React app is composed of React elements
-
type
- string ➡️ HTML element
- function / class ➡️ component
-
properties
- = props = data passed down
- used for attributes
-
...children
- content
- text / another element (single or array)
-
type
const myDiv = React.createElement('div', null, 'Hello World');Elements
const label = React.createElement('a', {
href: 'https://google.com'
}, 'Go to Google.com');<a href="https://google.com">Go to Google.com</a>children
props
type
Render
- display elements
- ReactDOM for HTML
<div id="app"></div>
<script>
const myDiv = React.createElement('h1', null, 'Hello World');
ReactDOM.render(myDiv, document.getElementById('app'));
</script>Create a table
- table with 2 columns, 3 rows
- text in every cell: Hello
- attribute: border="1"
| Hello | Hello |
|---|---|
| Hello | Hello |
| Hello | Hello |
Components
Component
- reusable unit
- just a function
-
input
- properties (data)
- executed only when props are changed
-
output
- React element
const myNameElement = React.createElement(NameComponent, {
name: 'Martin Nuc'
});
ReactDOM.render(myNameElement, document.getElementById('app'));
function NameComponent(props) {
return React.createElement('h1', null, props.name);
}Component tree
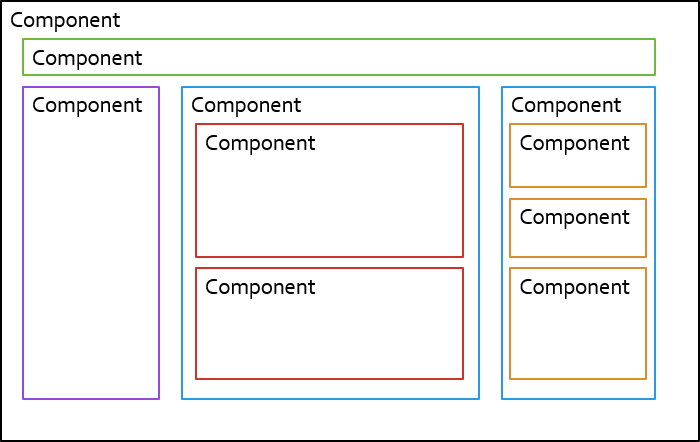
- split big problems to smaller ones
Component tree
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component
Component tree
- Stateful components (smart)
- used to fetch data
- data manipulation
- Stateless components (dumb)
- only display data
- pass data down, emit events up
Component tree
Component
User info
ArticleList
Article
Today Weather
Article
I am smart 💡
Dynamic table
- create a component which displays a table
- receives number of columns and rows as parameter
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
node.js
What is node.js?
- environment for running Javascript
- doesn't need browser
- using V8
Install node
Hello world
- create file index.js with Javascript code
- execute file using: node index.js
console.log('Hello world');Let's get serious...
- create new folder (mkdir my-app; cd my-app)
- initialize node package:
-
npm init
-
- it creates package.json file which contains
- basic package info (author, licence, repository url, etc.)
- dependencies
- scripts
Wait, what was that
npm
??
Node package manager
- when you want to use a code written by someone else
- packaging system
- large repository (>550k packages)
- https://www.npmjs.com
{
"name": "my-package",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "This is just description of my awesome package",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon --exec npm run start",
"start": "tsc && node dist/index.js",
"test": "mocha --opts mocha.opts"
},
"author": "Martin Nuc",
"license": "ISC",
"dependencies": {
"@types/chai": "4.0.4",
"@types/mocha": "2.2.43",
"@types/node": "8.0.28",
"@types/sinon": "2.3.4",
"chai": "4.1.2",
"mocha": "3.5.3",
"nodemon": "1.12.1",
"sinon": "3.2.1",
"ts-node": "3.3.0",
"typescript": "2.5.2"
}
}
package.json
yarn
- alternative app to manage dependencies
- made by facebook
- similar to npm
npm install
- installs dependencies based on package.json
- downloads into node_modules folder
yarn
Dependencies and GIT
- we don't commit dependencies
- put node_modules folder in .gitignore
- npm install to install dependencies
Scripts
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodemon --exec npm run start",
"start": "node index.js",
"test": "mocha --opts mocha.opts"
},
- used to execute commands
- npm dependencies executables resolution (from node_modules/.bin/*)
npm run <name>
Shortcut for start and test scripts only. For others you have to use npm run
Runs any script from npm.
npm start
npm test
👉
yarn <name>
Runs any script from npm.
👉
Create your script
- create script called start for running your app
- use yarn to execute it
npx
- part of npm
- downloads package and executes it
- executes apps in current project
create-react-app
create-react-app
- use to create new React project
- setups JSX, build process, dev server...
- command:
- npx create-react-app hello-world
Structure
- public
- index.html
- assets
- src
- index.js -> ReactDOM.render()
- App.js
- root component (JSX)
- we use PascalCase for component filenames
JSX
What is JSX?
- syntactic sugar around createElement
- almost like HTML
- transpiled to Javascript
- example in App.js:
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
Hello
</div>
);
}function App() {
return React.createElement('div', { className: 'App' }, 'Hello');
}Q: Why className?
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
Hello
</div>
);
}function App() {
return React.createElement('div', { className: 'App'}, 'Hello');
}Q: What happens now?
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<div>
Yes
</div>
<div>
No
</div>
);
}function App() {
return ????????
}Solution: React Fragment
- like empty element
- when you want to return multiple elements - wrap them in fragment
import React from 'react';
function App() {
return (
<>
<div>
Yes
</div>
<div>
No
</div>
</>
);
}Before we continue
- start project
- remove everything in the root component
- notice the browser reloads
Print a variable
function App() {
let something = 'hello';
return <div>{something}</div>;
}Print an array
function Array() {
let array = [1,2,3];
return <div>
{array.map((item, index) => <span key={index}>{item}</span>)}
</div>;
}
Stateless component
- everything to display is received via props
- just a function
- input: props (=properties)
- output: React element
- easy to test
function NameComponent(props) {
return React.createElement('h1', null, props.name);
}function NameComponent(props) {
return <h1>{props.name}</h1>;
}Use stateless component
- pass data down
function App() {
return <NameComponent name="Martin" />
}Dynamic table
- create a component which displays a table using JSX
- receives number of columns and rows as parameter
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
| Hello | Hello | Hello | Hello |
Children props
Children props
- you might pass HTML as body of element:
<Table columns={5} rows={2}>
<h1>Hello</h1>
</Table>- Table component receives react element via children prop:
function Table(props) {
return (
<table>
<tr>
<td>
{props.children}
</td>
</tr>
</table>
)
}Stateful component
Stateful components
- they hold state
- use classes
- state may change
import React from 'react';
export class Hello extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
name: 'Martin'
};
}
render() {
const name = this.state.name;
return <div>{name}</div>;
}
}How to change state?
- using setState
- only schedules change
- triggers rerender
- component must be already mounted
this.setState({
name: 'Renamed'
});Handeling events
- passing function as prop
- events are always camelCase
- eg. onClick
class Hello extends React.Component {
handleClick() {
this.setState({ name: 'ooooo' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return <div>
{name}
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
change
</button>
</div>
}
}Will it work?
- what is the value of this?
class Hello extends React.Component {
handleClick() {
this.setState({ name: 'ooooo' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return <div>
{name}
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
change
</button>
</div>
}
}Solution 1
- using arrow function
- creates a function on every render
class Hello extends React.Component {
handleClick() {
this.setState({ name: 'ooooo' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return <div>
{name}
<button onClick={() => this.handleClick()}>
change
</button>
</div>
}
}Solution 2
- binding handler to the class
class Hello extends React.Component {
constuctor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState({ name: 'ooooo' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return <div>
{name}
<button onClick={() => this.handleClick()}>
change
</button>
</div>
}
}Solution 3
- ES2018 syntax (experimental)
- https://babeljs.io/docs/en/babel-plugin-proposal-class-properties
class Hello extends React.Component {
handleClick = () => {
this.setState({ name: 'ooooo' })
}
render() {
const { name } = this.state;
return <div>
{name}
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
change
</button>
</div>
}
}Create counter
- create button with counter as text
- start from 0
- everytime you click the button the counter is increased
Conditions
- use if statement
- use ternary operator
render() {
const random = Math.random();
if (random < 0.5) {
return <span>lower</span>
} else {
return <span>higher</span>
}
}render() {
const random = Math.random();
return <span>
{random < 0.5 ? 'lower' : 'higher'}
</span>
}Component lifecycle
Lifecycle
- constructor
- mounted
- componentDidMount()
- state available
- render, render, render...
- unmounted
- componentWillUnmount()
- clean up
Caution !
beware of setting state after component has been unmounted
solutions:
- clean after yourself
- create flag whether component has been unmounted
Create automatic counter
- create component which increases counter every second
- in parent component create button which shows/hides this component
Creating own event
- component emits event up
class ChildComponent extends React.Component {
handleClick = () => {
this.props.doWork();
}
render() {
return <button onClick={this.handleClick}>emit event</button>;
}
}<ChildComponent doWork={() => console.log('triggered')} />parent component:
child component:
Hide counter
- when counter reaches 5 it hides itself
- emit event to the parent to hide component
Controlled input
- use component state as the only source of truth
class Component extends React.Component {
constructor() {
this.state = {
value: ''
};
}
handleChange = (event) => {
this.setState({
value: event.target.value
});
}
render() {
return <>
{this.state.value}
<input value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange}>
</>
}
}Create input
- input of type number
- how much the counter will increment
3rd party libs
Dependencies
- npm install <name>
- yarn add <name>
- download library to node_modules
- example:
- axios - used to make HTTP requests
- yarn add axios
- import in code:
import axios from 'axios';Let's make http request
- open API request in browser to see structure of response
- display joke in the component
- create a button to load another joke
GET https://api.chucknorris.io/jokes/randomComponent tree
Component
User info
JokeFetcher
Joke
I am smart 💡
data down
Conditional styling
- classnames library
- yarn add classnames
- key = class to be applied
- value = condition
import cn from 'classnames';
...
<div class={cn({ invalid: this.state.invalid })}>
</div>Component composition
Composition
- separate logic from view
- methods
- HOC = Higher order component
- render or children props
- counter example
- component for holding counter state
- component for displaying counter
Children props
- component accepts a function as children prop
- passes it's state to the children prop
- parent component uses and displays these data
Children props
export class CounterState extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
counter: 0
}
}
inc = () => {
this.setState({counter: this.state.counter + 1});
}
dec = () => {
this.setState({counter: this.state.counter - 1});
}
render() {
return this.props.children({
counter: this.state.counter,
increment: this.inc,
decrement: this.dec
});
}
}Children props in parent
render() {
return <CounterState>
{({counter, increment}) =>
<>
<div>Current value: {counter}</div>
<button onClick={increment}>inc</button>
</>
}
</CounterState>
}Fetch joke component
- encapsulate fetching joke logic
- use children props to display joke
Enriching component
- component may wrap another component
- passes all props down to the underlaying element
- example: ValidatedInput
Example: ValidatedInput
- displays red border when invalid
- usage:
<ValidatedInput type="number"
name="age"
validator={value => value < 10} />validator fn passed via props
Example: ValidatedInput
- displays red border when invalid
export class ValidatedInput extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
value: '',
invalid: true
}
}
handleChange = (event) => {
const value = event.target.value;
this.setState({value});
this.setState({
invalid: !this.props.validator(value)
});
}
render() {
return <div class={cn({ invalid: this.state.invalid })}>
<input {...this.props} value={this.state.value} onChange={this.handleChange} />
</div>
}
}validator fn passed via props
Formik
Formik
const schema = yup.object().shape({
email: yup.string().required().email(),
age: yup.number().required().positive().integer()
})
const initialValues = {
email: '',
age: 0
}
export function MyForm() {
return (
<Formik
initialValues={initialValues}
validationSchema={schema}
onSubmit={values => console.log(values)}
render={() => (
<Form>
<Field type="email" name="email" />
<ErrorMessage name="email" component="div" />
<Field type="number" className="error" name="age" />
<ErrorMessage name="age" className="error" component="div"/>
<button type="submit">
Submit
</button>
</Form>
)}
/>
);
}Registration form
- create form with fields:
- name
- age (>18)
Routing
React router
- used to create multiple pages
- install react-router-dom
- docs
Define pages and links
import { BrowserRouter as Router, Route, Link } from "react-router-dom";
function App() {
return (
<Router>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
<Link to="/categories">About</Link>
<Link to="/categories/animals">Joke about animals</Link>
<Link to="/categories/history">Joke about history</Link>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/categories" component={JokeCategories} />
<Route path="/categories/:category" component={Joke} />
</Router>
);
}- everything must be inside of <Router>
Reading parameters
function Joke({match}) {
return (
{match.params.category}
);
}- via props
Try routing
- Create routes
- / -> categories list
- /categories/:category -> joke from category
- load joke based on category
React hooks
React hooks
- way how to use state in functional component
- no need to use classses
- since React 16.8 (Feb 2019)
useState
- hook for storing data
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function Counter() {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
function handleIncrement() {
setCounter(counter + 1);
}
return <button onClick={handleIncrement}>{counter}</button>
}initial value
Try useState
- create functional component
- have button to toggle between two texts:
- awesome
- cool
useEffect
- hook for side effects
- second argument say when it runs
- empty - on every render
- [ ] - only at the begining (=componentDidMount)
- [ variable ] - only when variable changes
- should return cleanup function (=componentWillUnmount)
useEffect
- track mouse position
export const MyMouse = () => {
const [mousePosition, setMousePosition] = useState({x: 0, y: 0});
const onMouseMove = event => {
setMousePosition({
x: event.clientX,
y: event.clientY
});
};
useEffect(() => {
window.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
return () => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove);
};
}, []);
const {x, y} = mousePosition;
return (
<div>My mouse x position is {x} and y position is {y}</div>
);
};
Try useEffect
- rewrite JokeFetcher as functional component
- use useEffect hook to make http request
- show loading state