-DEEP DIVE-
PART 2

Contents
Advanced PostgreSQL
- VIEWS-
- Introduction
- Create
- Alter
- Remove
- Cascade
- INDEXES-
- Introduction
- Create
- Drop
- List
- Types
ADVANCED PostgreSQL
A database objecy that is of a stored query
-VIEWS-
Can be access as a virtual table in PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL - VIEWS
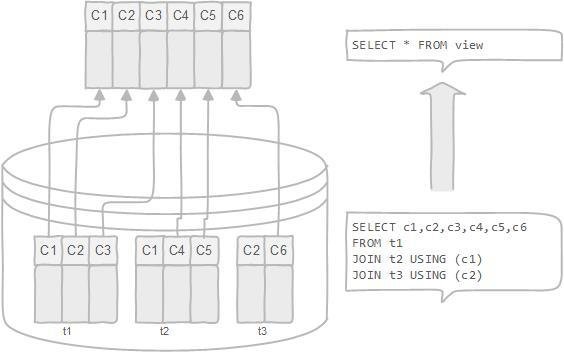
PostgreSQL - VIEWS
Create View
CREATE VIEW view_name AS query;CREATE VIEW customer_master AS
SELECT cu.customer_id AS id,
cu.first_name || ' ' || cu.last_name AS name,
a.address,
a.postal_code AS "zip code",
a.phone,
city.city,
country.country,
CASE
WHEN cu.activebool THEN 'active'
ELSE ''
END AS notes,
cu.store_id AS sid
FROM customer cu
INNER JOIN address a USING (address_id)
INNER JOIN city USING (city_id)
INNER JOIN country USING (country_id);PostgreSQL - VIEWS
ALTER VIEW
ALTER VIEW customer_master RENAME TO customer_info;REMOVING VIEW
DROP VIEW IF EXISTS customer_info;PostgreSQL - VIEWS
CASCADE
DROP VIEW film_master
CASCADE;DROP MULTIPLE VIEW
DROP VIEW film_length_stat, film_category_stat;ADVANCED PostgreSQL
Effective tools to enhance database performance
-INDEXES-
Help the database server fid specific rows much faster
CREATE INDEX
PostgreSQL - INDEXES
CREATE INDEX index_name ON table_name [USING method]
(
column_name [ASC | DESC] [NULLS {FIRST | LAST }],
...
);CREATE INDEX idx_address_phone
ON address(phone);PostgreSQL - INDEXES
BEFORE CREATE INDEX
AFTER CREATE INDEX
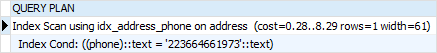
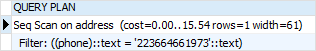
PostgreSQL - INDEXES
DROP INDEX
DROP INDEX [ CONCURRENTLY]
[ IF EXISTS ] index_name
[ CASCADE | RESTRICT ];INDEX_NAME - specify the name of the index that you want to remove
IF EXISTS - To avoid error when you remove a non-existent index
CASCADE - To automatically drop the objects and all objects depends on those objects
PostgreSQL - INDEXES
LIST INDEXES
SELECT
tablename,
indexname,
indexdef
FROM
pg_indexes
WHERE
schemaname = 'public'
ORDER BY
tablename,
indexname;PostgreSQL - INDEXES
- tablename - stores name of the table to which index belongs
LIST INDEXES - pg_indexes
- indexname - stores name of the index
- indexdef - stores index definition command in the form of CREATE INDEX statement
- schemaname - stores the name of the schema that contains tables and indexes
PostgreSQL - INDEXES
INDEX TYPES
B-TREE
HASH
GiST
SP-GiST
GIN
BRIN
PostgreSQL - INDEXES
| INDEXES | WHEN TO USE |
|---|---|
| B-TREE | For most datatypes and queries |
| GIN Generalized Inverted Indexes |
For JSON/hstore/array |
| GiST Generalized Search Tree |
For full text search and geopatial datatypes |
| SP-GiST Space Partitioned GiST |
For larger datasets with natural but uneven clustering |
| BRIN Block Range indexes |
For really large datasets that line up sequentially |
| HASH | For equality operations, generally still need B-Tree |
References


