INTRODUCTION TO
ENTITY FRAMEWORK CORE
Content
-
What is Entity Framework Core
-
Why use Entity Framework Core
-
Entity Framework Latest Version
-
EF Core Development Approaches
-
EF Core Database Provider
-
DbContext
-
EF Core Model
Entity Framework Core?
An open-source ORM(object-relational mapping) framework for .NET applications supported by Microsoft
A lightweight, extensible, open source and cross-platform version of the popular Entity Framework data access technology
WHY USE ENTITY FRAMEWORK CORE?
EF Core can served as an object-relational mapper (O/RM)
- Enables .NET developers to work with database using .NET objects.
- Eliminates the need for most of the data-access code that typically needs to be written.
ENTITY FRAMEWOK LATEST VERSION
| EF 6 | EF CORE |
|---|---|
| Open-source | Open-source |
| First released - 2008 with .NET Framework 3.5 SP1 |
First realeased - June 2016 with .NET Core 1.0 |
| Stable and feature rich | New and evolving |
| Windows only | Windows, Linux, OSX |
| Works on .NET Framework 3.5+ | Works on .NET Framework 4.5+ and .NET Core |
THE DIFFERENCES BETWEEN EF6 AND EF CORE
ENTITY FRAMEWOK CORE HISTORY
| VERSION | .NET FRAMEWORK |
|---|---|
| EF Core 2.0 | .NET Core 2.0 |
| EF Core 1.1 | .NET Core 1.1 |
| EF Core 1.0 | .NET Core 1.0 |
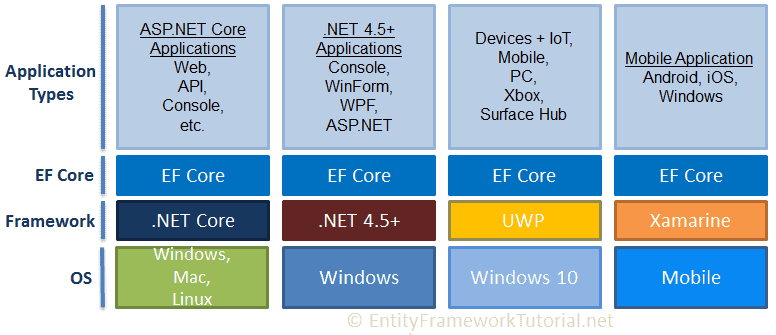
Supported Application types, .NET Framework and OSs
EF Core Development Approaches
Supports 2 development approaches
- Code-First
- Database-First
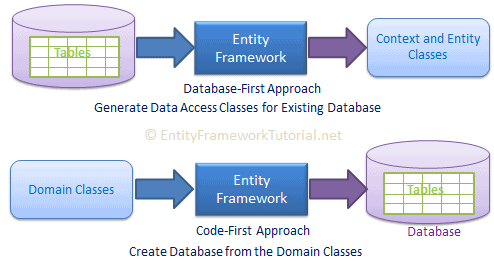
EF Core Development Approaches
1 ) Code-First Approach

- EF Core API creates the database and tables using migration based on the conventions and configuration provided in domain classes.
- Useful in Domain Driven Design (DDD)
EF Core Development Approaches
2 ) Database-First Approach

- EF Core API creates the domain and context classes based on existing database using EF Core commands.
- This has limited support in EF Core as it does not support Visual Designer/Wizard
EF Core Database Provider
EF Core uses a provider model to access many different database.
EF Core includes providers as NuGet packages
- need to install
The Lists of Database providers & NuGet packages
| DATABASE | NuGet PACKAGE |
|---|---|
| SQL SERVER | Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer |
| MySQL | MySql.Data.EntityFrameworkCore |
| PostgreSQL | Npgsql.EntityFrameworkCore.PostgreSQL |
| SQLite | Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SQLite |
| SQL Compact | EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerCompact40 |
| In-memory | Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.InMemory |
DbContext
An integral part of Entity Framework
An instance of DbContext represents a session with the database which can be used to query and save instances of your entities to a database
Combination of the Unit OF Work and Repository patterns
DbContext functions
-
Manage database connection
-
Configure model & relationship
-
Querying database
-
Saving data to the database
-
Configure change tracking
-
Caching
-
Transaction management
DbContext example
public class SchoolContext : DbContext
{
public SchoolContext()
{
}
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
}
//entities
public DbSet<Student> Students { get; set; }
public DbSet<Course> Courses { get; set; }
} Ways to create / configuring a MODEL
-
Use fluent API
-
Grouping
-
Use data annotations
Use fluent API
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFModeling.FluentAPI.Required
{
internal class MyContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
#region Required
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Blog>()
.Property(b => b.Url)
.IsRequired();
}
#endregion
}
public class Blog
{
public int BlogId { get; set; }
public string Url { get; set; }
}
}- Override the OnModelCreating method in derived context and use the ModelBuilder API to configure your model
Grouping
public class BlogEntityTypeConfiguration : IEntityTypeConfiguration<Blog>
{
public void Configure(EntityTypeBuilder<Blog> builder)
{
builder
.Property(b => b.Url)
.IsRequired();
}
}- To reduce the size of the OnModelCreating method all configuration for an entity type can be extracted to a separate class implementing IEntityTypeConfiguration<TEntity>
Use data annotations
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
namespace EFModeling.DataAnnotations.Required
{
internal class MyContext : DbContext
{
public DbSet<Blog> Blogs { get; set; }
}
#region Required
public class Blog
{
public int BlogId { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Url { get; set; }
}
#endregion
}- Data annotations will override conventions, but will be overridden by Fluent API configuration.