Discussion Midterm
Syntax
Identify part-of-speech
S
AUX
AdvP
NP
Det
Comp
Part
XP
Syntax
What is
(NP)
(NP)*
{NP AdjP}
Phrase Structure rules

Morphology-words
Find words:
1) simple, 2) complex, 3) compound, 4) non-compound,
5) content, 6) functional
cat, the, cat-walk, I, cats
morphology - types
Find: 1) Root, Affix, Prefix, Suffix
-able, un-, cat
replacement
reordering
2) free, bound, lexical, grammatical
dental
formation
3) inflexional, derivational
unfaithful
talked
True-false
1.In English, derivational morphemes occur before inflectional morphemes.
2. In English, derivational suffixes regularly occur before inflectional suffixes.
3. In English, a few inflectional morphemes can occur as prefixes.
4. Every root in English is a free morpheme (Hint: consider receive, deceive, conceive, perceive).
5. In English, some morphemes have both a free and a bound allomorph. (Hint: consider able, ability; France, Franco-)
True-false
1. Inflection creates another word
2.Inflection never changes the lexical category
3. Inflection is often unproductive and always optional
4.Derivation often involves a major change in the meaning of a word
5. Inflection follows derivation
6. Inflection involves more than one affix per word — in English
7. Inflection always involves a suffix — in English
8. Derivation typically involves a small, closed set of affixes.
Morphological processes
List 4 processes and provide an example
Phonology
phonetics
phonemics
phonotactics
distribution of sounds, concrete sounds, abstract sounds
Phonology
phonetics deals with
1) sounds and their production in the tract
2) sounds as sound-waives
3) sounds through hearing and ears
acoustic, auditory, articulatory
consonants
1) p t k
2) f, v
3) m,n
4) l
5) w
nasals, lateral, stops, fricatives, liquid, glide
Vowels
1) i, u
2) a
3) o, u
4) i, e , o, u, a
tense, close, open, rounded
5) find opposite lax vowels for (4)
Manner of articulation
List 5 different manners
Tract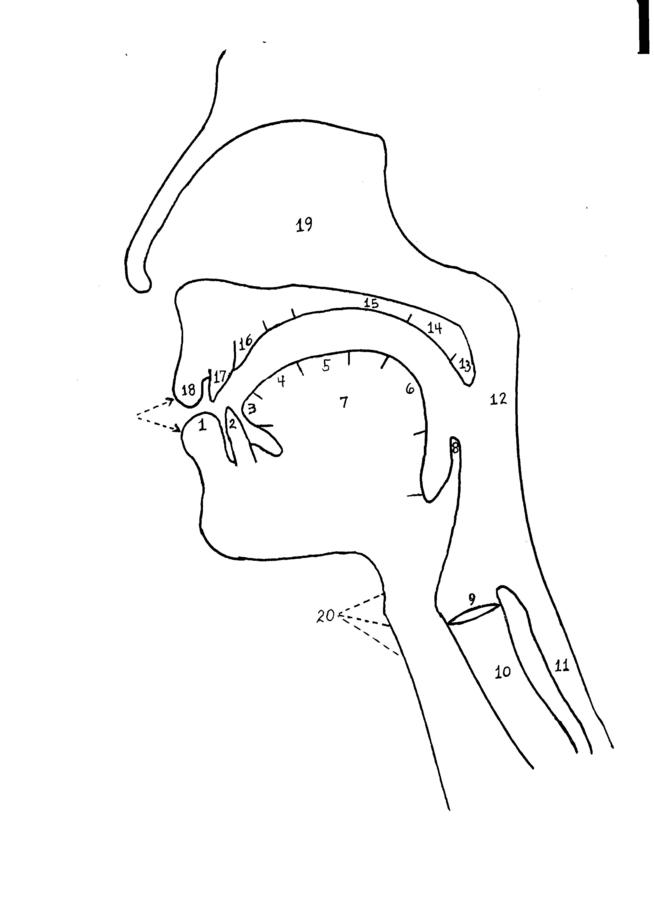
Title
Answers (derivation)
F T F T T F T F
answers (morpheme)
T T F F T