RegCM for the estimation of flood risk maps: providing driving data for the CHyM hydrological model
Adriano Fantini
30 May 2018
IX ICTP Workshop on the Theory and Use of Regional Climate Models



Aims
- Flood risk mapping over Italy
- scientific, reliable approach
- future projections
Models
- ICTP RegCM
- CHyM hydrological model
- CA2D hydraulic model
Project overview
Participants
- Erika Coppola
- Adriano Fantini
- Filippo Giorgi
- Rita Nogherotto
- Francesca Raffaele
- Marco Verdecchia
Methodology
Precipitation:
- Observations
- RCM output
Gridded netCDF:
- River network
- Discharges
hydrological model

For each RP, cell:
- Gumbel distr
- Hydrographs
Statistical RP analysis
hydraulic model
For each RP, cell:
- Flood extent
- Flood depth
(multiple simulations)
- RCM output
- Discharges
- Past floods
Validation for

RegCM
1.0 - Observations
We have access to several Italian observational datasets provided by the University of L'Aquila for:
- temperature
- precipitation
- water level
- discharge
~2000-2017
only!
1.1 - Observations
Some examples...
Outliers
1.2 - Observations
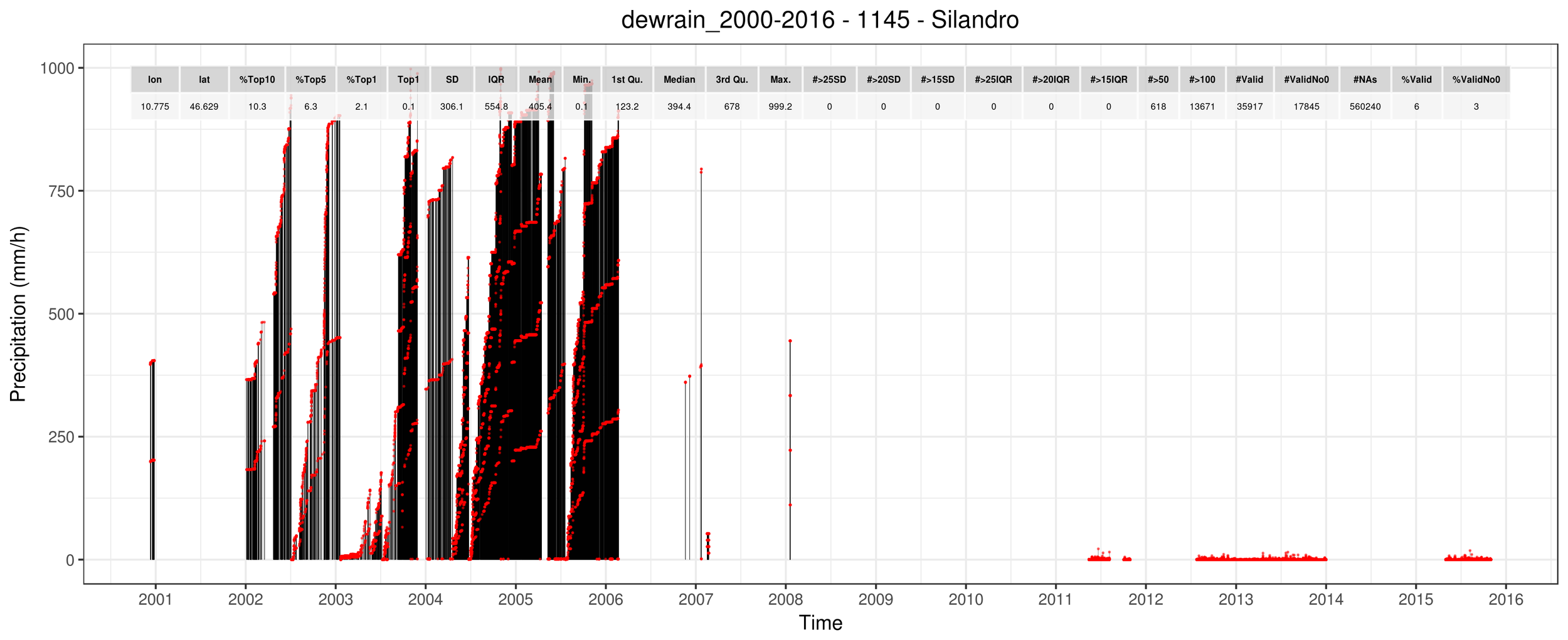
FIRST-STAGE FILTERING
FLAGGING
FLAG CHECKING
CLEANED DATASET!
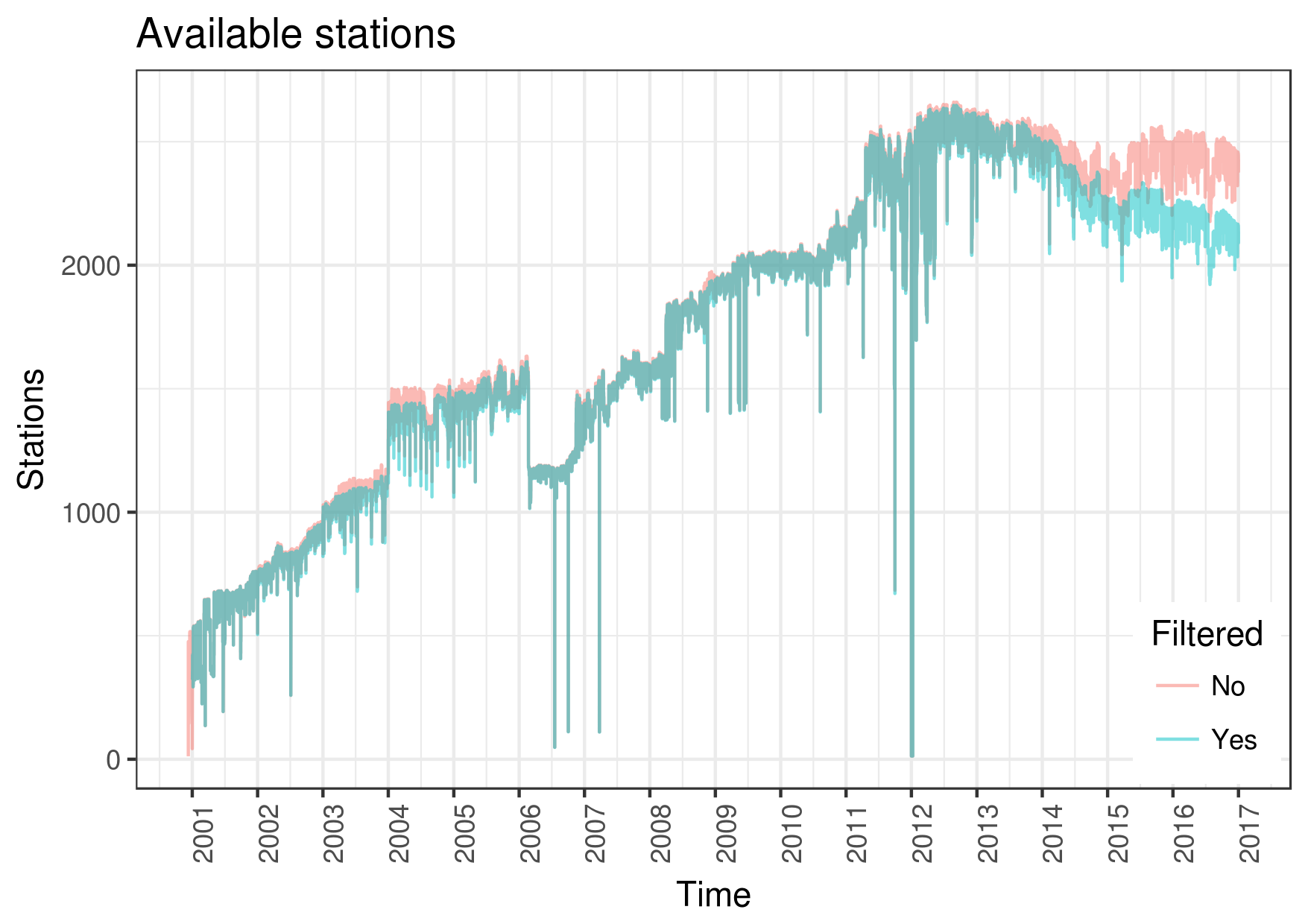
1.3 - Observations
First-stage filtering procedures
- Removal of extreme values > 200 mm/h
- Removal of isolated > 100 mm/h reports
- Removal of complete months with > 1800 mm (2.5 mm/h)
- Removal of continuous identical values
1.4 - Observations
Flagging procedures
- Mean + n*SD threshold
- Median + n*IQR threshold
- Peaks in the values distribution
- Isolated dry/wet event flagging
- Low correlation of close stations
Results so far...
(by applying first-stage filtering procedures only)
| Before | After | Diff | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total valid values | 250M | 243M | -2.6% |
| Total flags | 324468 | 58008 | -82.1% |
| pr > Mean + 20SD | 3240 | 2538 | -21.7% |
| pr > Median + 20IQR | 49753 | 22519 | -54.7% |
| pr > 100 mm/h | 221822 | 711 | -99.6% |
| Other softer flags | 49646 | 32240 | -35.1% |
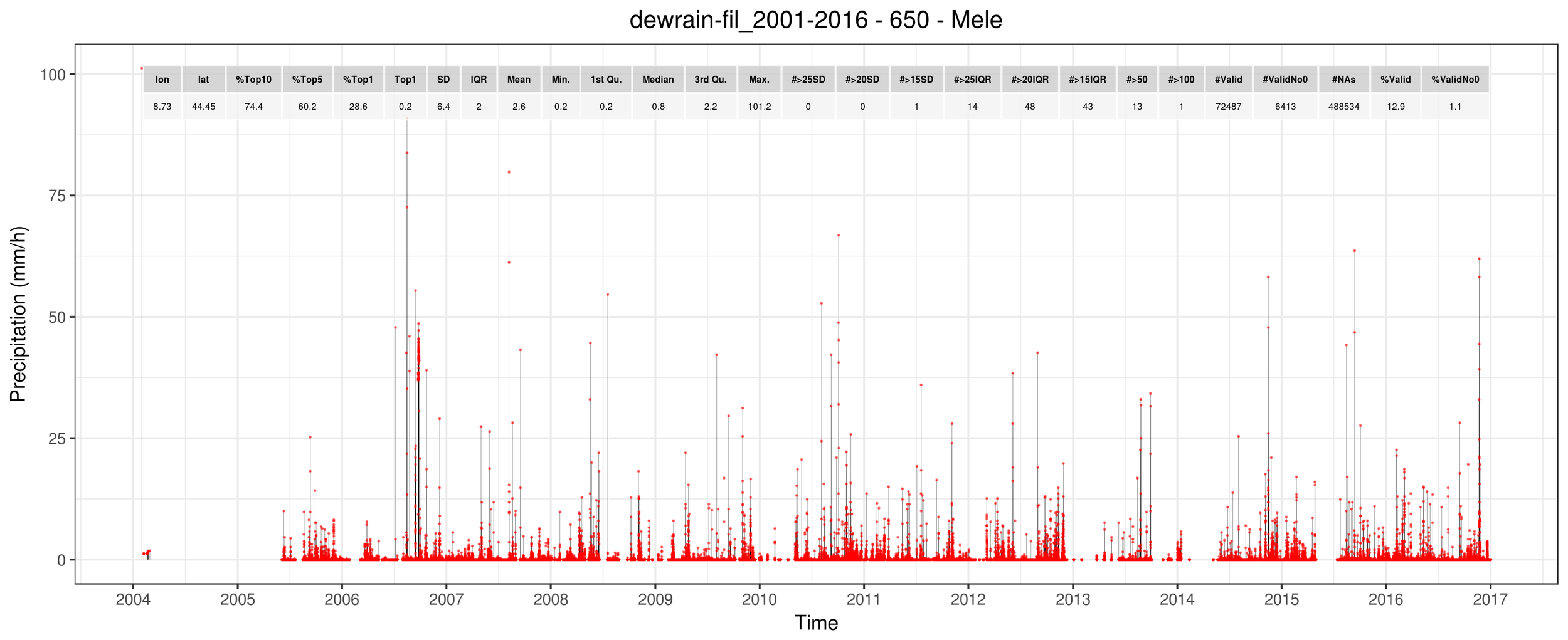
1.5 - Observations
FILTERED
ORIGINAL
1.6 - Observations
1.7 - Observations
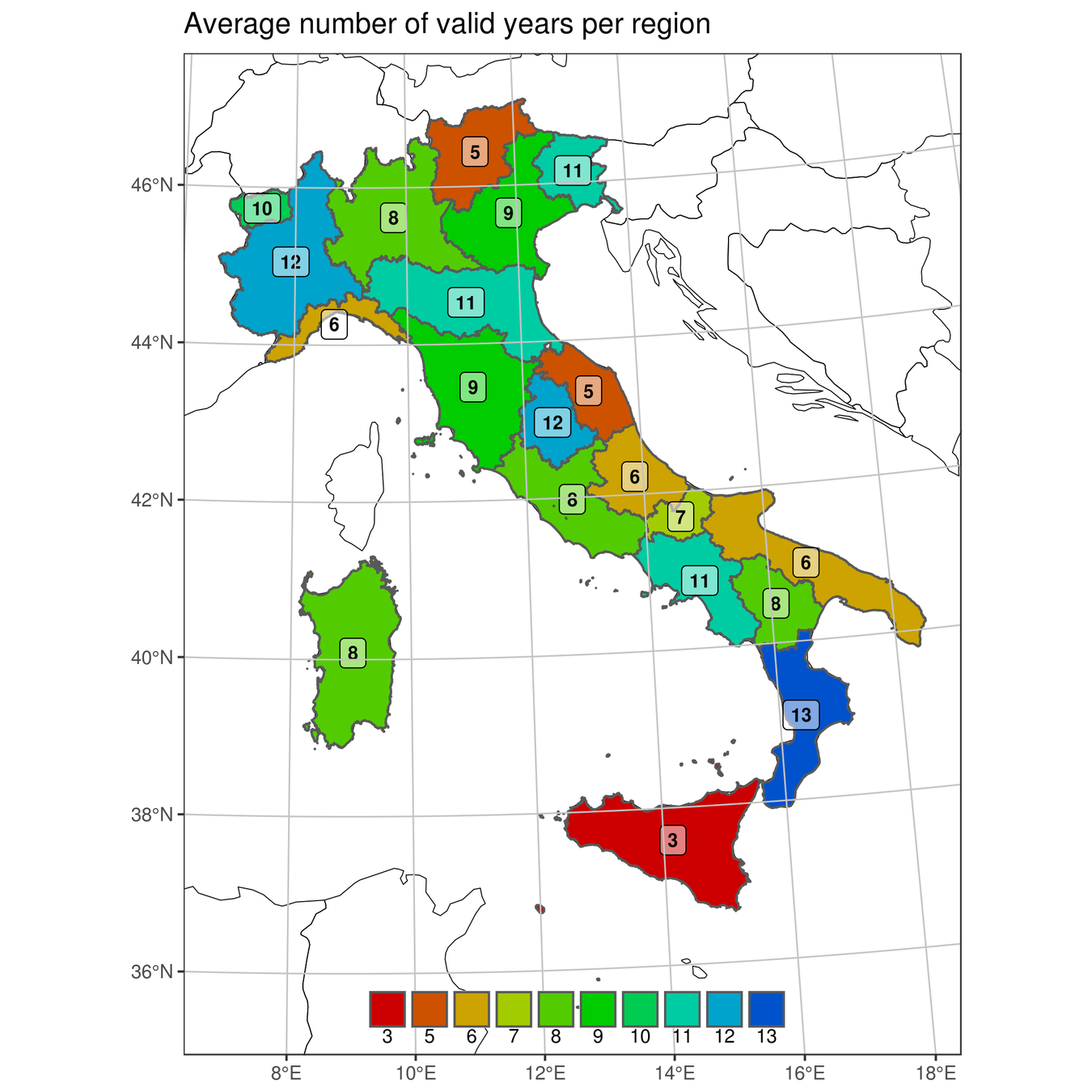
2.0 - Regional Climate Models
How to reproduce 200-years floods with just ~15 years of precipitation data?
Statistical analysis helps, but a longer time period is required
RegCM as driving data for the CHyM hydrological model
EURO-CORDEX Simulations (thanks James Ciarlo`!):
- RegCM 4.6.1 (ERA-Interim driven) 1979-2016
- RegCM 4.6.1 (HadGEM driven) 1971-2100 (WIP)
2.1 - Regional Climate Models
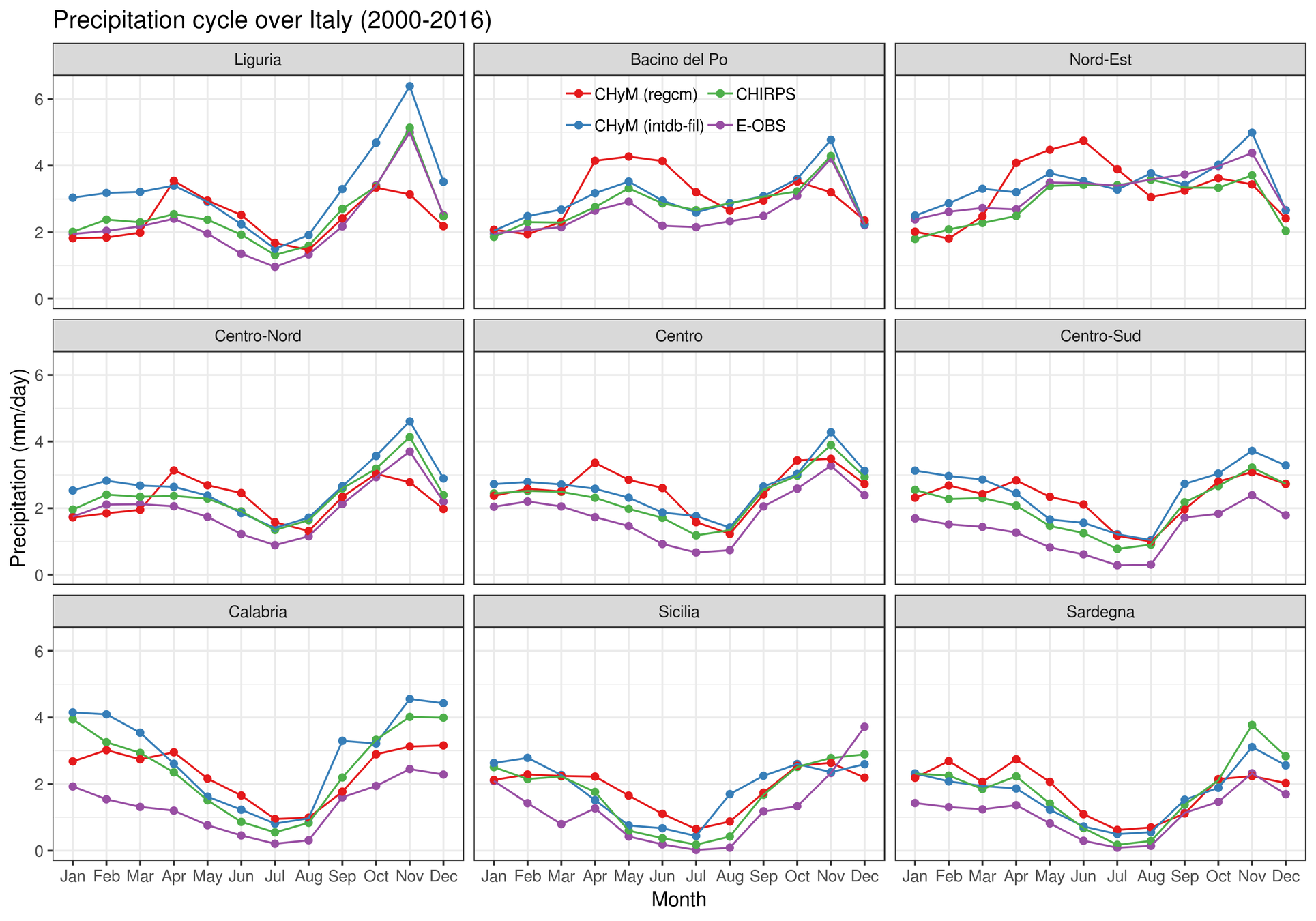
First, a basic validation of the data:

- 4 regions
- 2000-2016
- precipitation only
Available datasets:
- RegCM-ERA-In (12km)
- RegCM-HadGEM (12km)
- Italian OBS data (~12km)
- E-OBS (~25km)
- EURO4M-APGD (~5km)
- CHIRPS (~5km)
- ...
2.2 - Regional Climate Models
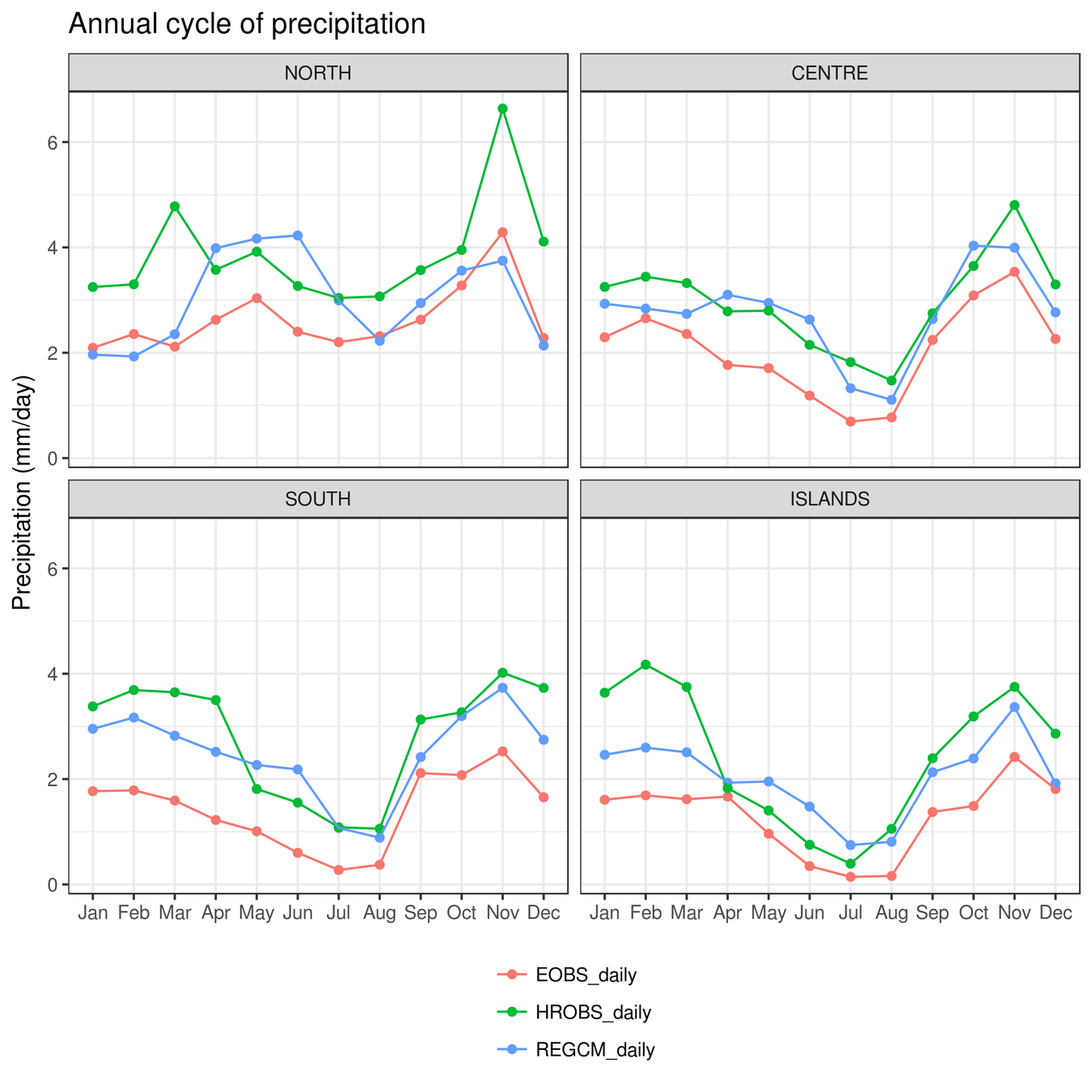
2.3 - Regional Climate Models
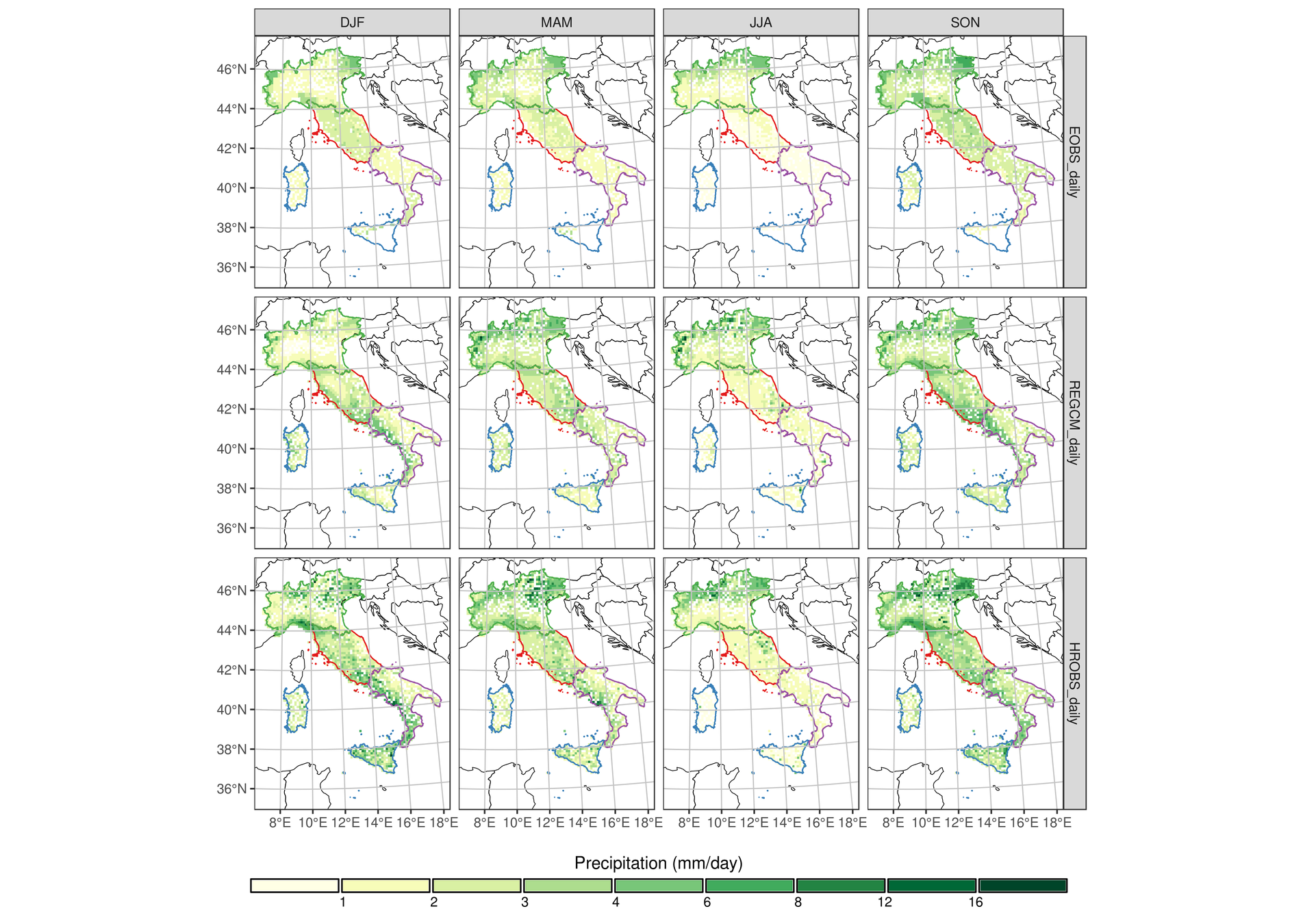
E-OBS
REGCM
HR-OBS
2.4 - Regional Climate Models
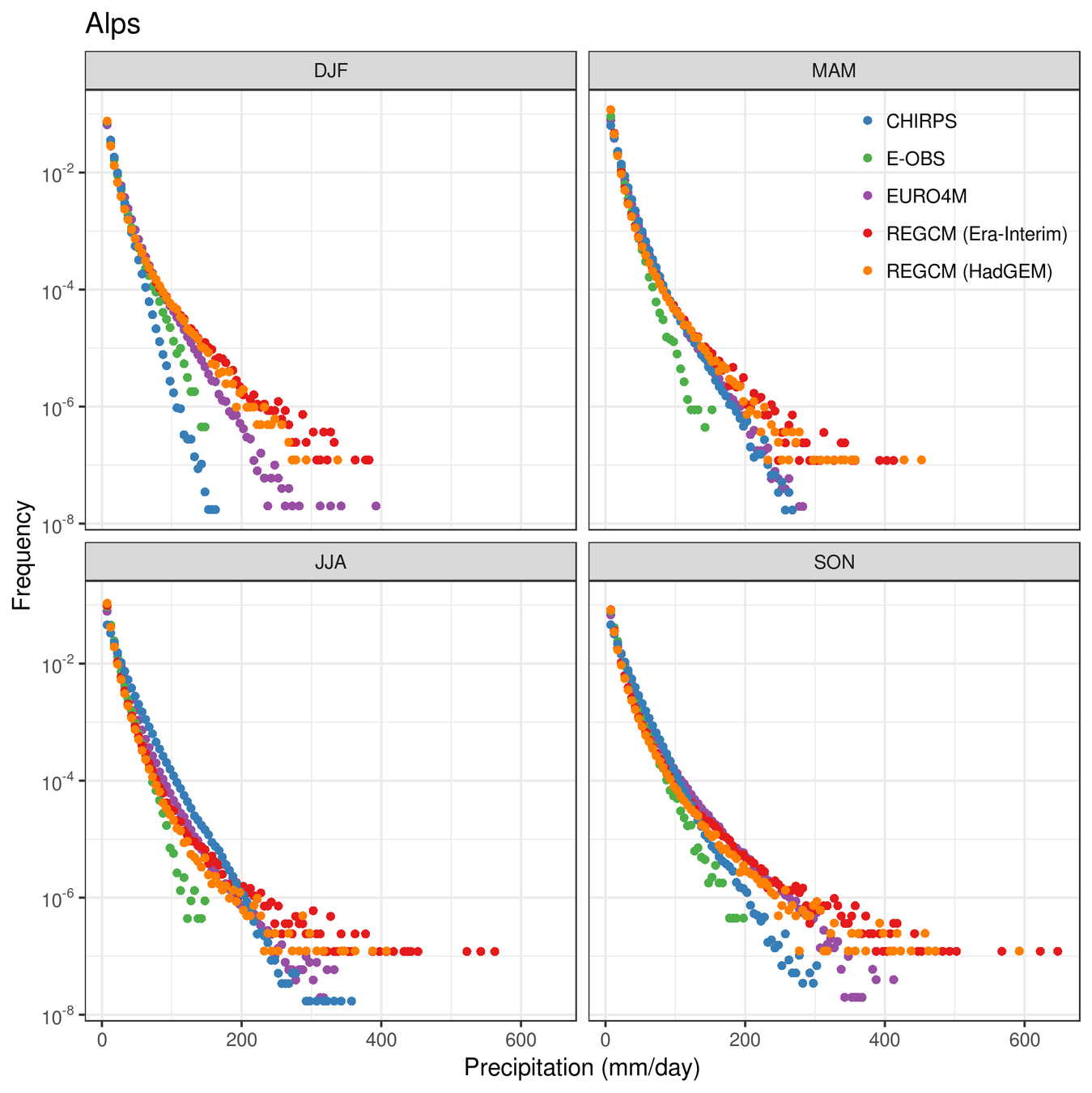
3.0 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
CHyM Is a distributed (gridded) hydrological model. Peculiarities:
- Can build DEM from various sources, smoothing by cellula automata algorithms
- Can use several kind of inputs, such as station observations, gridded model data, etc.
- Designed to work on any domain
- NetCDF output
- Maintained at the ICTP by Fabio Di Sante
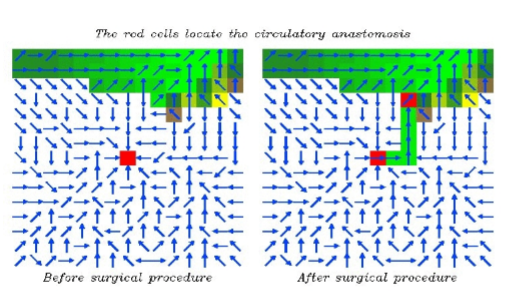


3.1 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
3.1 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
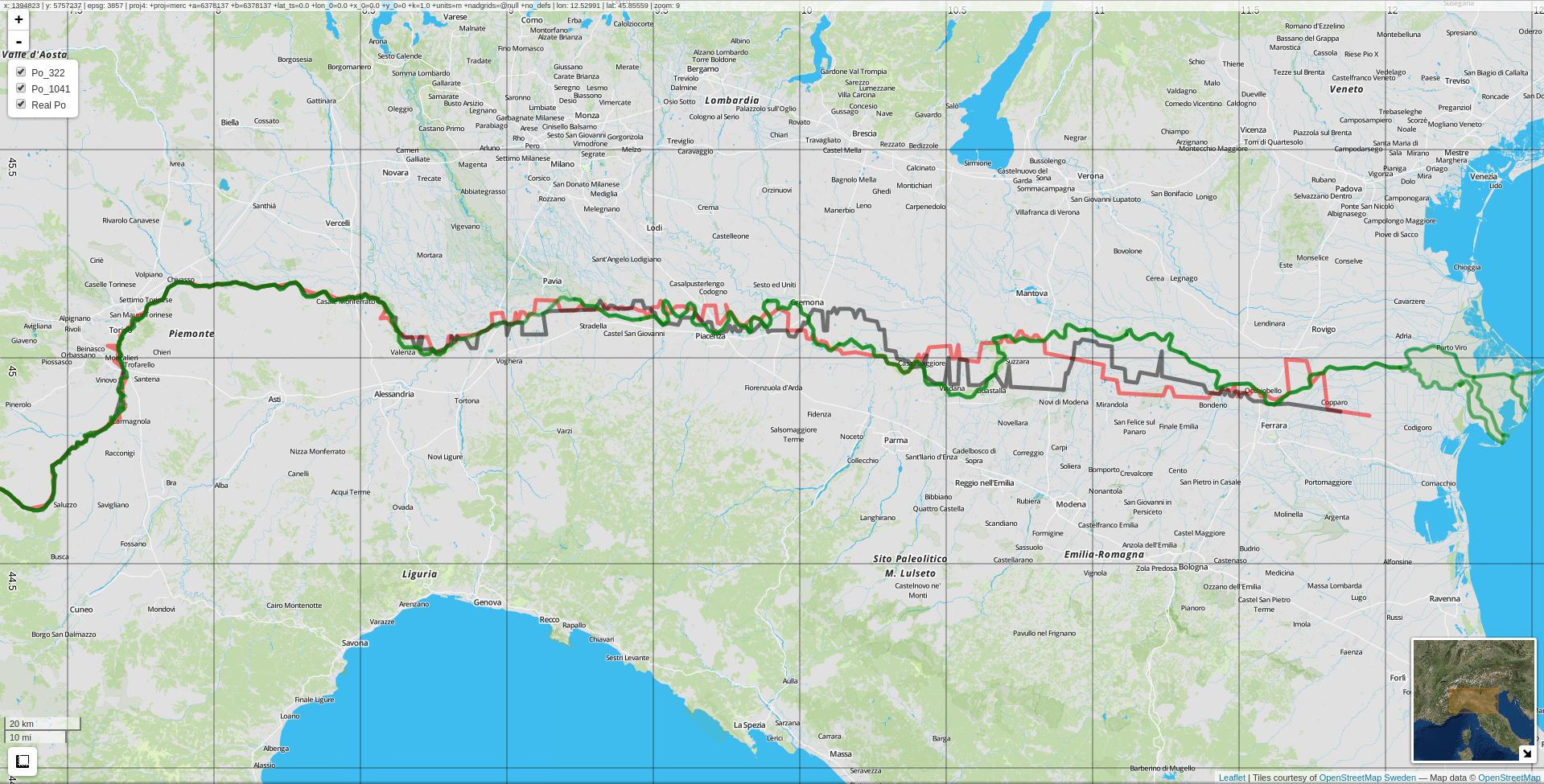
Creating the river network is sometimes easier said than done...
Real Po river
CHyM simulation 1
CHyM simulation 2
3.2 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
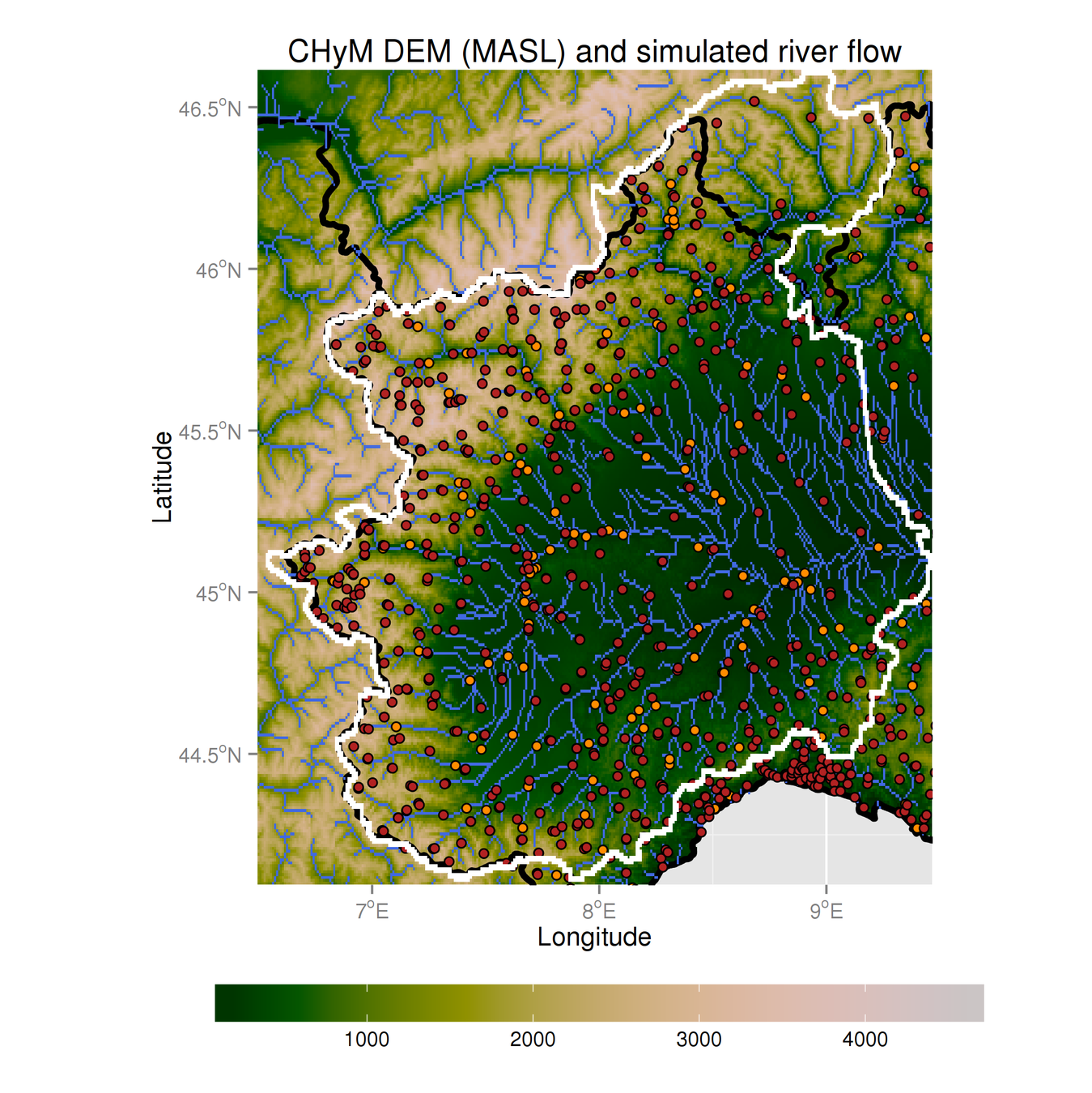
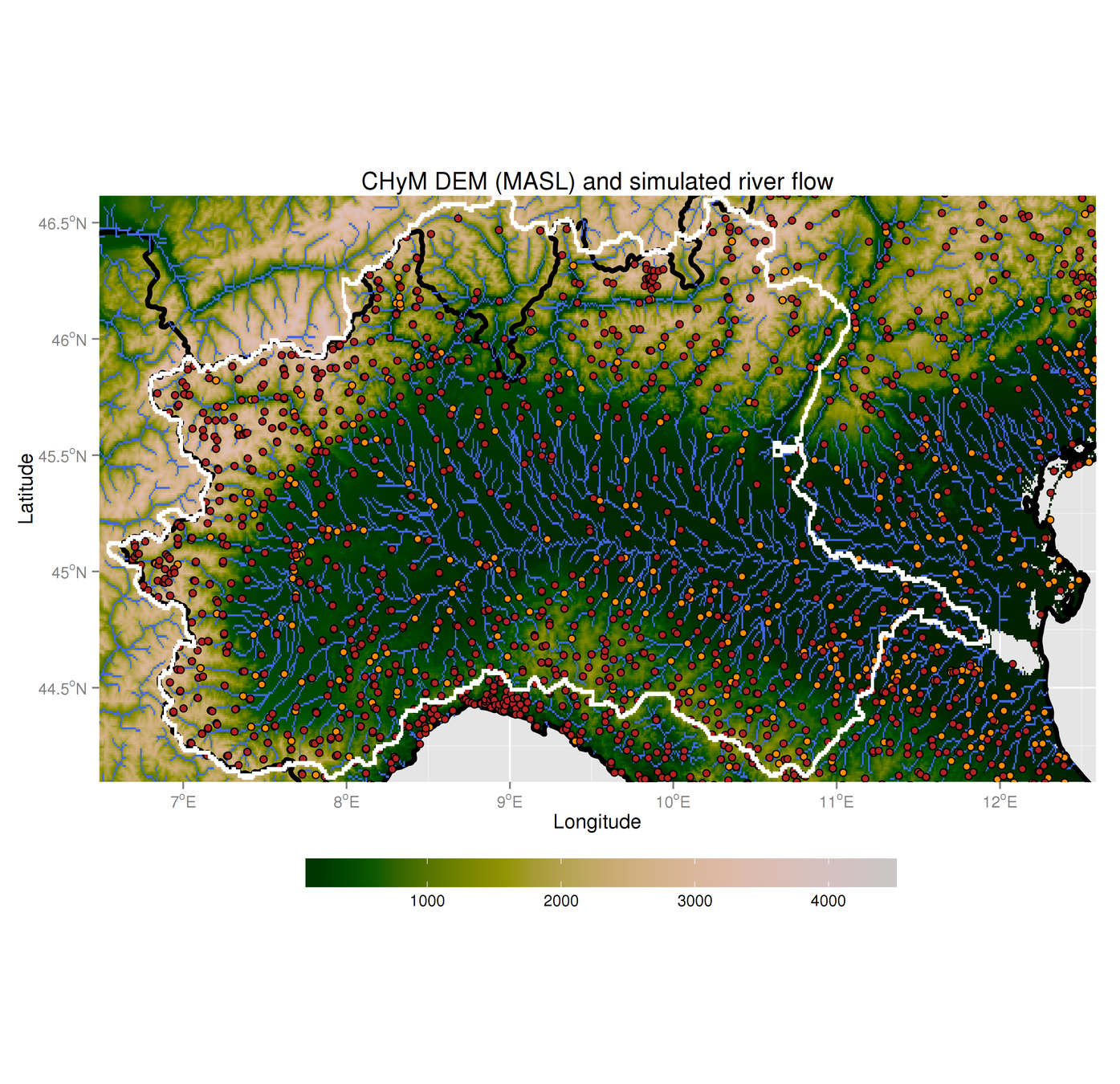
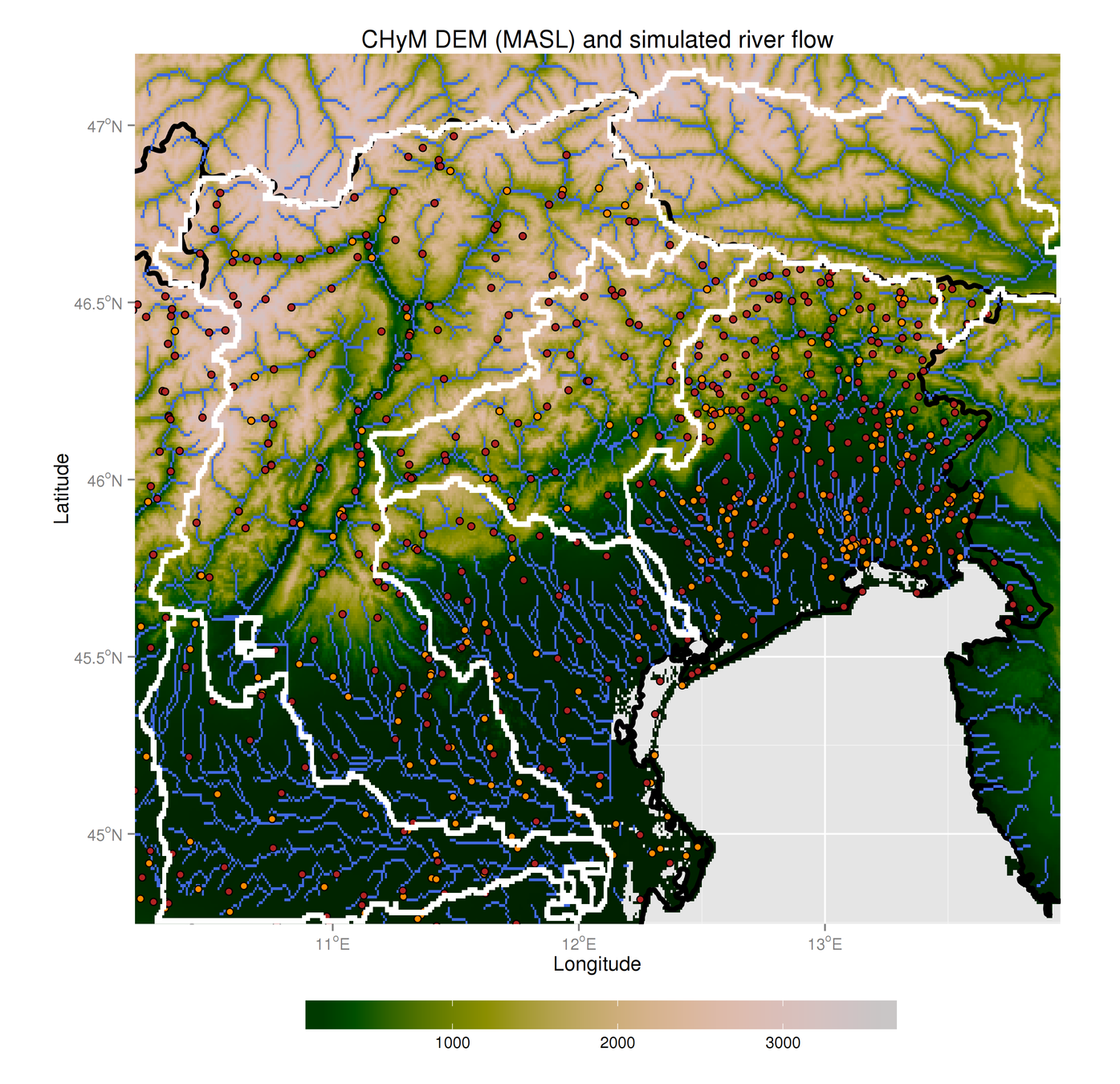
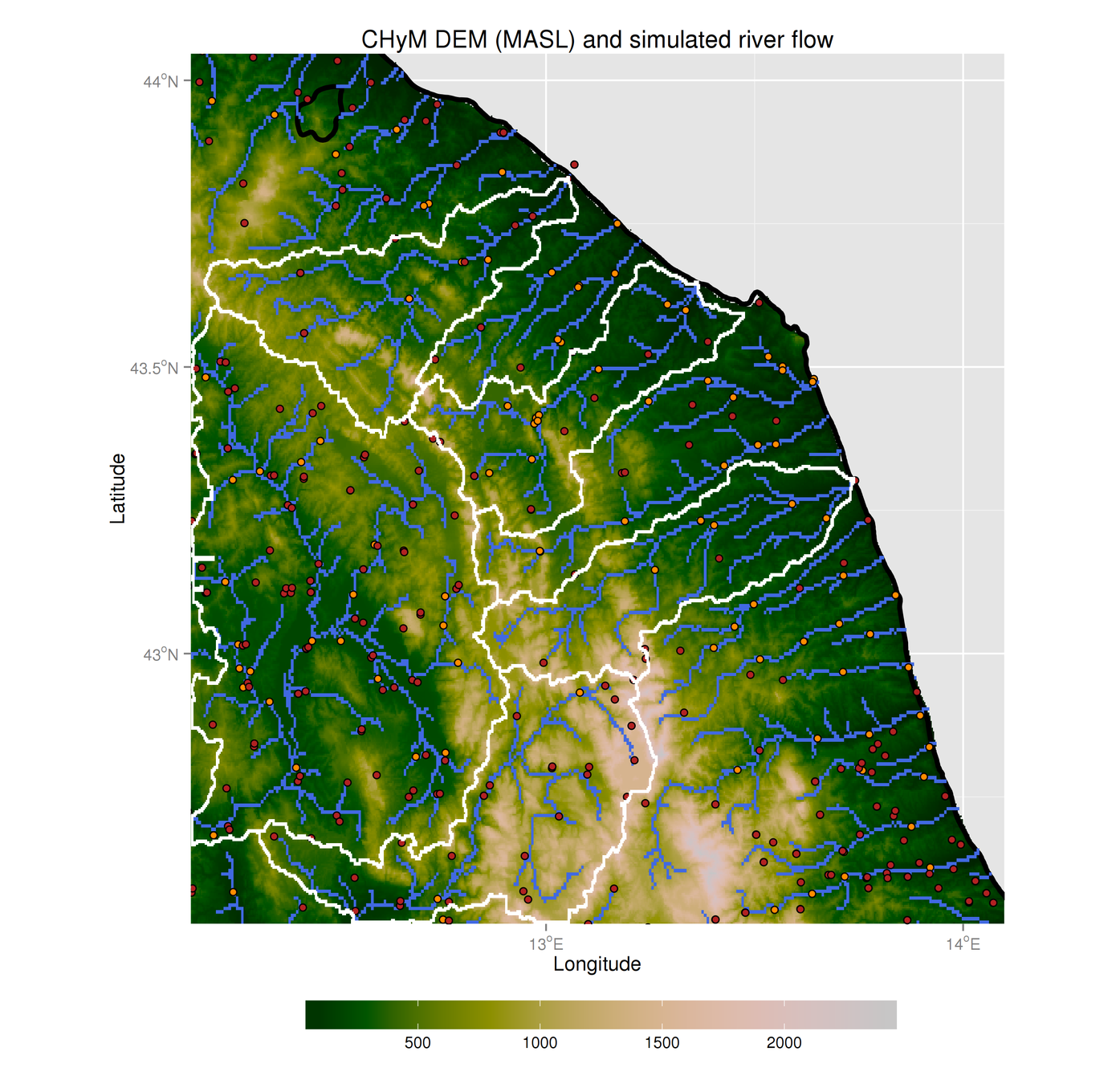
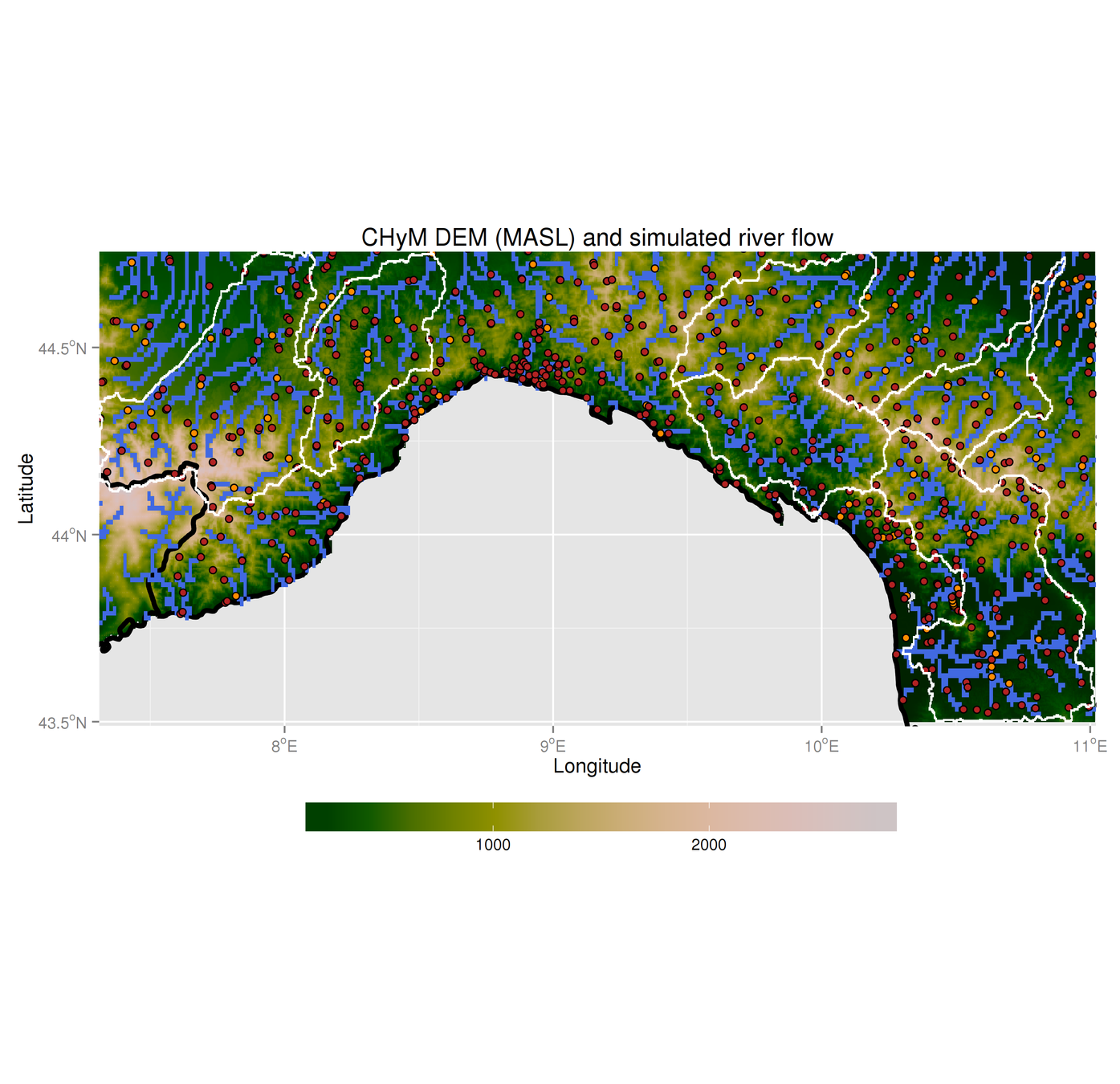
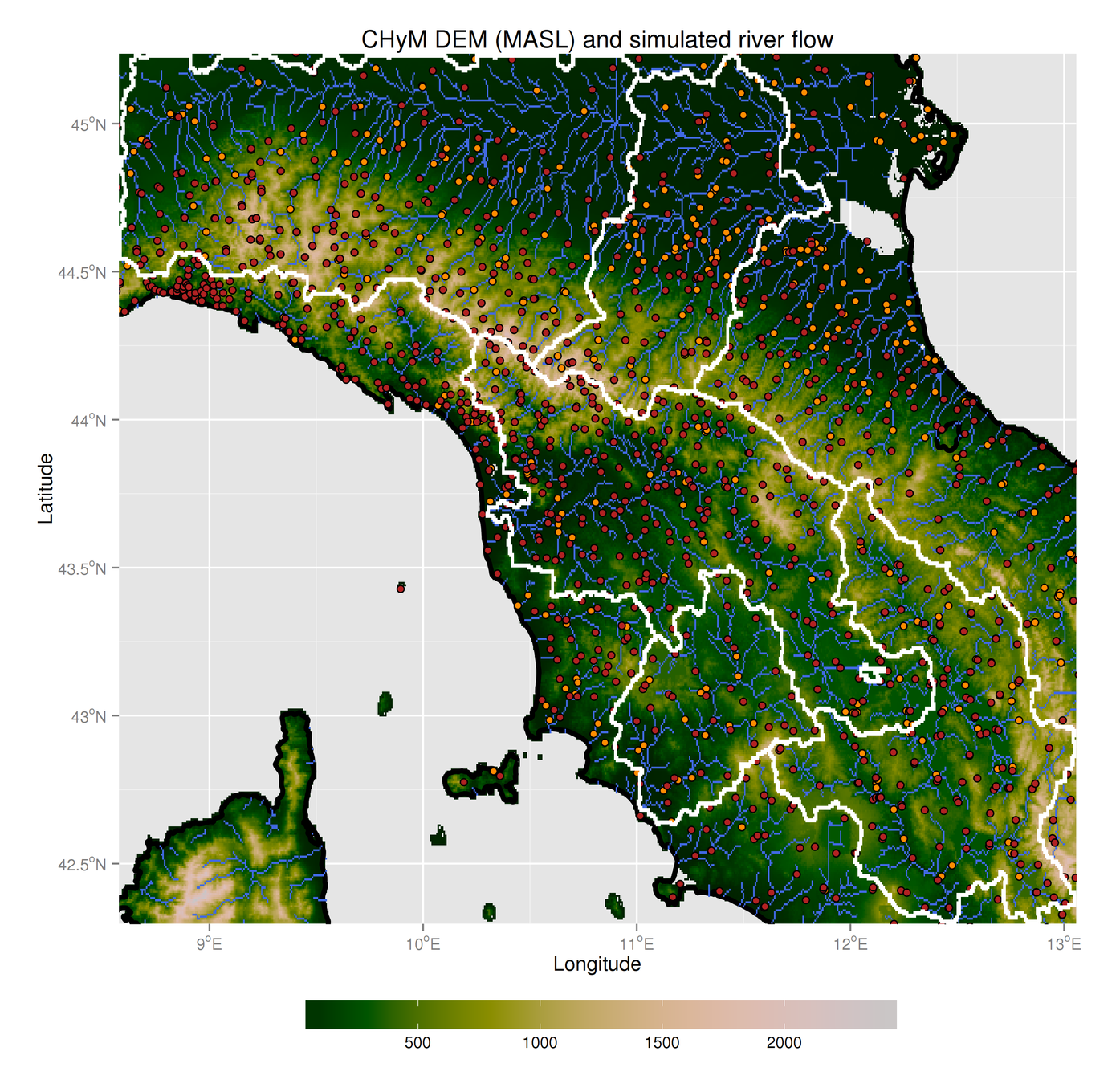
Sanity check:
can we reproduce river basins?
3.2 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
Sanity check: skill of the model driven with the observations
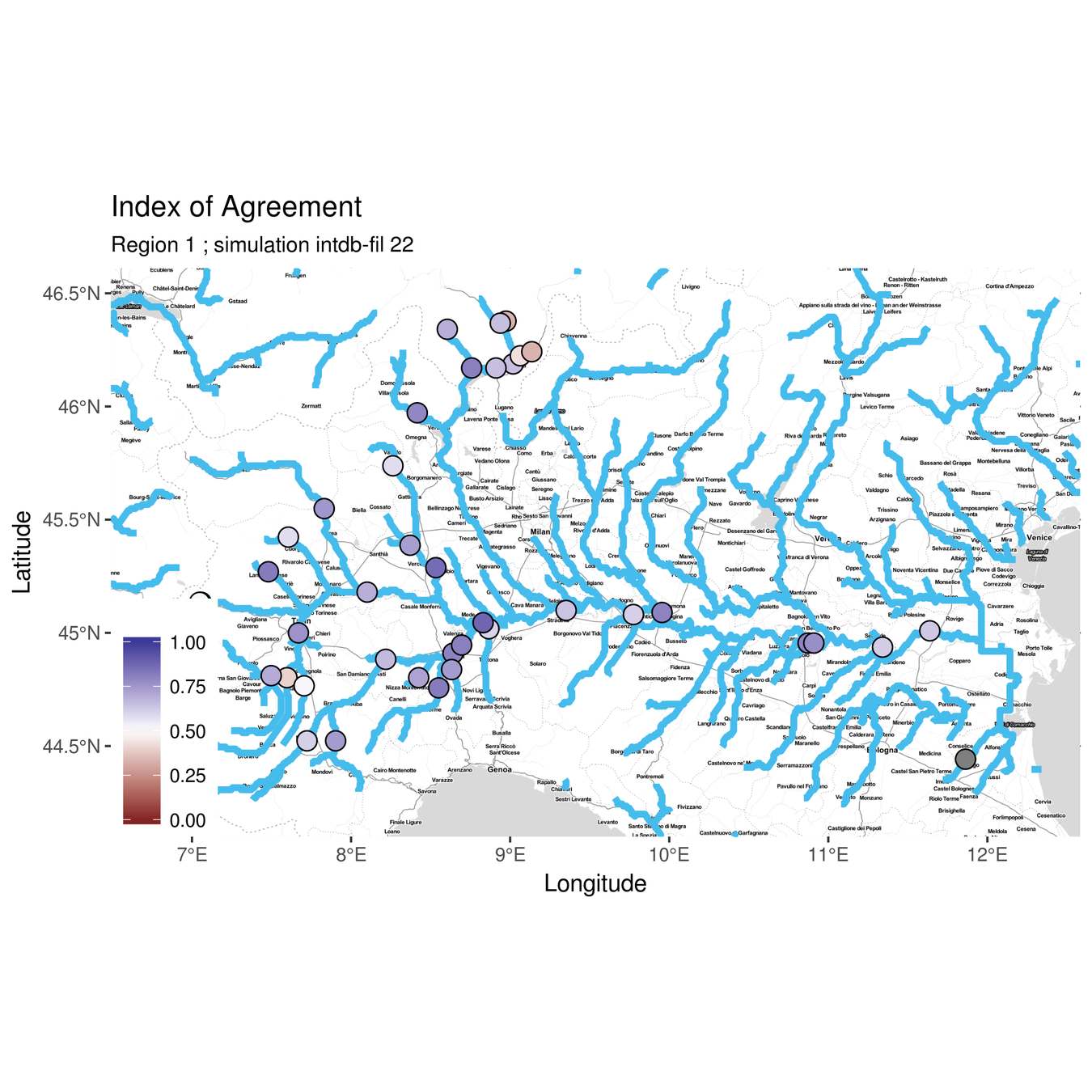
3.6 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
Sanity check: how does the model assimilate RegCM's precipitation?
3.5 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
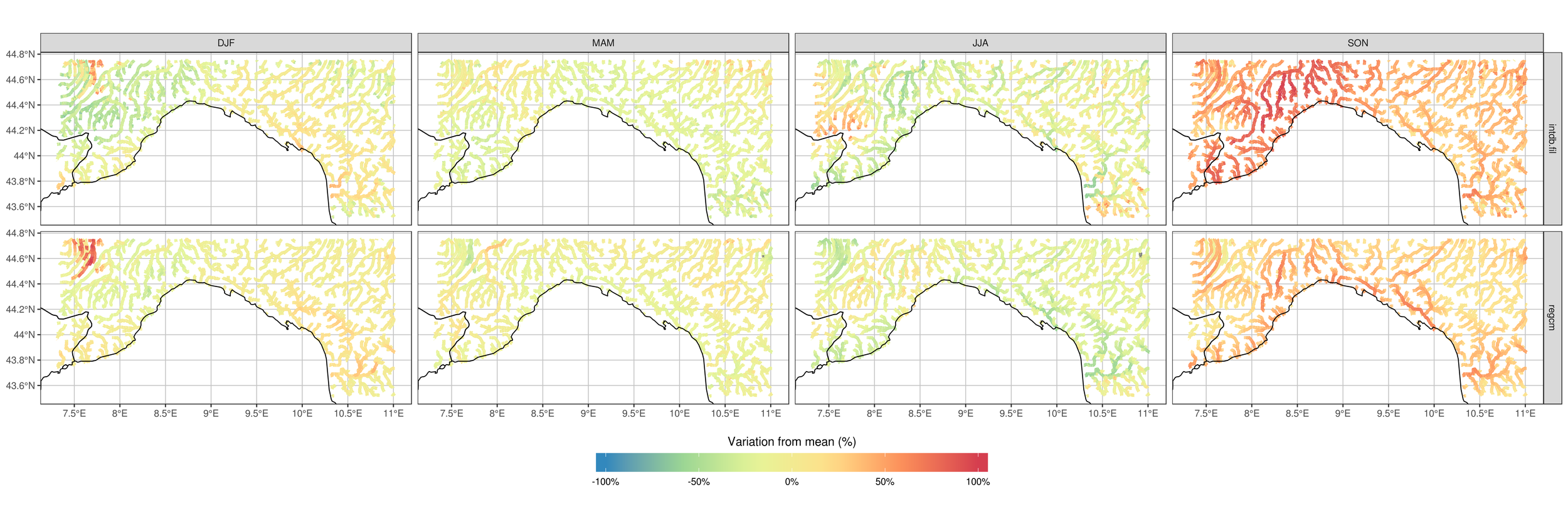
How does the model perform if driven with RegCM, compared with if driven with observations? (Liguria example)
CHyM (RegCM-driven)
CHyM (OBS-driven)
3.6 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
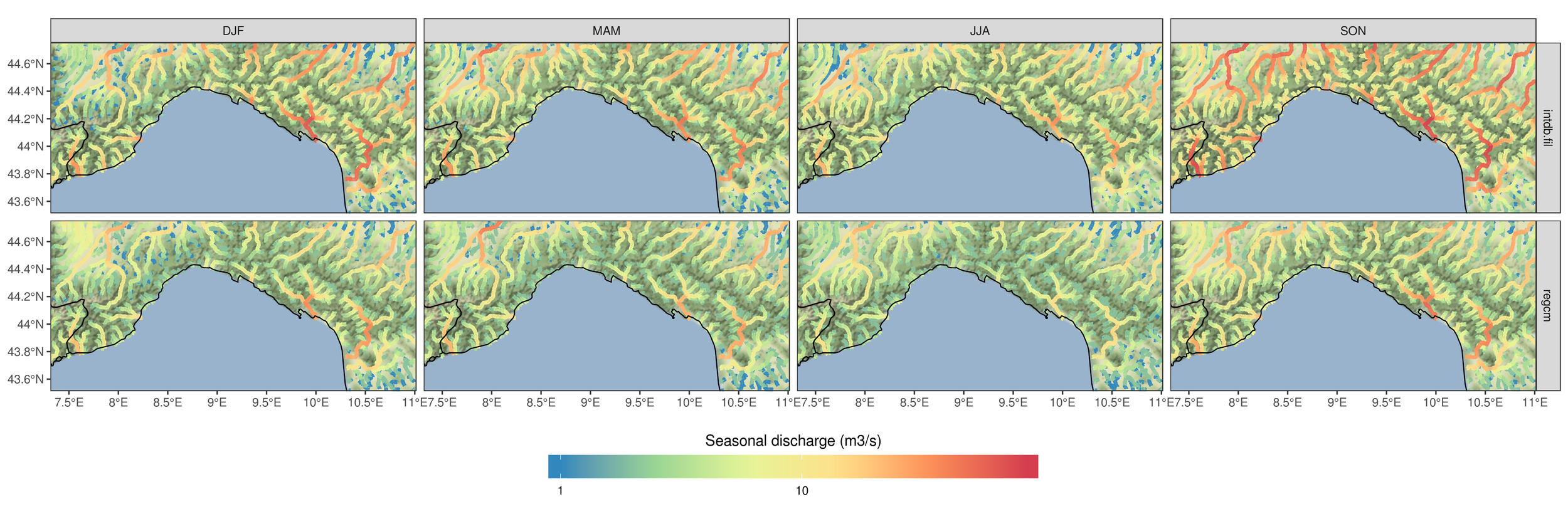
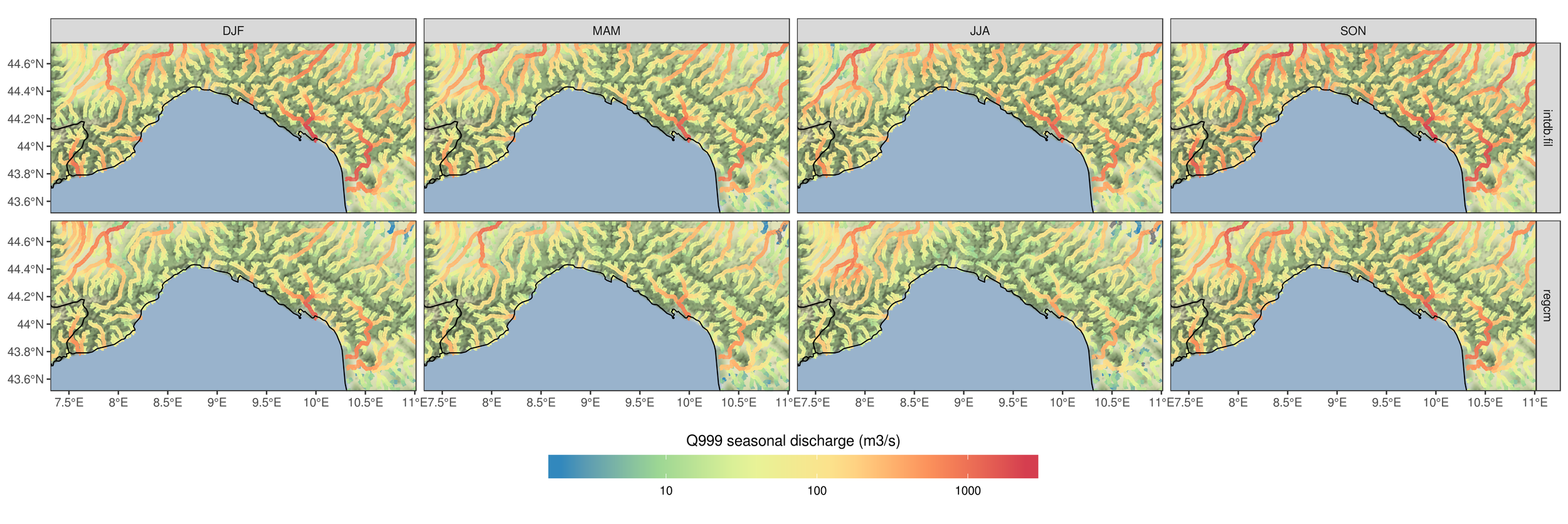
3.6 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
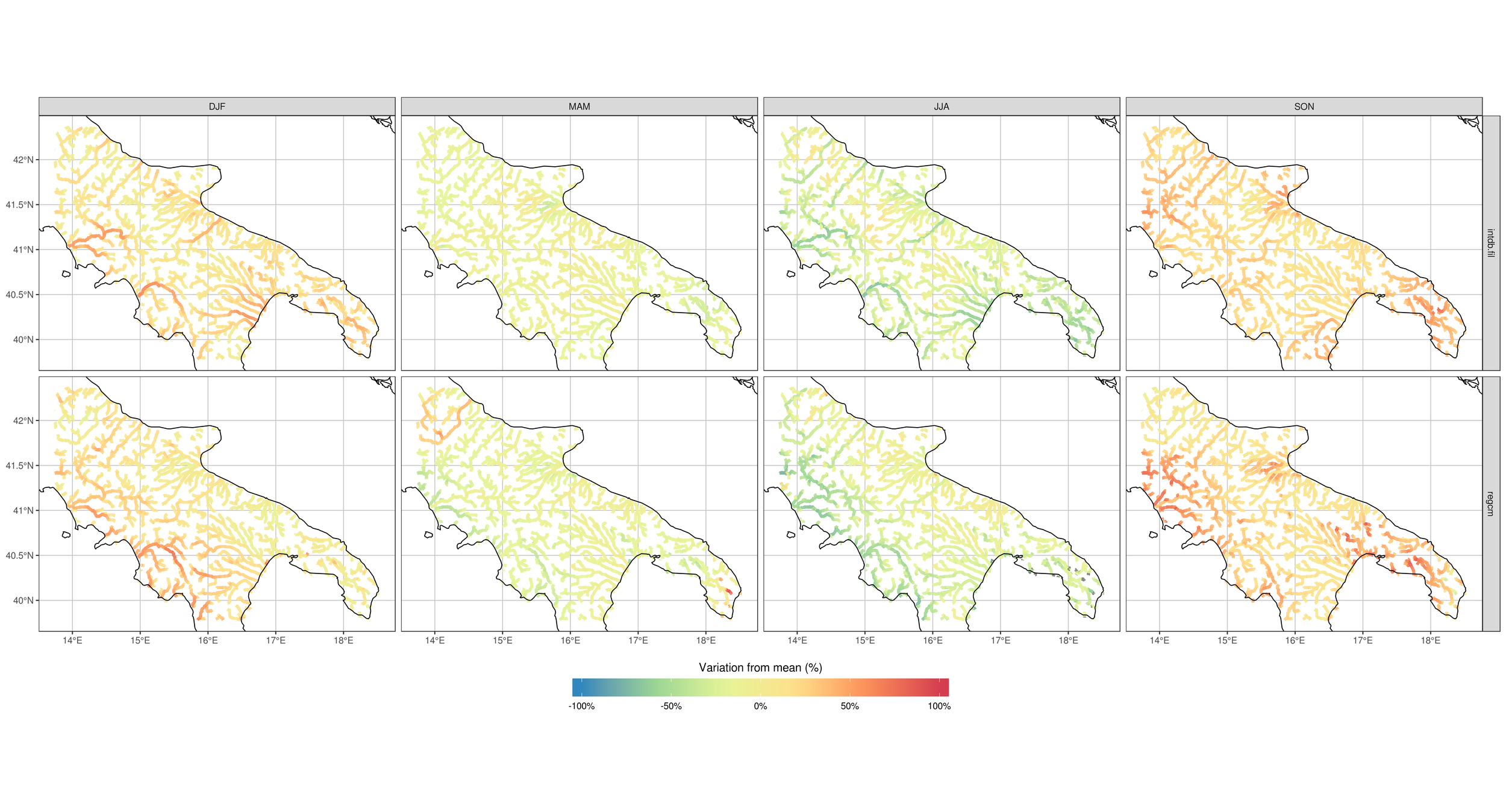
How does the model perform if driven with RegCM, compared with if driven with observations? (Central-South Italy example)
3.6 - Cetemps Hydrological Model
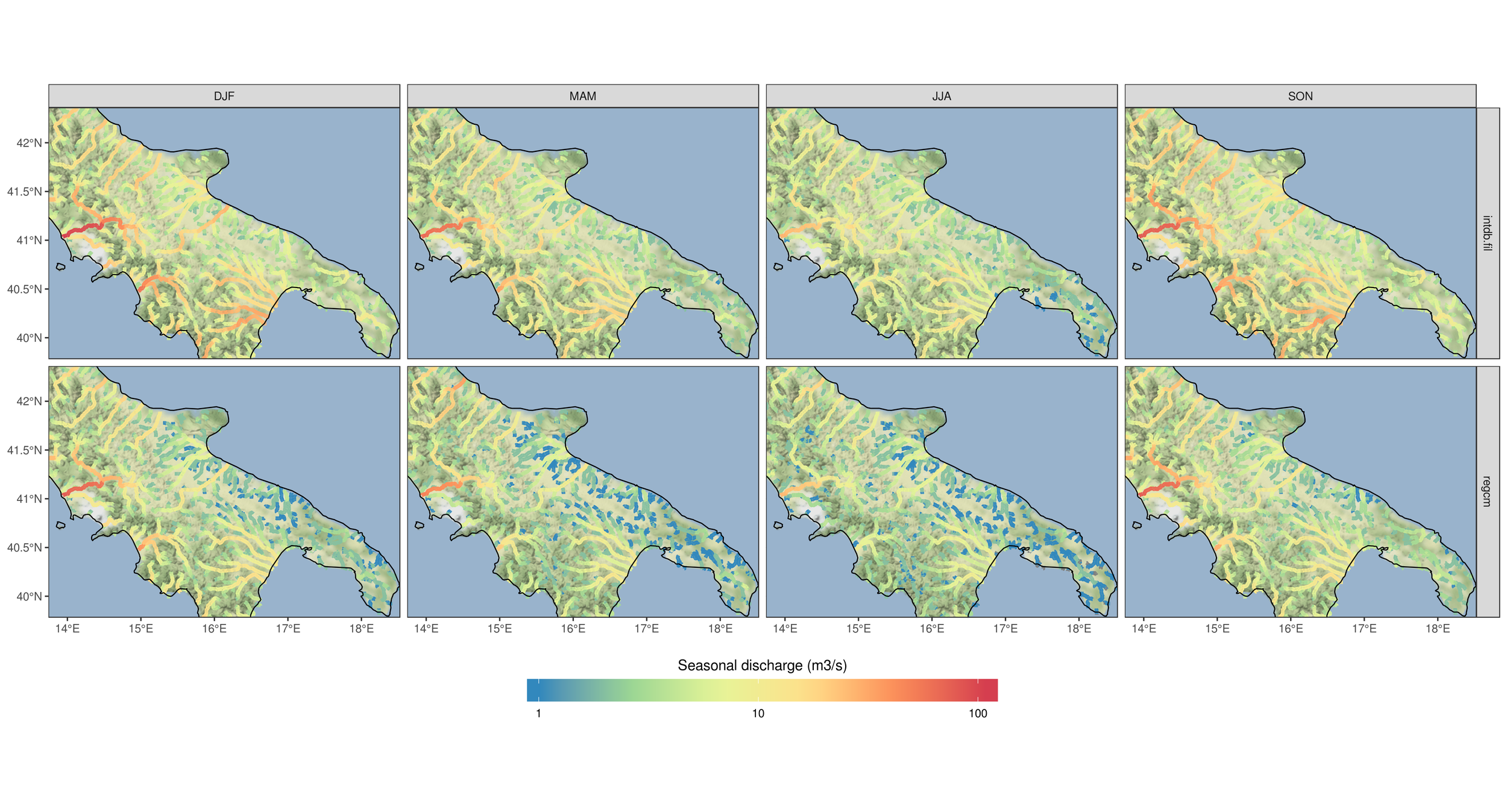
3.7 - Cetemps Hydrological Model

4 - Statistics
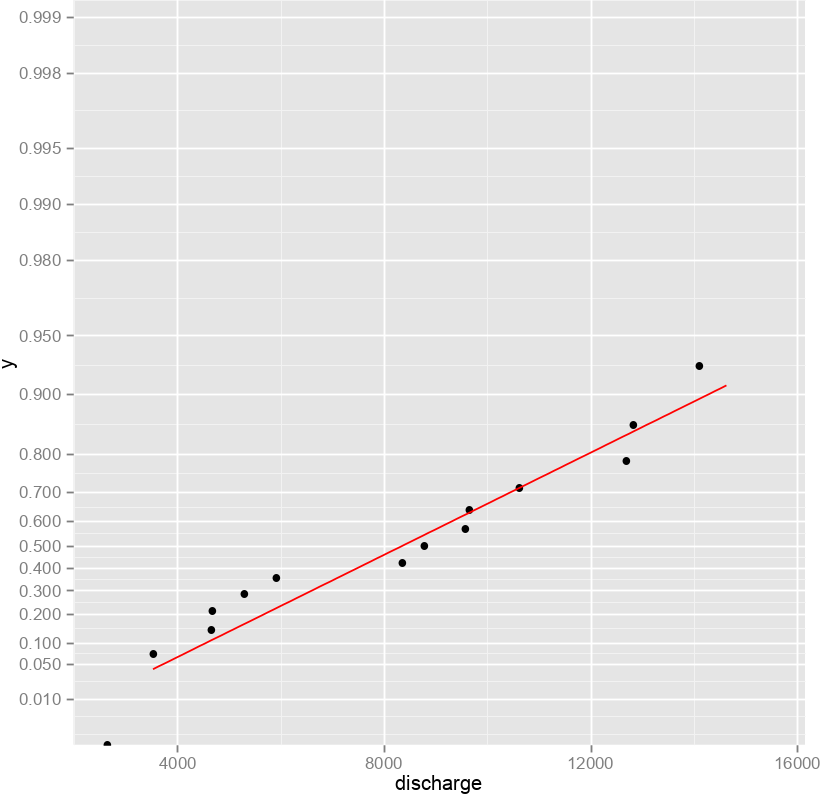
How to estimate hundred-years floods with only a few (~20) years worth of data?
The methodology is taken from Maione et al., 2003
Annual maxima
Gumbel extreme value distribution
Fit parameters
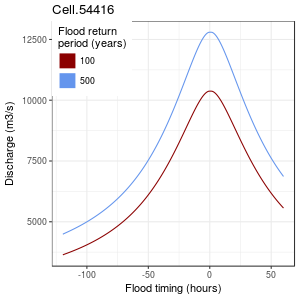
SDH: "Typical" flood timing curve for each river cell
CA2D input data
5.0 - Hydraulic model
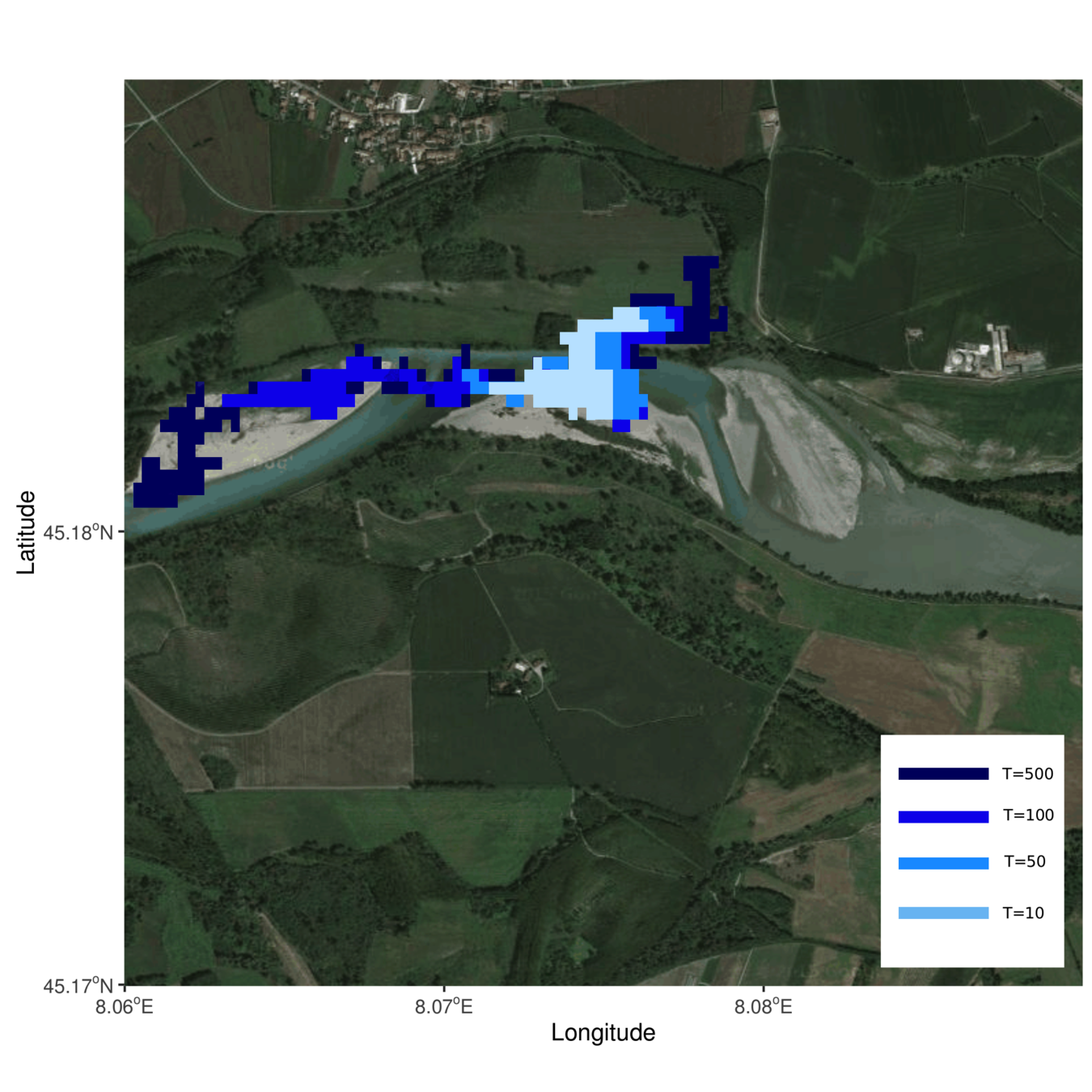
- DEM
- River network
- SDH

Thanks for your attention!
Precipitation:
- Observations
- RCM output
Gridded netCDF:
- River network
- Discharges
hydrological model

For each RP, cell:
- Gumbel distr
- Hydrographs
Statistical RP analysis
For each RP, cell:
- Flood extent
- Flood depth
(multiple simulations)
- RCM output
- Discharges
- Past floods
Validation for

CA2D model
afantini@ictp.it