Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Contents
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Copernicus

A historical perspective
Tycho

Keppler

Galileo

Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Copernicus played a central role in the emergence of modern Astronomy, shifting from the geocentric model to the heliocentric model.

A historical perspective
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Tycho Brahe collected meticulous data about the location of stars and planetary motion
A historical perspective
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler found a hidden pattern in the data collected by Brahe, and formulated an enduring model of planetary motion.
A historical perspective
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
A historical perspective
For those interested in a deeper dive in the historical perspective:
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
The Laws of Planetary Motion
Planetary Orbits
This video shows a summary of all three laws of planetary motion and the events leading to their discovery.
In the slides below, you will dive into the details of each law.
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s first law: Each planet moves around the Sun in an elliptical orbit, with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse.

Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion


- Why are the orbits elliptical?
- What is an ellipse?
Focus?
Semimajor axis?
Eccentricity?
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s second law: The straight line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in space in equal intervals of time.
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Notice how the eccentricity affects the orbital speed.

- The planet speeds up in its closest approach and slows down when it is the furthest.
- Higher eccentricity causes more variability in the orbital speed.
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s third law:
The square of a planet’s orbital period (P) is directly proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit (a).
Note: Some resources use the symbols T for period and d or r for average distance
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion
Kepler’s Laws examples:
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
Introduction to Newton's Laws of Motion
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion

Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
- Newton’s first law: Every object will continue to be in a state of rest or move at a constant speed in a straight line unless it is compelled to change by an outside force.

Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton’s second law: The change of motion of a body is proportional to and in the direction of the force acting on it, and inversely proportional to its mass.

Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
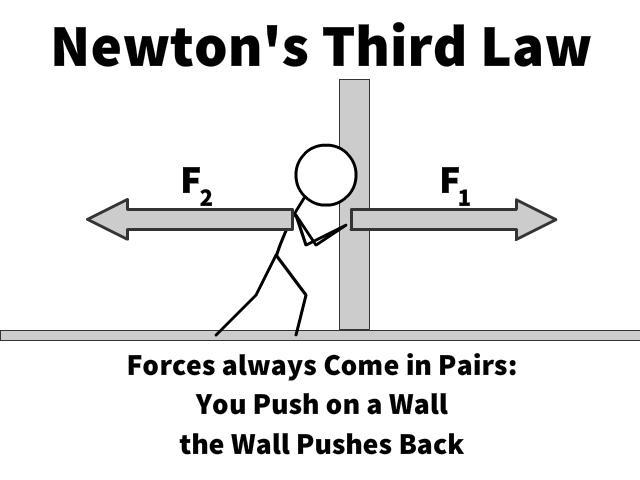
- Newton’s third law: The mutual actions of two bodies upon each other are always equal and act in opposite directions.
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
Three more videos about the three laws (different perspectives for deeper understanding.)
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Laws of Motion
Solved Examples
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
- Newton's insights
- Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
- Earth's Gravity
In this video
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
Even though the force of gravity depends on the masses of both objects, the rate at which an object falls only depends on the mass of the object attracting it.
In this video
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
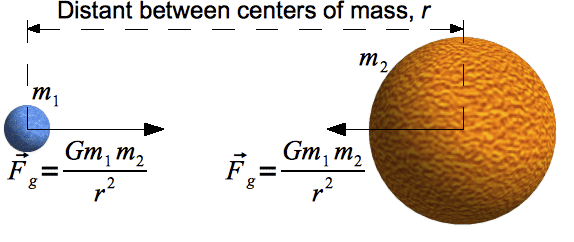
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
For any two bodies, with masses m1 and m2, and separated by a distance r, there is an attractive force between the bodies whose magnitude is proportional to both masses, and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
How to get into orbit!
- Mass
- Gravity
- Types of Orbits
- Escape Velocity
- "Weightlessness"
In this video
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
How to get into orbit!
- "Weightlessness" starting @4:00
In this video
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
How to get into orbit!
Gravity & Orbital Motion
In this video
Introduction to Astronomy
Orbits and Gravity
How to get into orbit!
Satellite traffic and other info
Explore