PHY2048C
"Laboratory" Activities
PHY2048C
Labs?
The problem


"Although the students are going through the motions of physics experimentation, their brains are not engaged in the process, and there is little need or reason to think about the physics content involved. That mental effort is made by instructors beforehand when they design the experiment and when they think about the research questions and how to test them. Our research suggests that instructors are erroneously assuming the students will go through a comparable thought process as they follow the instructions in the lab manual to complete the experiment in the allotted time."
PHY2048C
Labs?
Learning outcomes
Reinforce Course Learning Outcomes
Data Collection and Analysis
Reflection Skills
PHY2048C
Lab Activities
Kinematics
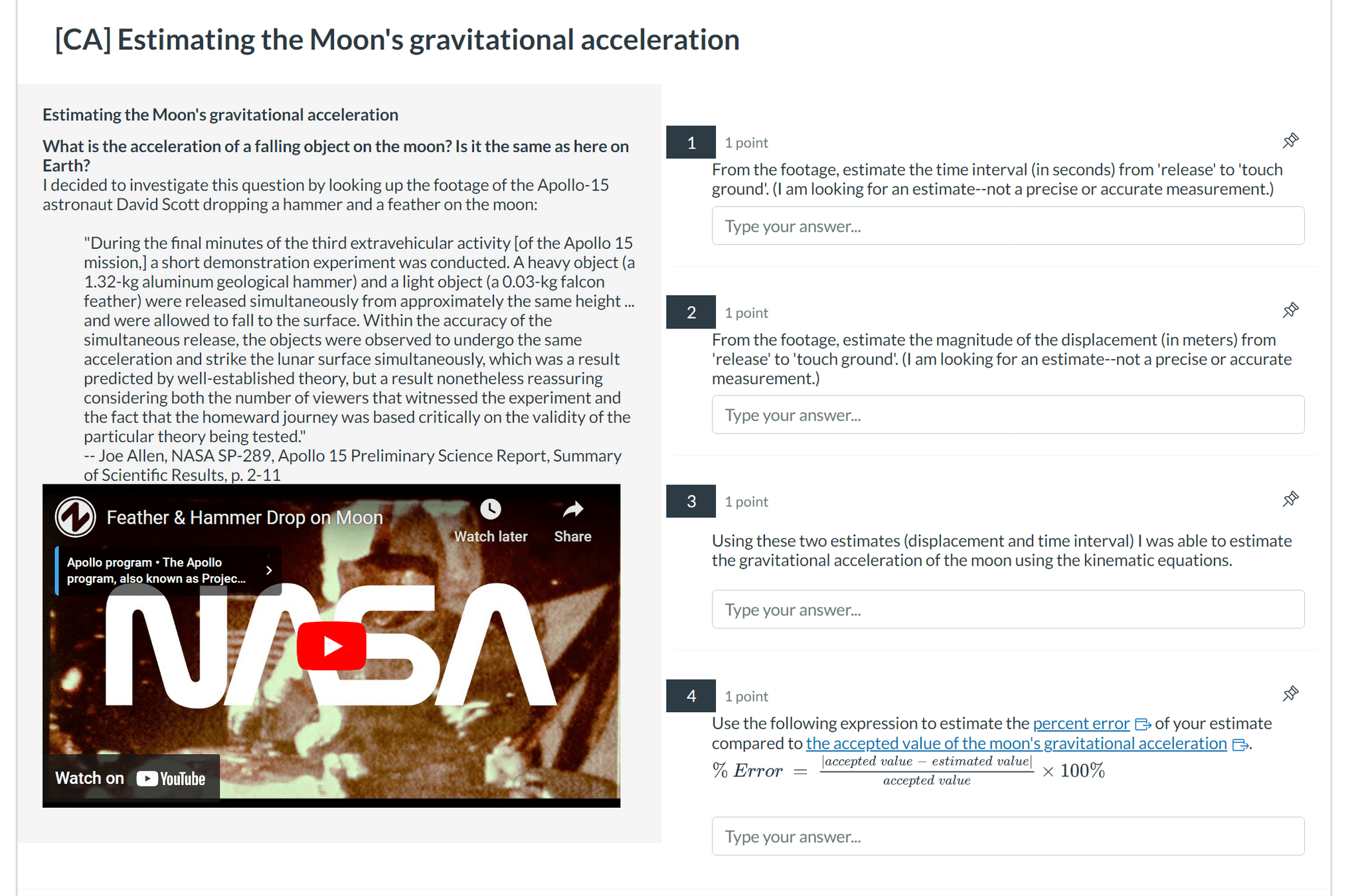
Free-fall
PHY2048C
Lab Activities
Kinematics

PHY2048C
Lab Activities
Kinematics in 2D -- projectile motion
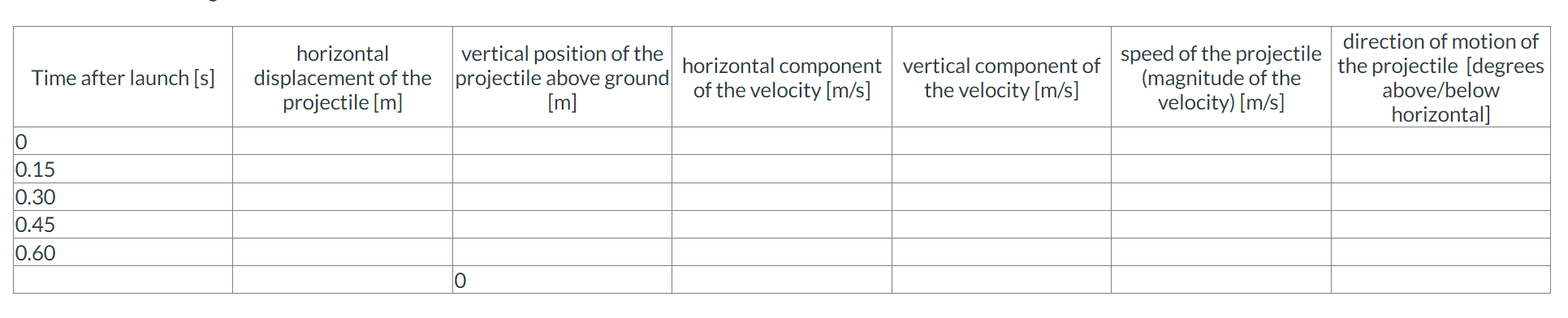
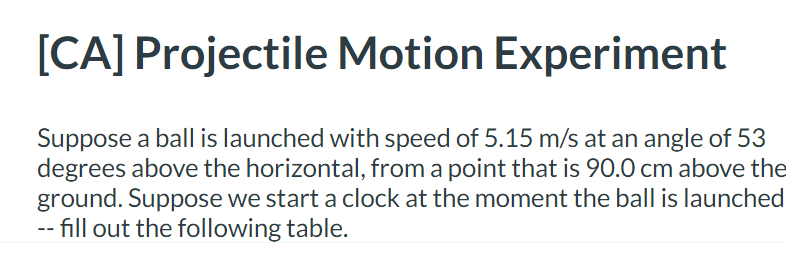
...
PHY2048C
Simple Harmonic Motion
Q
Simple harmonic motion: The position x of an object varies with time t. For which of the following equations relating x and t is the motion of the object simple harmonic motion? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) x = 5 sin23t
B) x = 8 cos 3t
C) x = 4 tan 2t
D) x = 5 sin 3t
E) x = 2 cos(3t - 1)
PHY2048C
Simple Harmonic Motion
Q
Simple harmonic motion: A restoring force of magnitude F acts on a system with a displacement of magnitude x. In which of the following cases will the system undergo simple harmonic motion?
a)
b)
c)
d)
PHY2048C
Simple Harmonic Motion
Q
An object is executing simple harmonic motion. What is true about the acceleration of this object? (There may be more than one correct choice.)
A) The acceleration is a maximum when its displacement is a maximum.
B) The acceleration is a maximum when its speed is a maximum.
C) The acceleration is a maximum when its displacement is zero.
D) The acceleration is zero when its speed is a maximum.
E) The acceleration is a maximum when the object is instantaneously at rest.
PHY2048C
Simple Harmonic Motion
Q
A mass M is attached to an ideal massless spring. When this system is set in motion with amplitude A, it has a period T. What is the period if the mass is doubled to 2M?
a)
b)
c)
d)
PHY2048C
Simple Harmonic Motion
Q
Motion is a change of the position of an object from one instant to the next.... so to start the task of describing motion, we ask: what is position? and what physical quantities do we use to describe a change in position?
Position is relative
- The first thing to know about position, is that it is a relative quantity -- meaning that it has to be defined relative to some frame of reference.
Later on (Physics 3) we will learn how to deal with moving reference frames. It was the long standing theory that there existed a universallystationary frame, a frame which was stationary to everything inthe universe, until the famous Michelson-Morley experiment provedotherwise. A few years later, Albert Einstein formulated the theory of special relativity which provided the framework to understand the universe with no absolutely stationary frames.- Watch (one or both of these) videos, as you contemplate the idea of relative position, and relative motion.
The Position Vector
Step 1: Set up a Reference Frame and a Coordinate System.
Step 2: Approximate the object in question as a point.
We will discuss multi-dimensional vectors later in this module,
but for now, just note thatis the unit vector along the x-axis,
is the unit vector along the y-axis, and
is the unit vector along the z-axis.
The Displacement Vector
The Greek letter capital Delta ![\Delta LaTeX: \Delta]() is often used to denote a change in a quantity, in this case, a change in position.
is often used to denote a change in a quantity, in this case, a change in position.-
The displacement vector
is defined as the final position minus the initial position:
- The displacement of an object during any segment of motion can be thought of as the position of the object at the end of the segment relative to its position at the beginning of the segment.
- Displacement is a vector, which means it represents both a magnitude (2 meters) and a direction (
). This indicates that the car is traveling in the opposite direction from which it is facing, in a typical case, backing up. The reverse orientation of the displacement vector (initial position minus final position) would indicate the car moving forward, hence the importance of the order.
- The SI unit for the magnitude of displacement is meters, which is consistent with our previous units.
The Distance Scalar
In summary, distance is a path dependent scalar quantity, whereas displacement is a path independent vector quantity.
